- 简单了解 JVM
记得开心一点啊
jvm
目录♫什么是JVM♫JVM的运行流程♫JVM运行时数据区♪虚拟机栈♪本地方法栈♪堆♪程序计数器♪方法区/元数据区♫类加载的过程♫双亲委派模型♫垃圾回收机制♫什么是JVMJVM是JavaVirtualMachine的简称,意为Java虚拟机。虚拟机是指通过软件模拟的具有完整硬件功能的、运行在一个完全隔离的环境中的完整计算机系统(如:JVM、VMwave、VirtualBox)。JVM和其他两个虚拟机
- 最超值的Mac——Mac mini
初心么么哒
你知道最超值的Mac是什么吗?自2005年以来,Macmini一直是Apple台式机产品线中的主要产品。最初推出是为了让对Mac好奇的Mac进入Apple生态系统的一种简单方式,现在新的AppleSiliconMacmini可能是任何寻找新Mac的人的最有吸引力的购买。什么是AppleSiliconMacmini?M1Macmini是Apple最小的台式电脑,同时也是最快的台式电脑之一。最新型号由
- 你可能遗漏的一些C#/.NET/.NET Core知识点
追逐时光者
C#.NETDotNetGuide编程指南c#.net.netcoremicrosoft
前言在这个快速发展的技术世界中,时常会有一些重要的知识点、信息或细节被忽略或遗漏。《C#/.NET/.NETCore拾遗补漏》专栏我们将探讨一些可能被忽略或遗漏的重要知识点、信息或细节,以帮助大家更全面地了解这些技术栈的特性和发展方向。拾遗补漏GitHub开源地址https://github.com/YSGStudyHards/DotNetGuide/blob/main/docs/DotNet/D
- 数据结构 | 栈和队列
TT-Kun
数据结构与算法数据结构栈队列C语言
文章目录栈和队列1.栈:后进先出(LIFO)的数据结构1.1概念与结构1.2栈的实现2.队列:先进先出(FIFO)的数据结构2.1概念与结构2.2队列的实现3.栈和队列算法题3.1有效的括号3.2用队列实现栈3.3用栈实现队列3.4设计循环队列结论栈和队列在计算机科学中,栈和队列是两种基本且重要的数据结构,它们在处理数据存储和访问顺序方面有着独特的规则和应用。本文将详细介绍栈和队列的概念、结构、实
- 基于STM32与Qt的自动平衡机器人:从控制到人机交互的的详细设计流程
极客小张
stm32qt机器人物联网人机交互毕业设计c语言
一、项目概述目标和用途本项目旨在开发一款基于STM32控制的自动平衡机器人,结合步进电机和陀螺仪传感器,实现对平衡机器人的精确控制。该机器人可以用于教育、科研、娱乐等多个领域,帮助用户了解自动控制、机器人运动学等相关知识。技术栈关键词STM32单片机步进电机陀螺仪传感器AD采集电路Qt人机界面实时数据监控二、系统架构系统架构设计本项目的系统架构设计包括以下主要组件:控制单元:STM32单片机传感器
- 基于STM32的汽车仪表显示系统:集成CAN、UART与I2C总线设计流程
极客小张
stm32汽车嵌入式硬件物联网单片机c语言
一、项目概述项目目标与用途本项目旨在设计和实现一个基于STM32微控制器的汽车仪表显示系统。该系统能够实时显示汽车的速度、转速、油量等关键信息,并通过CAN总线与其他汽车控制单元进行通信。这种仪表显示系统不仅提高了驾驶的安全性和便捷性,还能为汽车提供更智能的用户体验。技术栈关键词微控制器:STM32显示技术:TFTLCD/OLED传感器:速度传感器、温度传感器、油量传感器通信协议:CAN总线、UA
- 【c++基础概念深度理解——堆和栈的区别,并实现堆溢出和栈溢出】
XWWW668899
C++基本概念c++c语言开发语言青少年编程
文章目录概要技术名词解释栈溢出和堆溢出小结概要学习C++语言,避免不了要好好理解一下堆(Heap)和栈(Stack),有助于更好地管理内存,以及如何写出一段程序“成功实现”堆溢出和栈溢出。技术名词解释理解东西最快的方式是根据自己目前能理解的词语去关联新的概念,不断的纠正,向正确的深度理解靠近,当无限接近的时候也就理解了想要理解的概念。我们经常说堆栈,把这两个名词放到一起。其实,堆是堆,栈是栈,两种
