字典树trie
今天上网看别人说杭电oj的1251和1671两个题用了字典树的方法,菜鸟也研究了一下,做了两道题,做做总结。
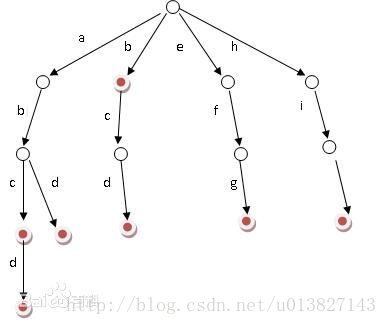
字典树原名叫Trie,取自单词retrieval,是用字典的方式存储数据的方法,截取百度的图片:
结构上的特点就是你得知道要存储的都有哪些字符才行,因为作为子节点的每个字符在父节点中都是有固定位置的,比如已知要存的只有小写字母,那定义node的时候为子节点预留26个指针,如果只有十个数字,就留10个。指针默认为NULL,如果不是NULL就说明这个位置已经存储过内容,就是说用指针是否为NULL判断有没有。
既然是字典,肯定就没有重复的单词了,上图中的abcd这个单词只有一个,再来一个abcd的话最多也只是修改一下这个单词出现的次数,其实这个东西主要就是用来统计频次的。其中根节点为空,然后定义“存储”,“查找”这两个操作就行了。
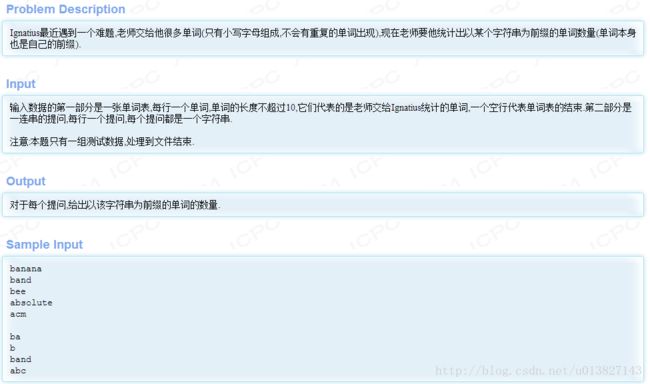
以1251为例,题目如下:
这个准确用到了存储store()查找check()两个操作,代码如下:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int times;
node*next[26];
node(){times=1;memset(next,0,26*sizeof(int));}
}root;
void store(char*st)
{
node*p=&root;
for(int i=0;st[i];++i)
{
int k=st[i]-'a';
if(p->next[k]==NULL)
p->next[k]=new node;
else
++(p->next[k]->times);
p=p->next[k];
}
}
int check(char*st)
{
node*p=&root;
for(int i=0;st[i];++i)
{
int k=st[i]-'a';
if(p->next[k]==NULL)
return 0;
else p=p->next[k];
}
return p->times;
}
int main()
{
char st[11];
while(cin.getline(st,11)&&strlen(st))
store(st);
while(cin.getline(st,11)&&strlen(st))
printf("%d\n",check(st));
return 0;
}很明显,存储时字母存在节点p->next[k]中,根节点只做标记用。
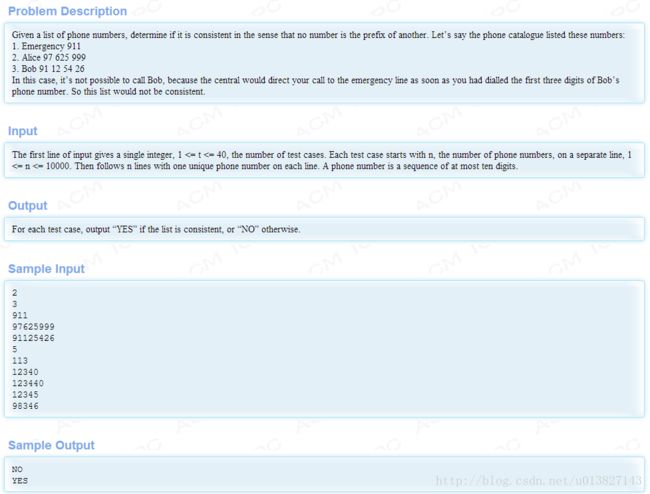
题目1671的要求如下:
字典树可以很方便的查找前缀,这里前缀冲突有两种,一是短的前缀已存在,存储长的时冲突,二是长的存在,存储短的是冲突。代码如下:
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
bool end;
node*next[10];
node()
{
end=false;
fill(next,next+10,(node*)NULL);
}
};
bool store(char*st,node*p)
{
for(int i=0;st[i];++i)
{
int k=st[i]-'0';
if(p->next[k]==NULL)
p->next[k]=new node;
else if(p->next[k]->end)
return false;
if(!st[i+1])
{
for(int j=0;j<10;++j)
if(p->next[k]->next[j])
return false;
p->next[k]->end=true;
}
p=p->next[k];
}
return true;
}
void free(node*p)
{
for(int i=0;i<10;++i)
if(p->next[i])
free(p->next[i]);
for(int i=0;i<10;++i)
if(p->next[i])
delete(p->next[i]);
}
int main()
{
int n; scanf("%d",&n);
while(n--)
{
node root;
int m,fail=0; scanf("%d",&m);
while(m--)
{
char no[12]; scanf("%s",no);
if(!fail&&!store(no,&root)) fail=1;
}
if(fail) printf("NO\n");
else printf("YES\n");
free(&root);
}
return 0;
}
这里只要对store()稍作改动就能用,因为数据比较大,要有一个回收垃圾的free,不然内存超限,用标记fail也能有效的优化。