实现同步与互斥的一个实例--生产者消费模型
1.基础知识
1).生产者消费模型中存在3种关系:
a.生产者与生产者之间是互斥的;
b.消费者与消费者之间是互斥的;
c.生产者与消费者之间是同步与互斥的;
2).生产者与消费者的场所,这儿我们选择单链表。
2.内容:a.单生产者生产一个结构体串在链表的表尾上,单消费者从表头取走结构体
代码实现
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<pthread.h>
4
5 typedef struct list
6 {
7 int _data;
8 struct list* _next;
9 }product_list;
10 product_list* head=NULL;
11
12 static pthread_mutex_t lock=PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; //加锁
13 static pthread_cond_t need_product=PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
14
15 product_list* createNode(int data)
16 {
17 product_list* tmp=malloc(sizeof(product_list));
18 tmp->_data=data;
19 tmp->_next=NULL;
20 return tmp;
21 }
22 void InitList(product_list** pHead) //&引用
23 {
24 *pHead=createNode(0);
25 }
26 int PushBack(product_list* pHead,int data)
27 {
28 product_list* tail=pHead;
29 while(tail->_next!=NULL)
30 {
31 tail=tail->_next;
32 }
33 product_list* new=createNode(data);
34 tail->_next=new;
35 return new->_data;
36 }
37 int PopFront(product_list* pHead)
38 {
39 product_list* tmp=pHead->_next;
40 // product_list* tmp=pHead;
41 pHead->_next=pHead->_next->_next;
42 pHead=pHead->_next;
43 tmp->_next=NULL; //易忘
44 int val=tmp->_data;
45 free(tmp); //易忘
46 tmp=NULL;
47 return val;
48 }
49 void* product(void* arg)
50 {
51 int i=0;
52 for(;i<10;i++)
53 {
54 pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
55 int val=PushBack(head,i);
56 pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
57 printf("call consumer!product success!product data is:%d\n",val);
58 pthread_cond_signal(&need_product);
59 sleep(2);
60 }
61 }
62 void* consumer(void* arg)
63 {
64 while(1)
65 {
66 pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
67 while(head->_next==NULL)
68 {
69 pthread_cond_wait(&need_product,&lock);
70 }
71 int val=PopFront(head);
72 pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
73 printf("comsumer success!consumer data is:%d\n",val);
74 sleep(4);
75 }
76 return NULL;
77 }
78 int main()
79 {
80 InitList(&head);
81 pthread_t product1;
82 pthread_t consumer1;
83
84 pthread_create(&product1,NULL,product,NULL);
85 pthread_create(&consumer1,NULL,consumer,NULL);
86
87 pthread_join(product1,NULL);
88 pthread_join(consumer1,NULL);
89
90 return 0;
91 }
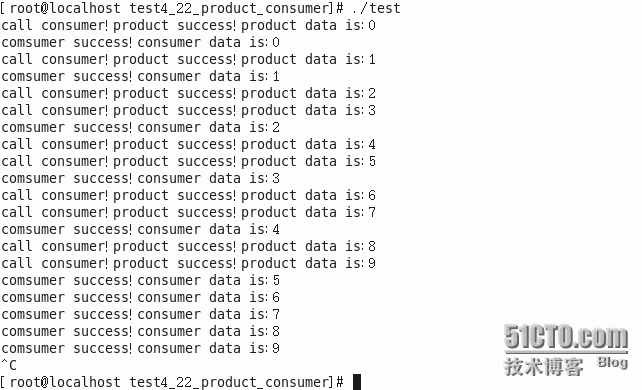
输出结果:
b.多生产者生产一个结构体串在链表的表尾上,多消费者从表头取走结构体。
代码实现
//test.c
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<pthread.h>
4
5 typedef struct list
6 {
7 int _data;
8 struct list* _next;
9 }product_list;
10 product_list* head=NULL;
11
12 static pthread_mutex_t lock=PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;//jia suo
13 static pthread_cond_t need_product=PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
14
15 product_list* createNode(int data)
16 {
17 product_list* tmp=malloc(sizeof(product_list));