- Golang语言基础知识点总结
最帅猪猪侠
golang开发语言后端
Golang语言基础知识点小总结1.go语言有两大类型:值类型:数值类型,bool,string,数组,struct结构体变量直接存储值,内存通常在栈中分配,修改值,不会对源对象产生影响引用类型:指针,slice切片,管道chan,map,interface变量存储的是一个地址,这个地址对应的空间才真正存储数据值,内存通常在堆上分配,当没有任何变量引用这个地址时,该地址对应的数据空间就成为一个垃圾
- Rust 所有权 简介
东离与糖宝
rust后端rust开发语言
文章目录发现宝藏1.所有权基本概念2.所有权规则3.变量作用域4.栈与堆4.1栈(Stack)4.2堆(Heap)5.String类型5.1String类型5.2String的内存分配5.3所有权与内存管理5.4String与切片6.变量与数据交互方式6.1移动(Move)6.2.克隆(Clone)7.所有权与函数7.1.传递参数7.2.返回值总结发现宝藏前些天发现了一个巨牛的人工智能学习网站,通
- golang学习笔记--MPG模型
xxzed
golang#学习笔记学习笔记golang
MPG模式:M(Machine):操作系统的主线程P(Processor):协程执行需要的资源(上下文context),可以看作一个局部的调度器,使go代码在一个线程上跑,他是实现从N:1到N:M映射的关键G(Goroutine):协程,有自己的栈。包含指令指针(instructionpointer)和其它信息(正在等待的channel等等),用于调度。一个P下面可以有多个G1、当前程序有三个M,
- LeetCode:2390. 从字符串移除*号 使用栈,时间复杂度O(N)
忍界英雄
每日一题leetcodelinux算法
2390.从字符串移除*号today2390.从字符中移除*号题目表述给你一个包含若干星号*的字符串s。在一步操作中,你可以:选中s中的一个星号。移除星号左侧最近的那个非星号字符,并移除该星号自身。返回移除所有星号之后的字符串。注意:生成的输入保证总是可以执行题面中描述的操作。可以证明结果字符串是唯一的。示例1:输入:s=“leet**cod*e”输出:“lecoe”解释:从左到右执行移除操作:距
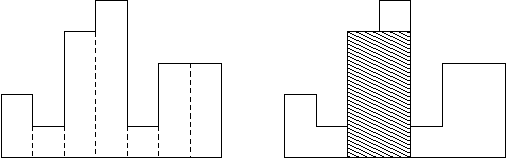
- 【LeetCode 算法笔记】84. 柱状图中最大的矩形
Sardar_
算法leetcode笔记
目录问题描述暴力求解:栈问题描述给定n个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为1。求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。示例1:输入:heights=[2,1,5,6,2,3]输出:10解释:最大的矩形为图中红色区域,面积为10示例2:输入:heights=[2,4]输出:4提示:1int:area=0n=len(heights)foriinrange(n):
- 【LeetCode 算法笔记】739. 每日温度
Sardar_
算法leetcode笔记
目录问题描述暴力解法栈问题描述给定一个整数数组temperatures,表示每天的温度,返回一个数组answer,其中answer[i]是指对于第i天,下一个更高温度出现在几天后。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用0来代替。示例1:输入:temperatures=[73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73]输出:[1,1,4,2,1,1,0,0]示例2:输入:temperatures=
