Cocos2d-x 定时器的浅析
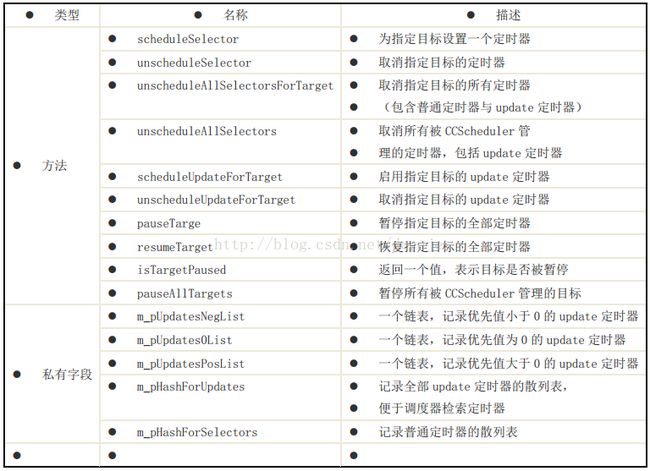
在游戏中,有一个比较重要的概念就是定时调度。简单来说就是当一个游戏在运行过程中,我们需要通过控制时间间隔来响应一些所需要的时间,从而形成整个游戏的主循环。cocos2d-x中为我们定义了个定时调度器CCScheduler,它是一个管理所有节点定时器的类,负责记录定时器,并在合适的时间触发定时事件。下图为CCScheduler的主要成员:(图摘自火烈鸟高级开发教程一书)
打开源代码,我们会发现在游戏主循环中会一直调用m_pScheduler的update方法,我们可以轻易发现m_pScheduler是CCScheduler的一个对象,也就是说主循环通过update方法来实现定时调度,我们进一步分析CCScheduler::update的源代码如下:
void CCScheduler::update(float dt)
{
m_bUpdateHashLocked = true;
if (m_fTimeScale != 1.0f)
{
dt *= m_fTimeScale;
}
// Iterate over all the Updates' selectors 枚举所有的Update定时器
tListEntry *pEntry, *pTmp;
// updates with priority < 0 优先级小于0
DL_FOREACH_SAFE(m_pUpdatesNegList, pEntry, pTmp)
{
if ((! pEntry->paused) && (! pEntry->markedForDeletion))
{
pEntry->target->update(dt);
}
}
// updates with priority == 0 优先级等于0
DL_FOREACH_SAFE(m_pUpdates0List, pEntry, pTmp)
{
if ((! pEntry->paused) && (! pEntry->markedForDeletion))
{
pEntry->target->update(dt);
}
}
// updates with priority > 0 优先级大于0
DL_FOREACH_SAFE(m_pUpdatesPosList, pEntry, pTmp)
{
if ((! pEntry->paused) && (! pEntry->markedForDeletion))
{
pEntry->target->update(dt);
}
}
// Iterate over all the custom selectors 枚举所有自定义的定时器
for (tHashTimerEntry *elt = m_pHashForTimers; elt != NULL; )
{
m_pCurrentTarget = elt;
m_bCurrentTargetSalvaged = false;
if (! m_pCurrentTarget->paused)
{
// The 'timers' array may change while inside this loop
for (elt->timerIndex = 0; elt->timerIndex < elt->timers->num; ++(elt->timerIndex))
{
elt->currentTimer = (CCTimer*)(elt->timers->arr[elt->timerIndex]);
elt->currentTimerSalvaged = false;
elt->currentTimer->update(dt);
if (elt->currentTimerSalvaged)
{
// The currentTimer told the remove itself. To prevent the timer from
// accidentally deallocating itself before finishing its step, we retained
// it. Now that step is done, it's safe to release it.
