java并发之ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal为每个使用该变量的线程提供独立的变量副本,即每个线程内部都会有一个该变量,且在线程内部任何地方都可以使用,线程之间互不影响,这样一来就不存在线程安全问题,也不会严重影响程序执行性能。所以每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会影响其它线程所对应的副本。
对比同步机制与ThreadLocal,可以得出同步通过加锁的方式实现了线程数据共享,也就是以时间换空间,而ThreadLocal则是以变量副本的方式通过以空间换时间的手段实现线程数据共享。
ThreadLocal类提供的几个方法:
public T get() { }
public void set(T value) { }
public void remove() { }
protected T initialValue() { }
get()方法是用来获取ThreadLocal在当前线程中保存的变量副本
set()用来设置当前线程中变量的副本
public void remove()将当前线程局部变量的值删除,目的是为了减少内存的占用,该方法是JDK 5.0新增的方法。需要指出的是,当线程结束后,对应该线程的局部变量将自动被垃圾回收,所以显式调用该方法清除线程的局部变量并不是必须的操作,但它可以加快内存回收的速度。
initialValue()是一个protected方法,一般是用来在使用时进行重写的,它是一个延迟加载方法
首先我们来看一下ThreadLocal类是如何为每个线程创建一个变量的副本的。
先看下get方法的实现:
第一句是取得当前线程,然后通过getMap(t)方法获取到一个map,map的类型为ThreadLocalMap。然后接着下面获取到<key,value>键值对,注意这里获取键值对传进去的是 this,而不是当前线程t。如果获取成功,则返回value值。如果map为空,则调用setInitialValue方法返回value。
我们上面的每一句来仔细分析:首先看一下getMap方法中做了什么:

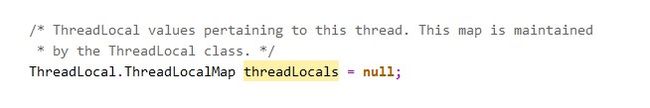
可能大家没有想到的是,在getMap中,是调用当期线程t,返回当前线程t中的一个成员变量threadLocals。
那么我们继续取Thread类中取看一下成员变量threadLocals是什么:
实际上就是一个ThreadLocalMap,这个类型是ThreadLocal类的一个内部类,我们继续取看ThreadLocalMap的实现:
可以看到ThreadLocalMap的Entry继承了WeakReference,并且使用ThreadLocal作为键值。
然后再继续看setInitialValue方法的具体实现:

很容易了解,就是如果map不为空,就设置键值对,为空,再创建Map,看一下createMap的实现:
首先,在每个线程Thread内部有一个ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap类型的成员变量threadLocals,这个threadLocals就是用来存储实际的变量副本的,键值为当前ThreadLocal变量,value为变量副本(即T类型的变量)。
初始时,在Thread里面,threadLocals为空,当通过ThreadLocal变量调用get()方法或者set()方法,就会对Thread类中的threadLocals进行初始化,并且以当前ThreadLocal变量为键值,以ThreadLocal要保存的副本变量为value,存到threadLocals。
首先通过getMap(Thread t)方法获取一个和当前线程相关的ThreadLocalMap,然后将变量的值设置到这个ThreadLocalMap对象中,当然如果获取到的ThreadLocalMap对象为空,就通过createMap方法创建。
线程隔离的秘密,就在于ThreadLocalMap这个类。ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal类的一个静态内部类,它实现了键值对的设置和获取(对比Map对象来理解),每个线程中都有一个独立的ThreadLocalMap副本,它所存储的值,只能被当前线程读取和修改。ThreadLocal类通过操作每一个线程特有的ThreadLocalMap副本,从而实现了变量访问在不同线程中的隔离。因为每个线程的变量都是自己特有的,完全不会有并发错误。还有一点就是,ThreadLocalMap存储的键值对中的键是this对象指向的ThreadLocal对象,而值就是你所设置的对象了
Thread使用:
package com.gpl.concurrent.lock;
public class ThreadLocalTest {
ThreadLocal<Long> longLocal = new ThreadLocal<Long>();
ThreadLocal<String> stringLocal = new ThreadLocal<String>();
public void set() {
longLocal.set(Thread.currentThread().getId());
stringLocal.set(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public long getLong() {
return longLocal.get();
}
public String getString() {
return stringLocal.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final ThreadLocalTest test = new ThreadLocalTest();
test.set();//主线程设置的ThreadLocal
System.out.println(test.getLong());
System.out.println(test.getString());
Thread thread1 = new Thread(){
public void run() {
test.set();//thread1设置的ThreadLocal变量
System.out.println(test.getLong());
System.out.println(test.getString());
};
};
thread1.start();
thread1.join();
System.out.println(test.getLong());
System.out.println(test.getString());
}
}
结果:
1
main
10
Thread-0
1
main
总结一下:
1)实际的通过ThreadLocal创建的副本是存储在每个线程自己的threadLocals中的;
2)为何threadLocals的类型ThreadLocalMap的键值为ThreadLocal对象,因为每个线程中可有多个threadLocal变量,就像上面代码中的longLocal和stringLocal;
3)在进行get之前,必须先set,否则会报空指针异常;
如果想在get之前不需要调用set就能正常访问的话,必须重写initialValue()方法。
因为在上面的代码分析过程中,我们发现如果没有先set的话,即在map中查找不到对应的存储,则会通过调用setInitialValue方法返回i,而在setInitialValue方法中,有一个语句是T value = initialValue(), 而默认情况下,initialValue方法返回的是null。
上面的例子如果在main线程中,没有先set,直接get的话,运行时会报空指针异常。
但是如果改成下面这段代码,即重写了initialValue方法:
package com.gpl.concurrent.lock;
public class ThreadLocalTest {
ThreadLocal<Long> longLocal = new ThreadLocal<Long>(){
protected Long initialValue() {
return Thread.currentThread().getId();
};
};
ThreadLocal<String> stringLocal = new ThreadLocal<String>(){;
protected String initialValue() {
return Thread.currentThread().getName();
};
};
public void set() {
longLocal.set(Thread.currentThread().getId());
stringLocal.set(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public long getLong() {
return longLocal.get();
}
public String getString() {
return stringLocal.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final ThreadLocalTest test = new ThreadLocalTest();
//test.set();//不需要了
System.out.println(test.getLong());
System.out.println(test.getString());
Thread thread1 = new Thread(){
public void run() {
test.set();//thread1设置的ThreadLocal变量
System.out.println(test.getLong());
System.out.println(test.getString());
};
};
thread1.start();
thread1.join();
System.out.println(test.getLong());
System.out.println(test.getString());
}
}
ThreadLocal的应用场景
最常见的ThreadLocal使用场景为 用来解决 数据库连接、Session管理等。
package com.gpl.concurrent.ThreadLocal;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class ConnectionManager {
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> connectionHolder=new ThreadLocal<Connection>(){
@Override
protected Connection initialValue(){
Connection conn=null;
try {
conn=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test", "user", "password");
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
};
public static Connection getConnection(){
return connectionHolder.get();
}
public static void setConnection(Connection conn) {
connectionHolder.set(conn);
}
}