- 【Java】面试题31:栈的压入,弹出序列
小小核桃
剑指offerjava版
~~题目:~~输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如,序列{1,2,3,4,5}是某栈的压栈序列,序列{4,5,3,2,1}是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但{4,3,5,1,2}就不可能是该栈序列的弹出序列。思路:首先借助一个辅助栈,把输入的第一个序列中的数字依次压入该辅助栈,并按照第二个序列的顺序依次从该栈中弹出数
- Vector与Stack简述
Sun_Jingjing
Java集合
Vector:线程安全,默认容量为10,容量增长量默认为0,每次进行扩容是旧的容量乘以2。支持null的添加。基于数组实现。Stack:Stack继承Vector的栈结构。
- 车载以太网之SOME/IP
IT_码农
车载以太网车载以太网SOME/IP
整体介绍SOME/IP(全称为:Scalableservice-OrientedMiddlewarEoverIP),是运行在车载以太网协议栈基础之上的中间件,或者也可以称为应用层软件。发展历程AUTOSAR4.0-完成宝马SOME/IP消息的初步集成;AUTOSAR4.1-支持SOME/IP-SD及其发布/订阅功能;AUTOSAR4.2-添加transformer用于序列化以及其他相关优化;AUT
- Rust: duckdb和polars读csv文件比较
songroom
rust开发语言后端
duckdb在数据分析上,有非常多不错的特质。1、快;2、客户体验好,特别是可以同时批量读csv(在一个目录下的csv等文件)。polars的性能比pandas有非常多的超越。但背后的一些基于arrow的技术栈有很多相同之类。今天想比较一下两者在csv数据读写的情况。一、文件准备csv样本内容,是N行9列的csv标准格式,有字符串,有浮点数,有整型。具体如下:本次准备了两个csv文件,一个大约是2
- 首次全面解析云原生成熟度模型:解决企业「诊断难、规划难、选型难」问题
阿里云云栖号
云原生云计算运维阿里云
从“上云”到“云上”原生,云原生提供了最优用云路径,云原生的技术价值已被广泛认可。当前行业用户全面转型云原生已是大势所趋,用户侧云原生平台建设和应用云原生化改造进程正在加速。然而,云原生复杂的技术栈和传统IT的历史包袱给用户带来了巨大挑战,针对平台建设和应用改造的能力要求缺少统一规范成为企业转型的最大障碍。在用户侧,企业执行层面存在“三难”问题,即诊断难、规划难、选型难,需求和供给不能精准对应,缺
- Android 开发必备知识点整理(1)
2401_84123113
程序员androidarm开发
1.虚拟机栈/本地方法栈中引用的对象2.方法区中常量/静态变量引用的对象四种引用强引用:不会被回收软引用:内存不足时会被回收弱引用:gc时会被回收虚引用:无法通过虚引用得到对象,可以监听对象的回收ClassLoader类的生命周期:1.加载;2.验证;3.准备;4.解析;5.初始化;6.使用;7.卸载类加载过程:1.加载:获取类的二进制字节流;生成方法区的运行时存储结构;在内存中生成Class对象
- Java 并发编程:Java 线程池的介绍与使用
栗筝i
栗筝i的Java技术栈#Java基础栗筝i的Java技术栈Java基础Java并发Java线程池
大家好,我是栗筝i,这篇文章是我的“栗筝i的Java技术栈”专栏的第024篇文章,在“栗筝i的Java技术栈”这个专栏中我会持续为大家更新Java技术相关全套技术栈内容。专栏的主要目标是已经有一定Java开发经验,并希望进一步完善自己对整个Java技术体系来充实自己的技术栈的同学。与此同时,本专栏的所有文章,也都会准备充足的代码示例和完善的知识点梳理,因此也十分适合零基础的小白和要准备工作面试的同
- 第二章 按问题编程
ronghuilin
程序特征程序设计
