高级数据结构-树状数组总结
高级数据结构-树状数组总结
一维树状数组
1.更改单点,输出区间和
一般用向上修改,向下统计, 也就是在updata函数里面使用+=,在 sum函数里面使用-=
完整代码如下
void updata(int x, int num)
{
while (x <= n) //树状数组的大小
{
bit[x] += num;
x += lowbit(x); //lowbit返回2^k 函数内容为return x&-x;
}
}
int sum(int x)
{
int sum = 0;
while (x > 0)
{
sum += bit[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return sum;
}
例题如下 杭电 敌兵布阵
题意就是对n个阵地中的某个,进行数目的加减操作,然后输出从a到b阵地的总人数。
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 50000 + 10;
int BIT[MAXN], t;
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&-x;
}
void updata(int x, int num)
{
while (x <= t)
{
BIT[x] += num;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
int sum(int x)
{
int sum = 0;
while (x > 0)
{
sum += BIT[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
//freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif // LOCAL
int T;
int num, a, b;
int Ncase = 1;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--)
{
memset(BIT, 0, sizeof(BIT));
scanf("%d", &t);
for (int i = 1; i <= t; ++i)
{
scanf("%d", &num);
updata(i, num); //单点更新
}
printf("Case %d:\n", Ncase++);
char command[10];
while (scanf("%s", command) != EOF)
{
if (command[0] == 'E')
break;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
if (command[0] == 'S')
updata(a, -b); //单点更新
else if (command[0] == 'A')
updata(a, b); //单点更新
else
printf("%d\n", sum(b) - sum(a-1)); //返回总和 因为sum(b) 返回从1到b的值,然后 sum(a-1)返回从1到a-1的值 相减就是a到b的值。
}
}
return 0;
}
一般用向下修改,向上统计, 也就是在updata函数里面使用-=,在 sum函数里面使用+=
完整代码如下
void updata(int x, int num)
{
while (x > 0)
{
bit[x] += num;
x -= lowbit(x); //lowbit返回2^k 函数内容为return x&-x;
}
}
int sum(int x)
{
int sum = 0;
while (x <= n) //树状数组的大小
{
sum += bit[x];
x += lowbit(x);
}
return sum;
}
例题如下杭电 Color the ball
题意 在一段连续的区间上 从a到b依次 涂色 也就是值+1 然后输出某个单点的值
代码如下
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100000 + 10;
int bit[MAXN], n;
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&-x;
}
void updata(int x, int num)
{
while (x > 0)
{
bit[x] += num;
x -= lowbit(x);
}
}
int sum(int x)
{
int sum = 0;
while (x <= n)
{
sum += bit[x];
x += lowbit(x);
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
//freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif // LOCAL
int a, b;
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF && n != 0)
{
memset(bit, 0 ,sizeof(bit));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
updata(b, 1); //单点更新
updata(a - 1, -1); //单点更新
}
printf("%d", sum(1)); //因为单点更新的时候取+1, -1 相互抵消,所以sum(1)就是单点的值
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
printf(" %d", sum(i));
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
一维树状数组更新和求和可以在数轴上进行模拟,用区间来表示。理解更快。
二维树状数组
二维树状数组在操作是,是以二维的直角坐标系为基准,在更新时应该注意边界问题
1.单点更新,输出区间
在updata里面使用 += 在Query里面使用-=
实例如下
void updata(int x, int y, int num)
{
int temp = x;
while (y <= n)
{
x = temp;
while (x <= n)
