JAVA基础之二:变量和数据类型
原文链接:http://happyshome.cn/blog/java/basics/variable.html
本文主要介绍了Java中基本的数据类型,以及如何在程序中正确的使用。
1. 变量
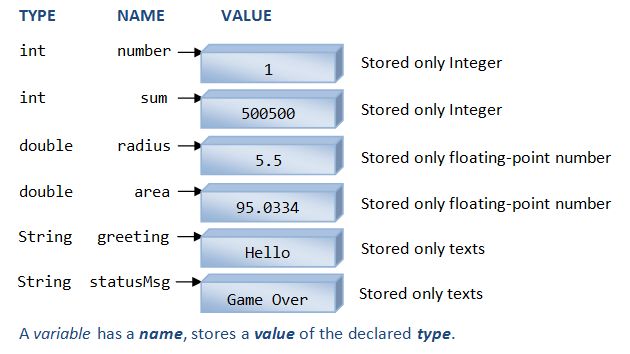
计算机处理数据,变量被用来存储处理的数据,之所以叫做变量因为你可以改变存储的值。更确切的说,一个变量指向着一块存储特定类型值的地址,换句话说,一个变量有名称、类型和值。一个变量有一个名称,例如radius、area、age和height,每个变量的名称都是唯一的,这边可以方便我们设置和获取变量的值。
一个变量有一种类型,下面是Java类型的列子:
- int: 表示整数例如123和-456
- double: 表示浮点数例如3.1416、-55.66、1.2e3和-4.5E-6
- String: 表示文本例如"Hello"、"Good Morning!",文本通常嵌入在双引号里面
- char: 表示单个字符例如'a','8',单个字符通常嵌入在单引号里面。
变量存储特定类型的值,编程中要特别注意变量类型,举例:一个int变量存储整数123,但是不能存储浮点数12.34,同样也不能存储文本"Hello"。
早期的编程语言中引入了类型的概念来解释二进制01数据,类型定义了数据的结构、大小、范围以及针对该类型的一系列操作。
2. 名称
需要唯一的标识来命名变量,Java遵循以下标识的命名方式:
- 标识由大小写字母、数字、下划线和$的任意长度的字符序列组成。
- 空白 (空格、制表符、换行符)和其他特殊字符 (如+ - * / @ &, 等)是不允许的,错误的命名方式:max value和max-value。
- 标识符不能以数字(0-9)开头必须以字母(a-z, A-Z)、下划线(_)和$开头,系统保留以$开头的标识。
- 标识符不能使用关键字和预留字段 (例如:class,int,double,if,else,for,true,false,null)。
- 标识符是区分大小写的,rose、Rose和ROSE是3个不同的变量。
使用驼峰给变量命名:theFontSize、roomNumber、xMax、yMin、xTopLeft和thisIsAVeryLongVariableName, 可以参考下面的建议:
- 选择一个有意义的变量名是非常重要的,建议使用numberOfStudents和numStudents来表示学生人数,而不是n或x。
- 这些变量名a, b, c, d, i, j, k, i1, j99毫无意义
- x通常用作异常,y、z用来表示坐标,i表示循环索引。
- 对单复数变量加以区分,row表示单行,rows表示多行。
3. 定义变量
你需要定义变量的名称和类型才能在程序中使用变量,你可以使用下面的其中一种语法:
// 定义特定类型的变量, type identifier
int option;
// 定义多个同类型变量,变量之间用逗号分隔,type identifier1, identifier2, ..., identifierN
double sum, difference, product, quotient;
// 定义变量并初始化, type identifier = initialValue
int magicNumber = 88;
// 定义多个同类型变量并初始化, type identifier1 = initValue1, ..., identifierN = initValueN
String greetingMsg = "Hi!", quitMsg = "Bye!";
注意:
- Java是强类型的语言,一个变量对应着一种类型,变量声明后不能存储其它类型的数据。
- 每个变量只能声明一次。
- 使用前你可以在程序的任意位置进行声明。
- 变量声明之后它的类型不能更改。
- 一个变量声明的语句以类型开始,变量自始自终都为这种类型服务,一个变量声明的语句只能使用单一的类型。
4. 常量
常量的命名规范:使用大写的单词,多个单词使用下划线连接,例如:MIN_VALUE,MAX_SIZE。
常量是不可变的,使用关键字final进行声明,常量声明后需要初始化
final double PI = 3.1415926; 5. 表达式
表达式是由运算符和操作数组合而成,通过计算可以输出单个类型的值,例如
1 + 2 * 3 // 计算得到7
int sum, number;
sum + number // 计算得到一个int值
double principal, interestRate;
principal * (1 + interestRate) // 计算得到一个double值
6. 赋值
指派一个右操作数赋值给左操作数,例如:x=1。
计算表达式的值并赋值给左操作数,例如:x=(y + z) / 2。
赋值语句的语法:
// 直接赋值, variable = literalValue
number = 88;
// 计算表达式之后赋值, variable = expression
number = number + 1; // 计算表达式number+1,最后将结果赋值给number
8 = number; // 错误的使用
number + 1 = sum; // 错误的使用
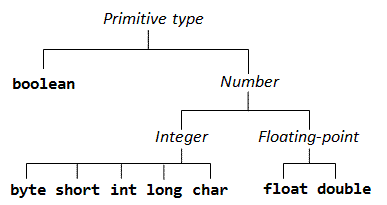
7. 基本类型
在Java中有两种类型:基本类型 (int、double等)和引用类型 (类和数组)。
- byte: 8位有符号整型取值范围:[-2^7, 2^7-1] = [-128, 127]。
- short: 16位有符号整型取值范围:[-2^15, 2^15-1] = [-32768, 32767]。