程序设计的基础,建立计算机编程思维,掌握基本问题的分析,与编写源程序。1.在一组数据中寻找一个元素操作“寻找”在计算机软件中是“搜索”,近几年称为“扫描”。首先应了解这些数据存放在什么结构中。一组数据能存储在线性表(one-to-one)中,每个元素只有一个前趋和后继,常用的是数组array,应用性能高的是栈Stack与队列queue。数学计算在计算机程序中的基础是矩阵计算,矩阵存放在二维数组中。
- 栈区-----顺序栈------队列
(笑)z
数据结构
栈栈(Stack)是一种遵循后进先出(LIFO,LastInFirstOut)原则的有序集合。这种数据结构只允许在栈顶进行添加(push)或删除(pop)元素的操作。换句话说,最新添加的元素会被最先移除。栈的这种特性使得它在多种编程和应用场景中非常有用,比如函数调用、括号匹配、表达式求值、页面访问历史等。只允许从一端进行数据的插入和删除的线性存储结构顺序栈:类似数组满增栈,满减栈,空增栈,空减栈空
- 数据结构,有头链表
(笑)z
数据结构
数据结构基本概念:1.定义一组用来保存一种或者多种特定关系的数据的集合(组织和存储数据)程序的设计:将现实中大量而复杂的问题以特定的数据类型和特定的存储结构存储在内存中,并在此基础上实现某个特定的功能的操作;程序=数据结构+算法2.数据与数据之间的关系数据的逻辑结构:数据元素与元素之间的关系集合:关系平等线性结构:元素之间一对一的关系(表(数组,链表),队列。栈。。。)树型结构:元素之间一对多的关
- Google大数据架构技术栈
剑海风云
BigData大数据架构GoogleBigData
数据存储层ColossusColossus作为Google下一代GFS(GoogleFileSystem)。GFS本身存在一些不足单主瓶颈GFS依赖单个主节点进行元数据管理,随着数据量和访问请求的增长,出现了可扩展性瓶颈。想象一下,只有一位图书管理员管理着一个庞大的图书馆——最终,事情变得难以承受。元数据可扩展性有限主节点上的集中元数据存储无法有效扩展,影响了性能并妨碍了PB和EB级数据的管理。实
- 返利APP排行榜的实时更新与维护策略
weixin_836869520
springboot微服务java
返利APP排行榜的实时更新与维护策略大家好,我是微赚淘客返利系统3.0的小编,是个冬天不穿秋裤,天冷也要风度的程序猿!今天我们来探讨如何实现返利APP排行榜的实时更新与维护策略。排行榜的数据更新是提升用户体验、保持应用竞争力的关键部分。接下来,我将介绍如何通过设计有效的数据更新机制和使用合适的技术栈来实现这一目标。1.数据源的选择与整合排行榜的核心在于数据源。我们需要选择合适的第三方API或内部数
- Activity->Activity中动态添加Fragment->Fragment回退栈BackStack
Yang-Never
Activityandroidkotlinandroidstudio开发语言
Fragment回退栈Fragment回退栈用于管理Fragment的导航历史(添加、删除、替换)。每个Activity都有一个包含其所有Fragment的FragmentManager,调用其addToBackStack方法时,这个事务就会被添加到FragmentManager的回退栈中当用户按下返回键时,系统就会从回退栈中弹出并反向执行最近的事务。如果你替换了一个Fragment,并将这个操作
- 探索ASP.NET Core 8.0的奇妙世界
郎凌队Lois
探索ASP.NETCore8.0的奇妙世界practical-aspnetcore该项目提供了关于ASP.NETCore实际应用开发的一系列教程和示例,涵盖了从基础知识到高级主题,是一个实用的学习资源库。适合于想要掌握ASP.NETCore技术栈的开发者进行学习和参考。项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/pr/practical-aspnetcore随着微软的A