{
bit[x][y] += num;
x += lowbit(x);
}
y += lowbit(y);
}
}
int Query(int x, int y)
{
int sum = 0;
int temp = x;
while (y > 0)
{
x = temp; //指针一定要初始化
while (x > 0)
{
sum += bit[x][y];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
y -= lowbit(y);
}
return sum;
} 例题 POJ Mobile phones
题意 在一个已知的二维空间,输入命令1 表示 在 所指示的点加上指定的 数 输入命令2 则输出所指向的二维区间的和
用向上更新,向下求和
代码如下
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1250;
int bit[MAXN][MAXN], n;
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&-x;
}
void updata(int x, int y, int num)
{
int temp = x;
while (y <= n)
{
x = temp;
while (x <= n)
{
bit[x][y] += num;
x += lowbit(x);
}
y += lowbit(y);
}
}
int Query(int x, int y)
{
int sum = 0;
int temp = x;
while (y > 0)
{
x = temp;
while (x > 0)
{
sum += bit[x][y];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
y -= lowbit(y);
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
//freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif // LOCAL
int com;
int x, y, a, b;
while (scanf("%d", &com) != EOF && com != 3)
{
if (com == 0)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
memset(bit, 0, sizeof(bit));
}
else if (com == 1)
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &a);
updata(x + 1, y + 1, a); //单点向上更新
}
else
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x, &y, &a, &b);
x++; y++; a++; b++;
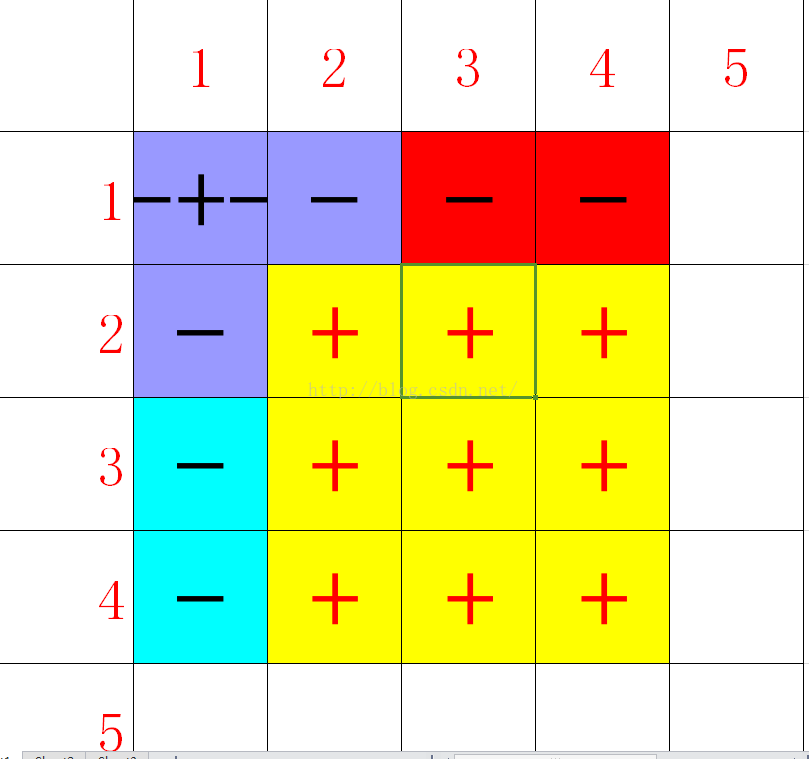
printf("%d\n", Query(a, b) - Query(a, y - 1) - Query(x - 1, b) + Query(x - 1, y - 1)); //向下求和 求和注意筛选区间以及边界问题
}
}
return 0;
}
关于区间的筛选和边界 如图所示
2.区间更新,输出单点
和一维的类似 ,在二维里面,仍然是用两个坐标之间的差值,代表所更新的区间,而坐标之间的差值,需要考虑,上图所示
例子代码,就不写了,和一维类似,只是改变单点更新里面的大小。
直接上例题: POJ Matrix
题意: 给定大小的矩阵中,C表示更新区段,Q表示,输入单点值 这里只有0和1 两种 所以采用累加 然后求和
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1010;
int bit[MAXN][MAXN], n;
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&-x;
}
void updata(int x, int y, int num)
{
int temp = x;
while (y <= n)
{
x = temp;
while (x <= n)
{
bit[x][y] += num;
x += lowbit(x);
}
y += lowbit(y);
}
}
int Query(int x, int y)
{
int sum = 0;
int temp = x;
while ( y > 0)
{
x = temp;
while( x > 0)
{
sum += bit[x][y];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
y -= lowbit(y);
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
//freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif // LOCAL
int t, T;
int blank = 0;
int x1, x2, y1, y2;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--)
{
memset(bit, 0, sizeof(bit));
scanf("%d%d", &n, &t);
if (blank++ != 0)
printf("\n");
while (t--)
{
char command[3];
scanf("%s", command);
if (command[0] == 'C')
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2);
updata(x1, y1, 1);
updata(x2 + 1, y1, -1);
updata(x1, y2 + 1, -1);
updata(x2 + 1, y2 + 1, 1); //更新时 区间的选用 参照上面的图片
}
else
{
scanf("%d%d", &x1, &y1);
printf("%d\n", Query(x1, y1) % 2);
}
}
}
return 0;
}