笔记:了解GLSL (OpenGL Shading Language)
GLSL 的产生,可以为了更灵活的3D图像编程
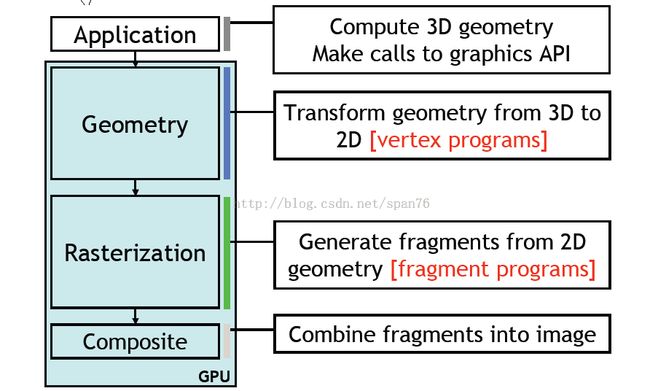
APP和GPU的关系图
GLSL 包括 Vertex programs 和 Fragment pgrograms, 实际是对 Geometry 和 Rasterization 的输出
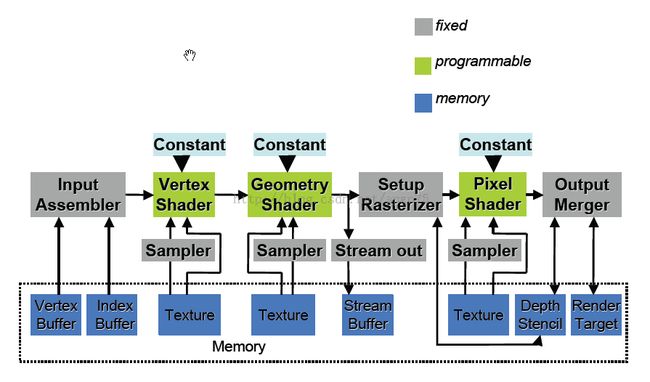
管线处理如下,以前管线不能编程,现在GLSL让管线更灵活了。
Shader 的知识总结:
Shader: a small program for GPU ( like c language, 由 CPU 负责变异,GPU 负责运行,可以使用llvm技术)
Vertex Processor ( handle Vertex shader, Vertex shader 是一个 main() 程序,作用在每一个Vertex上,控制量的输出:gl_Position)
Fragment Processor ( handle Fragment shader,也是一main 程序,作用在???上(待了解), gl_FragColor)
其它:shader Log and Cleanup
communication openGL -> GLSL
Uniform variables: set by primitive ( example see : http://www.clockworkcoders.com/oglsl/tutorial2.htm )
Attribute Variables: set inside glBegin/glEnd ()
Simple: float, bool, int
vec{2,3,4} a vector of 2,3,or 4 floats
bvec{2,3,4} bool vector
ivec{2,3,4} vector of integers
matrices 2×2, 3×3 and 4×4
The data types for texture sampling are:
sampler1D – for 1D textures
sampler2D – for 2D textures
sampler3D – for 3D textures
samplerCube – for cube map textures
sampler1DShadow – for shadow maps
sampler2DShadow – for shadow maps
Variable Qualifiers
const/attribute/uniform/varying
arrays and structs as C
Control Flow Statements as C
Functions
The parameters of a function have the following qualifiers available:
in – for input parameters
out – for outputs of the function. The return statement is also an option for sending the result of a function.
inout – for parameters that are both input and output of a function
Varying Variables
varying float intensity;
A varying variable must be written on a vertex shader, where we compute the value of the variable for each vertex.
( varying example see : http://www.clockworkcoders.com/oglsl/tutorial4.htm)
http://www.clockworkcoders.com/oglsl/tutorials.html
http://www.opengl.org/documentation/glsl/