- 探索未来Web开发的精简之道:ASP.NET Core 8.0 Minimal API 示例项目
尚舰舸Elsie
探索未来Web开发的精简之道:ASP.NETCore8.0MinimalAPI示例项目随着微服务和云原生架构的兴起,轻量级API成为了开发社区的新宠。ASP.NETCore8.0MinimalAPIExample正是这样一个项目,它集成了最新技术栈,简化了API开发过程,让开发者能够以最少的代码实现强大的功能。本文将带你深入了解这一开源杰作,揭示其技术魅力,并探索其应用场景。项目介绍ASP.NET
- 安卓将本地日志上传到服务器
胡子洲
Androidandroid服务器
在安卓开发中,将本地日志上传到服务器是一个常见的需求,特别是在开发需要远程监控或调试的应用时。以下是一个基本的步骤和示例,说明如何实现这一功能:1本地日志上传到服务器1.1准备服务器首先,你需要在服务器上设置一个接口,用于接收上传的日志文件。这个接口可以是RESTfulAPI,使用HTTPPOST方法接收文件。你可以使用各种后端技术栈来实现这个接口,如Node.js、Python(Flask或Dj
- git 压栈存储当前分支修改,出栈使用保存
星叔
gitgit
当你在修改当前分支时。突然有个更紧急的任务,或者需要将当前分支保存到其它分支,这个时候就能用到这个命令gitstash。本章只记录存储一次修改的操作,其它拓展命令可以在git文档中检索gitstash。当当前文档修改完成$gitbranch-a查看当前远程仓库有几个分支mainremotes/origin/Dev分支$gitstash保存当前分支的修改Savedworkingdirectoryan
- SQL的各种连接查询
xieke90
UNION ALLUNION外连接内连接JOIN
一、内连接
概念:内连接就是使用比较运算符根据每个表共有的列的值匹配两个表中的行。
内连接(join 或者inner join )
SQL语法:
select * fron
- java编程思想--复用类
百合不是茶
java继承代理组合final类
复用类看着标题都不知道是什么,再加上java编程思想翻译的比价难懂,所以知道现在才看这本软件界的奇书
一:组合语法:就是将对象的引用放到新类中即可
代码:
package com.wj.reuse;
/**
*
* @author Administrator 组
- [开源与生态系统]国产CPU的生态系统
comsci
cpu
计算机要从娃娃抓起...而孩子最喜欢玩游戏....
要让国产CPU在国内市场形成自己的生态系统和产业链,国家和企业就不能够忘记游戏这个非常关键的环节....
投入一些资金和资源,人力和政策,让游
- JVM内存区域划分Eden Space、Survivor Space、Tenured Gen,Perm Gen解释
商人shang
jvm内存
jvm区域总体分两类,heap区和非heap区。heap区又分:Eden Space(伊甸园)、Survivor Space(幸存者区)、Tenured Gen(老年代-养老区)。 非heap区又分:Code Cache(代码缓存区)、Perm Gen(永久代)、Jvm Stack(java虚拟机栈)、Local Method Statck(本地方法栈)。
HotSpot虚拟机GC算法采用分代收
- 页面上调用 QQ
oloz
qq
<A href="tencent://message/?uin=707321921&Site=有事Q我&Menu=yes">
<img style="border:0px;" src=http://wpa.qq.com/pa?p=1:707321921:1></a>
- 一些问题
文强chu
问题
1.eclipse 导出 doc 出现“The Javadoc command does not exist.” javadoc command 选择 jdk/bin/javadoc.exe 2.tomcate 配置 web 项目 .....