- int: 32位有符号整型取值范围:[-2^31, 2^31-1] = [-2147483648, 2147483647] (≈9 digits)。
- long: 64位有符号整型取值范围:[-2^63, 2^63-1] = [-9223372036854775808, +9223372036854775807] (≈19 digits)。
- float: 32位单精度浮点数(≈6-7位小数, 取值范围:±[≈10^-45, ≈10^38])。
- double: 64位双精度浮点数(≈精确到14-15位小树, 取值范围:±[≈10^-324, ≈10^308])。
- char: 表示16位Unicode编码,取值范围:'\u0000' 到 '\uFFFF', 可以理解成16位无符号整型,取值范围:[0, 65535]。
- boolean: 布尔取值只能是true或false,布尔数据类型的大小在Java虽然没有定义, 但是至少需要1比特。
内建的基本类型
基本类型内建在程序语言中,从上面的图中我们可以看出Java有8种基本类型。
- 有4种有符号的整型:8位byte,16位short,32位int,64位long。
- 32位单精度类型float,float近似的取值范围±1.40239846×10^-45到±3.40282347×10^38。
- 64位双精度类型double, double近似的取值范围±4.94065645841246544×10^-324到±1.79769313486231570×10^308。
- char表示单个字符,例如'0', 'A', 'a',在Java中,char采用16位Unicode(UCS-2格式)来支持国际化(i18n)。
- Java中引入了二进制的布尔类型,它只能包含true和false两个值。
例子:下面的程序用来输出打印基本类型的最大值、最小值和比特长度。
/* * 输出基本类型的最大值、最小值和比特长度 */
public class PrimitiveTypesMinMax {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int (32位有符号整型)
System.out.println("int(min) = " + Integer.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("int(max) = " + Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("int(bit-length) = " + Integer.SIZE);
// byte (8位有符号整型)
System.out.println("byte(min) = " + Byte.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("byte(max) = " + Byte.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("byte(bit-length)=" + Byte.SIZE);
// short (16位有符号整型)
System.out.println("short(min) = " + Short.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("short(max) = " + Short.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("short(bit-length) = " + Short.SIZE);
// long (64位有符号整型)
System.out.println("long(min) = " + Long.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("long(max) = " + Long.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("long(bit-length) = " + Long.SIZE);
// char (16位字符或者16位无符号整型)
System.out.println("char(min) = " + (int)Character.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("char(max) = " + (int)Character.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("char(bit-length) = " + Character.SIZE);
// float (32位浮点数)
System.out.println("float(min) = " + Float.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("float(max) = " + Float.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("float(bit-length) = " + Float.SIZE);
// double (64位浮点数)
System.out.println("double(min) = " + Double.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("double(max) = " + Double.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("double(bit-length) = " + Double.SIZE);
