反素数学习
原始链接: ACdreamers: 反素数深度分析
反素数的定义:对于任何正整数![]() ,其约数个数记为
,其约数个数记为![]() ,例如
,例如![]() ,如果某个正整数
,如果某个正整数![]() 满足:对任意的正整
满足:对任意的正整
数![]() ,都有
,都有![]() ,那么称
,那么称![]() 为反素数。
为反素数。
从反素数的定义中可以看出两个性质:
(1)一个反素数的所有质因子必然是从2开始的连续若干个质数,因为反素数是保证约数个数为![]() 的这个数
的这个数![]() 尽量小
尽量小
(2)同样的道理,如果![]() ,那么必有
,那么必有![]()
在ACM竞赛中,最常见的问题如下:
(1)给定一个数![]() ,求一个最小的正整数
,求一个最小的正整数![]() ,使得
,使得![]() 的约数个数为
的约数个数为![]()
(2)求出![]() 中约数个数最多的这个数
中约数个数最多的这个数
从上面的性质中可以看出,我们要求最小的![]() ,它的约数个数为
,它的约数个数为![]() ,那么可以利用搜索来解。
,那么可以利用搜索来解。
以前我们求一个数的所有因子也是用搜索,比如![]() ,以每一个
,以每一个![]() 为树的一层建立搜索树,深度为
为树的一层建立搜索树,深度为![]()
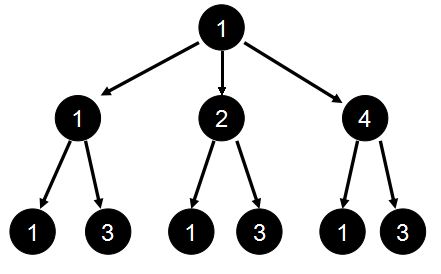
以![]() 为例进行说明,建树如下:
为例进行说明,建树如下:
可以看出从根节点到每一个叶子结点这条路径上的所有数字乘起来都是12的约数,所以12有6个约数。
反素数个人打表模版如下:
//
// Created by TaoSama on 2015-06-11
// Copyright (c) 2015 TaoSama. All rights reserved.
//
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include <algorithm>
#include <cctype>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
typedef long long LL;
int p[] = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53};
map<LL, LL> mp, rmp; //divisors .. anti-prime
LL a[100], b[100], ct; //a: anti-prime b: its divisors
void dfs(int k, LL cur, LL cnt, int limit) {
if(cur > N) return;
if(!mp.count(cnt)) mp[cnt] = cur;
else mp[cnt] = min(cur, mp[cnt]);
for(int i = 1; i <= limit; ++i) {
if(1.0 * cur * p[k] > N) break;
dfs(k + 1, cur *= p[k], cnt * (i + 1), i);
}
}
//when try to iterate, do not forget to control the bound (< ct)
void init() {
dfs(0, 1, 1, 60);
map<LL, LL>::iterator i = mp.begin();
for(; i != mp.end(); ++i) rmp.insert(make_pair(i->second, i->first));
i = rmp.begin();
for(; i != rmp.end(); ++i) {
if(ct > 0 && i->second < b[ct - 1]) continue;
a[ct] = i->first;
b[ct++] = i->second;
}
}
题目:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/27/E
题意:给一个数![]() ,求一个最小的正整数,使得它的因子个数为
,求一个最小的正整数,使得它的因子个数为![]() 。
。
题目:http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemId=1562
题意:求![]() 以内的因子最多的那个数。
以内的因子最多的那个数。
题目:http://acm.timus.ru/problem.aspx?space=1&num=1748
分析:这道题主要注意数据处理。对于上面的两题,数据范围小,所以可以不用剪枝,本题就需要了。
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4542
题意:
给出一个数K和两个操作
如果操作是0,就求出一个最小的正整数X,满足X的约数个数为K。
如果操作是1,就求出一个最小的X,满足X的约数个数为X-K。
分析:对于操作0,就是求反素数,直接搜索搞定。对于操作1,代表1至X中不是X的约数个数为K。
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 50005;
typedef long long LL;
const LL INF = (((LL)1)<<62)+1;
int p[16] = {2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29,31,37,41,43,47,53};
LL ans;
int n;
int d[N];
void Init()
{
for(int i=1;i<N;i++) d[i] = i;
for(int i=1;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=i;j<N;j+=i) d[j]--;
if(!d[d[i]]) d[d[i]] = i;
d[i] = 0;
}
}
void dfs(int dept,int limit,LL tmp,int num)
{
if(num > n) return;
if(num == n && ans > tmp) ans = tmp;
for(int i=1;i<=limit;i++)
{
if(ans / p[dept] < tmp || num*(i+1) > n) break;
tmp *= p[dept];
if(n % (num*(i+1)) == 0)
dfs(dept+1,i,tmp,num*(i+1));
}
}
int main()
{
Init();
int T,tt=1;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
int type;
scanf("%d%d",&type,&n);
if(type) ans = d[n];
else
{
ans = INF;
dfs(0,62,1,1);
}
printf("Case %d: ",tt++);
if(ans == 0) puts("Illegal");
else if(ans >= INF) puts("INF");
else printf("%I64d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}