SQL:3.mysql * 必须得放前面 否则 select&nbs
- 生活没有安全感
小桔子
生活孤独安全感
圈子好小,身边朋友没几个,交心的更是少之又少。在深圳,除了男朋友,没几个亲密的人。不知不觉男朋友成了唯一的依靠,毫不夸张的说,业余生活的全部。现在感情好,也很幸福的。但是说不准难免人心会变嘛,不发生什么大家都乐融融,发生什么很难处理。我想说如果不幸被分手(无论原因如何),生活难免变化很大,在深圳,我没交心的朋友。明
- php 基础语法
aichenglong
php 基本语法
1 .1 php变量必须以$开头
<?php
$a=” b”;
echo
?>
1 .2 php基本数据库类型 Integer float/double Boolean string
1 .3 复合数据类型 数组array和对象 object
1 .4 特殊数据类型 null 资源类型(resource) $co
- mybatis tools 配置详解
AILIKES
mybatis
MyBatis Generator中文文档
MyBatis Generator中文文档地址:
http://generator.sturgeon.mopaas.com/
该中文文档由于尽可能和原文内容一致,所以有些地方如果不熟悉,看中文版的文档的也会有一定的障碍,所以本章根据该中文文档以及实际应用,使用通俗的语言来讲解详细的配置。
本文使用Markdown进行编辑,但是博客显示效
- 继承与多态的探讨
百合不是茶
JAVA面向对象 继承 对象
继承 extends 多态
继承是面向对象最经常使用的特征之一:继承语法是通过继承发、基类的域和方法 //继承就是从现有的类中生成一个新的类,这个新类拥有现有类的所有extends是使用继承的关键字:
在A类中定义属性和方法;
class A{
//定义属性
int age;
//定义方法
public void go
- JS的undefined与null的实例
bijian1013
JavaScriptJavaScript
<form name="theform" id="theform">
</form>
<script language="javascript">
var a
alert(typeof(b)); //这里提示undefined
if(theform.datas
- TDD实践(一)
bijian1013
java敏捷TDD
一.TDD概述
TDD:测试驱动开发,它的基本思想就是在开发功能代码之前,先编写测试代码。也就是说在明确要开发某个功能后,首先思考如何对这个功能进行测试,并完成测试代码的编写,然后编写相关的代码满足这些测试用例。然后循环进行添加其他功能,直到完全部功能的开发。
- [Maven学习笔记十]Maven Profile与资源文件过滤器
bit1129
maven
什么是Maven Profile
Maven Profile的含义是针对编译打包环境和编译打包目的配置定制,可以在不同的环境上选择相应的配置,例如DB信息,可以根据是为开发环境编译打包,还是为生产环境编译打包,动态的选择正确的DB配置信息
Profile的激活机制
1.Profile可以手工激活,比如在Intellij Idea的Maven Project视图中可以选择一个P
- 【Hive八】Hive用户自定义生成表函数(UDTF)
bit1129
hive
1. 什么是UDTF
UDTF,是User Defined Table-Generating Functions,一眼看上去,貌似是用户自定义生成表函数,这个生成表不应该理解为生成了一个HQL Table, 貌似更应该理解为生成了类似关系表的二维行数据集
2. 如何实现UDTF
继承org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.udf.generic
- tfs restful api 加auth 2.0认计
ronin47
目前思考如何给tfs的ngx-tfs api增加安全性。有如下两点:
一是基于客户端的ip设置。这个比较容易实现。
二是基于OAuth2.0认证,这个需要lua,实现起来相对于一来说,有些难度。
现在重点介绍第二种方法实现思路。
前言:我们使用Nginx的Lua中间件建立了OAuth2认证和授权层。如果你也有此打算,阅读下面的文档,实现自动化并获得收益。SeatGe
- jdk环境变量配置
byalias
javajdk
进行java开发,首先要安装jdk,安装了jdk后还要进行环境变量配置:
1、下载jdk(http://java.sun.com/javase/downloads/index.jsp),我下载的版本是:jdk-7u79-windows-x64.exe
2、安装jdk-7u79-windows-x64.exe
3、配置环境变量:右击"计算机"-->&quo
- 《代码大全》表驱动法-Table Driven Approach-2
bylijinnan
java
package com.ljn.base;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.uti
- SQL 数值四舍五入 小数点后保留2位
chicony
四舍五入
1.round() 函数是四舍五入用,第一个参数是我们要被操作的数据,第二个参数是设置我们四舍五入之后小数点后显示几位。
2.numeric 函数的2个参数,第一个表示数据长度,第二个参数表示小数点后位数。
例如:
select cast(round(12.5,2) as numeric(5,2))
- c++运算符重载
CrazyMizzz
C++