}
}
int(min) = -2147483648
int(max) = 2147483647
int(bit-length) = 32
byte(min) = -128
byte(max) = 127
byte(bit-length)=8
short(min) = -32768
short(max) = 32767
short(bit-length) = 16
long(min) = -9223372036854775808
long(max) = 9223372036854775807
long(bit-length) = 64
char(min) = 0
char(max) = 65535
char(bit-length) = 16
float(min) = 1.4E-45
float(max) = 3.4028235E38
float(bit-length) = 32
double(min) = 4.9E-324
double(max) = 1.7976931348623157E308
double(bit-length) = 64
String
String不是基本类型,是另外一种常用的类型,它表示文本内容,在Java中字符串使用双引号。
String message = "Hello, world!"; // 字符串使用双引号
char gender = 'm'; // 字符使用单引号
为变量选择数据类型
开发中需要设计合适的变量类型,多数时我们不难选择,你可以用int来存储整型,用float来存储有小数的数值,用String来存储文本,用char来存储单个字符和用boolean来存储二元结果。
经验法则
- 由于int类型非常精确、运行效率高,因此常被用作计数和索引。
- 尽可能的使用int类型。
数据表示
值得注意的是char '1'与int 1、byte 1、short 1、float 1.0、double 1.0、String "1"是不相同的,它们在计算机的内存中有着不同的精度和说明,举例说明:
- byte 1表示00000001
- short 1表示00000000 00000001
- int 1表示00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001
- long 1表示00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001
- float 1.0表示0 01111111 0000000 00000000 00000000
- double 1.0表示0 01111111111 0000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
- char '1'表示00000000 00110001
- String "1"表示复杂的对象
下面我们来看一个变量名称和类型的例子:
Paul买了一台abc品牌的笔记本电脑,3.2GHZ高速处理器、4GB内存、500GB硬盘、15英寸显示器,总价为$1650.45,在现场从服务计划A、B、C中选择了B计划,定义涉及的相关变量和类型。
String name = "Paul";
String brand = "abc";
double processorSpeedInGHz = 3.2; // 或者 float
double ramSizeInGB = 4; // 或者 float
int harddiskSizeInGB = 500; // 或者 short
int monitorInInch = 15; // 或者 byte
double price = 1650.45;
char servicePlan = 'B';
boolean onSiteService = true;
练习:
假设你正在为学校开发一款收集学生信息的软件,学生的信息包括年龄、地址、电话、性别、生日、身高、体重、年级、入学时间等,每个学生被分配一个8位数字标识,下面来使用变量定义它们吧。
8. 用于基本类型和String类型的字面值
编程中使用的文字、字面值都是特定的常量,例如123,-456,3.14,-1.2e3,'a',"Hello", 可以用做赋值或表达式。
Integer(int,long,short,byte)字面值
// 整数默认的都被视作int类型,例如123和-456,在Java中32位的int取值范围从-2,147,483,628(-2^31)到2,147,483,627(2^31-1)
int number = -123;
int sum = 1234567890; // 这个值在int取值范围内
int bigSum = 8234567890; // 错误: 这个值超出了int取值范围
// int字面值没有特殊说明都表示10进制,以0开头的数字表示8进制,以'0x'开头的数字表示16进制。
int number = 1234; // 10进制1234
int number = 01234; // 8进制1234, 10进制668
int number = 0x1abc; // 16进制1ABC, 10进制6844
// 从JDK1.7开始,你可以使用'0b'或者'0B'为前缀来表示二进制,你也可以使用下划线_对数字进行分组来提高可读性,但是开头和结尾必须使用数字。
int number1 = 0b01010000101000101101000010100010;
int number2 = 0b0101_0000_1010_0010_1101_0000_1010_0010;
int number3 = 2_123_456;
// long字面值用数字加上后缀'L'或'l'来表示
long bigNumber = 1234567890123L;