18 tmp->_data=data;
19 tmp->_next=NULL;
20 return tmp;
21 }
22 void InitList(product_list** pHead)//&yingyong
23 {
24 *pHead=createNode(0);
25 }
26 int PushBack(product_list* pHead,int data)
27 {
28 product_list* tail=pHead;
29 while(tail->_next!=NULL)
30 {
31 tail=tail->_next;
32 }
33 product_list* new=createNode(data);
34 tail->_next=new;
35 return new->_data;
36 }
37 int PopFront(product_list* pHead)
38 {
39 product_list* tmp=pHead->_next;
40 pHead->_next=pHead->_next->_next;
41 pHead=pHead->_next;
42 tmp->_next=NULL;//
43 int val=tmp->_data;
44 free(tmp);//
45 tmp=NULL;
46 return val;
47 }
48 void* product(void* arg)
49 {
50 int i=0;
51 for(;i<10;i++)
52 {
53 pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
54 int val=PushBack(head,i);
55 pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
56 printf("call consumer!product%s success!product data is:%d\n",(char*)arg,val);
57 pthread_cond_broadcast(&need_product);
58 sleep(1);
59 }
60 }
61 void* consumer(void* arg)
62 {
63 while(1)
64 {
65 pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
66 while(head->_next==NULL)
67 {
68 pthread_cond_wait(&need_product,&lock);
69 }
70 int val=PopFront(head);
71 pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
72 printf("comsumer success!consumer%s data is:%d\n",(char*)arg,val);
73 // sleep(2);
74 }
75 }
76 int main()
77 {
78 InitList(&head);
79 pthread_t product1;
80 pthread_t product2;
81 pthread_t product3;
82 pthread_t consumer1;
83 pthread_t consumer2;
84 pthread_t consumer3;
85
86 char* p1="1";
87 char* p2="2";
88 char* p3="3";
89
90 pthread_create(&product1,NULL,product,(void*)p1);
91 pthread_create(&product2,NULL,product,(void*)p2);
92 pthread_create(&product3,NULL,product,(void*)p3);
93 pthread_create(&consumer1,NULL,consumer,(void*)p1);
94 pthread_create(&consumer2,NULL,consumer,(void*)p2);
95 pthread_create(&consumer3,NULL,consumer,(void*)p3);
96
97 pthread_join(product1,NULL);
98 pthread_join(product2,NULL);
99 pthread_join(product3,NULL);
100 pthread_join(consumer1,NULL);
101 pthread_join(consumer2,NULL);
102 pthread_join(consumer3,NULL);
103
104 return 0;
105 }
//makefile
1 test:test.c
2 gcc -o $@ $^ -lpthread
3 .PHONY:clean
4 clean:
5 rm -f test
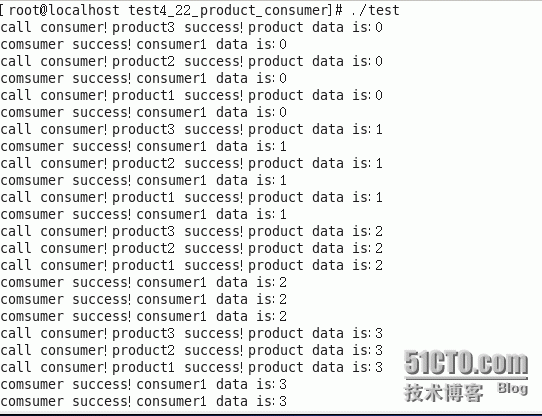
输出结果:
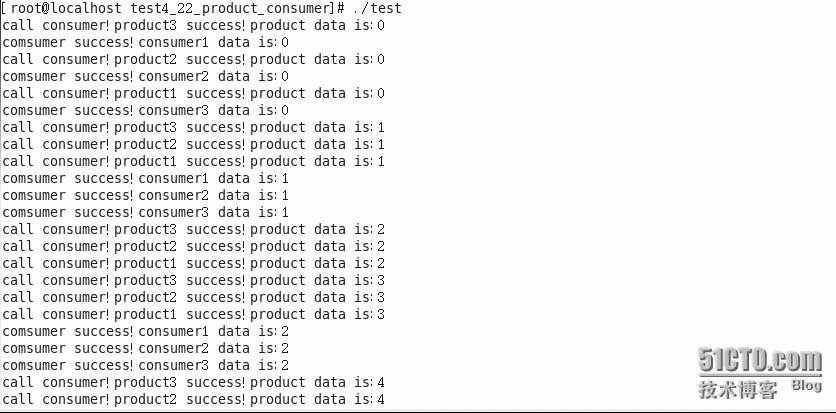 把consumer中的sleep(2)注释,则,消费者消费会加快,但它会跟随成产者的生产的步伐,结果如下:
把consumer中的sleep(2)注释,则,消费者消费会加快,但它会跟随成产者的生产的步伐,结果如下:
3.总结:
1)a,b主要就是生产者通知的方式不同,单生产者单消费者采用pthread_cond_signal,多生产者多消费者采用pthread_cond_broadcast
2)生产者消费模型,它们访问临界资源--产品的操作必须是互斥的,且操作为原子操作,否则会发生访问冲突,如上篇我们所验证的,最终得到结果和我们所预测的有很大差别,所以我们加入了互斥锁
3)为了提高效率,我们引入了条件变量,即实现生产者每生产出了一件产品,就通知消费者过来取数据,反过来,消费者每消费完一件产品就告诉生产者,这样就提高了效率实现了线程之间的顺序性,实现同步
疑问:忘了pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
是product()destroy一次就够了,还是product()和consumer()两个都要