uva 12165 - Triangle Hazard(几何)
题目链接:uva 12165 - Triangle Hazard
梅涅劳斯定理:
当直线交
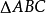 三边所在直线
于点
三边所在直线
于点
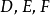 时,
时,
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Point {
double x, y;
Point (double x = 0, double y = 0): x(x), y(y) {}
void read () { scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y); }
void write () { printf("%lf %lf", x, y); }
Point operator + (const Point& u) { return Point(x + u.x, y + u.y); }
Point operator - (const Point& u) { return Point(x - u.x, y - u.y); }
}P, Q, R;
Point resize(Point u, double k) {
return Point(u.x * k, u.y * k);
}
int main () {
int cas;
double m1, m2, m3, m4, m5, m6;
scanf("%d", &cas);
while (cas--) {
P.read(), Q.read(), R.read();
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", &m1, &m2, &m3, &m4, &m5, &m6);
double k = (m1/m2) * (m3/m4) * (m5/m6);
double a = (m5/m6) * (m1/m2 + 1);
double b = (m1/m2) * (m3/m4 + 1);
double c = (m3/m4) * (m5/m6 + 1);
Point pa = R + resize(R - P, (a + k) / (1 - k));
Point pb = P + resize(P - Q, (b + k) / (1 - k));
Point pc = Q + resize(Q - R, (c + k) / (1 - k));
pa.write(), printf(" ");
pb.write(), printf(" ");
pc.write(), printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}