long sum = 123; // int类型123会被自动转换成long类型123L
// byte和short字面值不需要添加后缀,你可以直接使用整数初始化
byte smallNumber = 12345; // 错误: 超出了byte取值范围
byte smallNumber = 123;
short midSizeNumber = -12345;
// 有小数点的数值例如55.66和-33.44默认的被视作double类型,同样你可以用科学计数法表示,例如1.2e3, -5.5E-6, 大写E小写e表示10的指数,你可以用数字加上后缀'd'或'D'表示。
float average = 55.66; // 错误! 右操作是double类型, 需要后缀'f'来表示
float average = 55.66f;
字符字面值和转义序列
// 字符嵌入在单引号里面表示char类型,char类型使用16位的Unicode编码,算术运算上等同于16位无符号整型
char letter = 'a'; // 等同于97
char anotherLetter = 98; // 等同于'b'
System.out.println(letter); // 输出'a'
System.out.println(anotherLetter); // 输出'b'代替数字
anotherLetter += 2; // 100或'd'
System.out.println(anotherLetter); // 输出'd'
非打印的控制字符通常被称为转义序列,通常以反斜线\开始,下面是常用的转义序列:
- 换行符: \n等同于000AH (10D)
- 回车符: \r等同于000DH (13D)
- 制表符: \t等同于0009H (9D)
- 双引号: \"等同于0022H (34D)
- 单引号: \'等同于0027H (39D)
- 反斜线: \\等同于005CH (92D)
说明:
- 用转义序列\n和\r分别表示换行符(000AH)和回车符(000DH),值得注意的是在Unix和Mac中使用\n(0AH)表示换行,而Windows使用\r\n(0D0AH)表示。
- 用转义序列\t表示制表符(0009H)。
- 为了解决歧义,反斜线(\),单引号('),双引号("),分别用转义序列\\,\'和\"来表示。
- 其它不太常用的转义序列: \a警报, \b退格, \f换页, \v垂直标签,某些控制台可能无法支持。
String字面值
长度不定的字符串嵌入在双引号里面表示字符串字面值,例如"Hello, world!","The sum is: ",举例说明:
String directionMsg = "Turn Right";
String greetingMsg = "Hello";
String statusMsg = ""; // 空字符串
// 字符串字面值可能包含转义序列,在字符串你里面,你需要使用 \"来表示双引号,单引号不需要转义,举例说明:
System.out.println("Use \\\" to place\n a \" within\ta\tstring");
Use \" to place a " within a string
练习:编写程序打印输出下面的字符。
'__'
(oo)
+========\/
/ || %%% ||
* ||-----||
"" ""
boolean字面值
// boolean字面值紧包含两个值:true和false
boolean done = true;
boolean gameOver = false;
字面值的例子
public class LiteralTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "Tan Ah Teck"; // String使用双引号
char gender = 'm'; // char使用单引号
boolean isMarried = true; // true或者false
byte numChildren = 8; // byte取值范围[-127, 128]
short yearOfBirth = 1945; // short取值范围[-32767, 32768]
int salary = 88000;
long netAsset = 8234567890L;
double weight = 88.88;
float gpa = 3.88f;
// 输出
System.out.println("Name is " + name);
System.out.println("Gender is " + gender);
System.out.println("Is married is " + isMarried);
System.out.println("Number of children is " + numChildren);
System.out.println("Year of birth is " + yearOfBirth);
System.out.println("Salary is " + salary);
System.out.println("Net Asset is " + netAsset);
System.out.println("Weight is " + weight);
System.out.println("GPA is " + gpa);
}
}
Name is Tan Ah Teck
Gender is m
Is married is true
Number of children is 8
Year of birth is 1945
Salary is 88000
Net Asset is 1234567890
Weight is 88.88
Height is 188.8