一、加+,减-,乘*,除/ 的运算符重载
Rational operator*(const Rational &x) const{
return Rational(x.a * this->a);
}
在这里只写乘法的,加减除的写法类似
二、<<输出,>>输入的运算符重载
&nb
- hive DDL语法汇总
daizj
hive修改列DDL修改表
hive DDL语法汇总
1、对表重命名
hive> ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME TO new_table_name;
2、修改表备注
hive> ALTER TABLE table_name SET TBLPROPERTIES ('comment' = new_comm
- jbox使用说明
dcj3sjt126com
Web
参考网址:http://www.kudystudio.com/jbox/jbox-demo.html jBox v2.3 beta [
点击下载]
技术交流QQGroup:172543951 100521167
[2011-11-11] jBox v2.3 正式版
- [调整&修复] IE6下有iframe或页面有active、applet控件
- UISegmentedControl 开发笔记
dcj3sjt126com
// typedef NS_ENUM(NSInteger, UISegmentedControlStyle) {
// UISegmentedControlStylePlain, // large plain
&
- Slick生成表映射文件
ekian
scala
Scala添加SLICK进行数据库操作,需在sbt文件上添加slick-codegen包
"com.typesafe.slick" %% "slick-codegen" % slickVersion
因为我是连接SQL Server数据库,还需添加slick-extensions,jtds包
"com.typesa
- ES-TEST
gengzg
test
package com.MarkNum;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation
- 为何外键不再推荐使用
hugh.wang
mysqlDB
表的关联,是一种逻辑关系,并不需要进行物理上的“硬关联”,而且你所期望的关联,其实只是其数据上存在一定的联系而已,而这种联系实际上是在设计之初就定义好的固有逻辑。
在业务代码中实现的时候,只要按照设计之初的这种固有关联逻辑来处理数据即可,并不需要在数据库层面进行“硬关联”,因为在数据库层面通过使用外键的方式进行“硬关联”,会带来很多额外的资源消耗来进行一致性和完整性校验,即使很多时候我们并不
- 领域驱动设计
julyflame
VODAO设计模式DTOpo
概念:
VO(View Object):视图对象,用于展示层,它的作用是把某个指定页面(或组件)的所有数据封装起来。
DTO(Data Transfer Object):数据传输对象,这个概念来源于J2EE的设计模式,原来的目的是为了EJB的分布式应用提供粗粒度的数据实体,以减少分布式调用的次数,从而提高分布式调用的性能和降低网络负载,但在这里,我泛指用于展示层与服务层之间的数据传输对
- 单例设计模式
hm4123660
javaSingleton单例设计模式懒汉式饿汉式
单例模式是一种常用的软件设计模式。在它的核心结构中只包含一个被称为单例类的特殊类。通过单例模式可以保证系统中一个类只有一个实例而且该实例易于外界访问,从而方便对实例个数的控制并节约系统源。如果希望在系统中某个类的对象只能存在一个,单例模式是最好的解决方案。
&nb
- logback
zhb8015
loglogback
一、logback的介绍
Logback是由log4j创始人设计的又一个开源日志组件。logback当前分成三个模块:logback-core,logback- classic和logback-access。logback-core是其它两个模块的基础模块。logback-classic是log4j的一个 改良版本。此外logback-class
- 整合Kafka到Spark Streaming——代码示例和挑战
Stark_Summer
sparkstormzookeeperPARALLELISMprocessing
作者Michael G. Noll是瑞士的一位工程师和研究员,效力于Verisign,是Verisign实验室的大规模数据分析基础设施(基础Hadoop)的技术主管。本文,Michael详细的演示了如何将Kafka整合到Spark Streaming中。 期间, Michael还提到了将Kafka整合到 Spark Streaming中的一些现状,非常值得阅读,虽然有一些信息在Spark 1.2版
- spring-master-slave-commondao
王新春
DAOspringdataSourceslavemaster
互联网的web项目,都有个特点:请求的并发量高,其中请求最耗时的db操作,又是系统优化的重中之重。
为此,往往搭建 db的 一主多从库的 数据库架构。作为web的DAO层,要保证针对主库进行写操作,对多个从库进行读操作。当然在一些请求中,为了避免主从复制的延迟导致的数据不一致性,部分的读操作也要到主库上。(这种需求一般通过业务垂直分开,比如下单业务的代码所部署的机器,读去应该也要从主库读取数
![]() Home Page
Home Page ![]() Go Back
Go Back ![]() To top
To top