elt->currentTimer->release();
}
elt->currentTimer = NULL;
}
}
// elt, at this moment, is still valid
// so it is safe to ask this here (issue #490)
elt = (tHashTimerEntry *)elt->hh.next;
// only delete currentTarget if no actions were scheduled during the cycle (issue #481)
if (m_bCurrentTargetSalvaged && m_pCurrentTarget->timers->num == 0)
{
removeHashElement(m_pCurrentTarget);
}
}
// Iterate over all the script callbacks 处理脚本相关事件
if (m_pScriptHandlerEntries)
{
for (int i = m_pScriptHandlerEntries->count() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
CCSchedulerScriptHandlerEntry* pEntry = static_cast<CCSchedulerScriptHandlerEntry*>(m_pScriptHandlerEntries->objectAtIndex(i));
if (pEntry->isMarkedForDeletion())
{
m_pScriptHandlerEntries->removeObjectAtIndex(i);
}
else if (!pEntry->isPaused())
{
pEntry->getTimer()->update(dt);
}
}
}
// delete all updates that are marked for deletion 删除所有被标记了删除几号的update方法
// updates with priority < 0
DL_FOREACH_SAFE(m_pUpdatesNegList, pEntry, pTmp)
{
if (pEntry->markedForDeletion)
{
this->removeUpdateFromHash(pEntry);
}
}
// updates with priority == 0
DL_FOREACH_SAFE(m_pUpdates0List, pEntry, pTmp)
{
if (pEntry->markedForDeletion)
{
this->removeUpdateFromHash(pEntry);
}
}
// updates with priority > 0
DL_FOREACH_SAFE(m_pUpdatesPosList, pEntry, pTmp)
{
if (pEntry->markedForDeletion)
{
this->removeUpdateFromHash(pEntry);
}
}
m_bUpdateHashLocked = false;
m_pCurrentTarget = NULL;
}
借助注释,我们会发现会发现update中分开处理了两种定时器,一种为update selector,另一种为custom selector。原来cocos2d-x为我们提供了两种定时器,分别为:
Update定时器,每一帧都被触发,使用scheduleUpdate方法来启动。
Schedule定时器,可以设置触发的间隔,使用schedule方法来启动。
对于update定时器来说,每一个节点只可能注册一个定时器,因此调度器中存储定时数据的结构体_listEntry主要保存了注册者与优先级,而对于普通定时器来说,每一个节点可以注册多个定时器,引擎使用回调函数(选择器)来区分同一节点下注册的不同定时器。而且调度器为每一个定时器创建一个CCTImer对象,它记录了定时器的目标、回调函数、触发周期、重复触发还是一次触发等属性。(本段摘自火烈鸟高级开发教程一书)
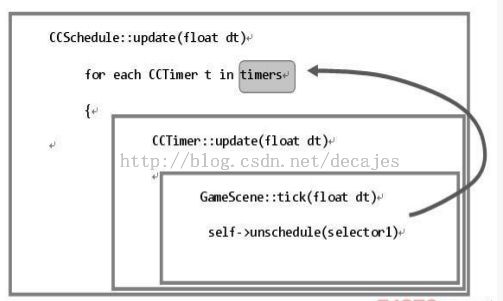
回到源代码,我们可以知道Update函数是把update和schedule分开处理。遍历完每个节点的update定时器都会调用对应target中的update方法来响应更新事件,这个update方法是CCobject中定义的一个方法,在CCNode中也继承了这个方法,并写成了virtual类型。也就是说我们要重载update才能实现我们想要的update定时器的响应事件。而在遍历完每个节点的普通定时器的时候,会调用CCTimer中的update方法把每一次调用时接收的时间间隔dt记录下来,当达到参数所制定的周期事,就会引发响应时间,这个事件是通过类似函数指针的机制来实现的,在object-c中称呼为选择器。这个事件我们可以在所在节点处定义即可。下图给出了schedule的调度迭代关系:(此图摘自火烈鸟高级开发教程一书)
下面我们来介绍一下定时器的基础用法,在开发中我们通常会用到3种调度器:(接下来的内容参考Cocos2d-x官方中文文档 v3.x)
1. 默认调度器:schedulerUpdate()
2. 自定义调度器:schedule(SEL_SCHEDULE selector, float interval, unsigned intrepeat, float delay)
3. 单次调度器:scheduleOnce(SEL_SCHEDULE selector, float delay)
以下我们来对这3种调度器做简单的介绍。
默认调度器(schedulerUpdate)
该调度器是使用Node的刷新事件update方法,该方法在每帧绘制之前都会被调用一次。由于每帧之间时间间隔较短,所以每帧刷新一次已足够完成大部分游戏过程中需要的逻辑判断。
Cocos2d-x中Node默认是没有启用update事件的,因此你需要重载update方法来执行自己的逻辑代码。
通过执行schedulerUpdate()调度器每帧执行 update方法,如果需要停止这个调度器,可以使用unschedulerUpdate()方法。
以下代码用来测试该调度器:
HelloWorldScene.h
void update(float dt) override;
HelloWorldScene.cpp
boolHelloWorld::init()
{
...
scheduleUpdate();
returntrue;
}
voidHelloWorld::update(float dt)
{
log("update");
}
你会看到控制台不停输出如下信息
cocos2d: update
cocos2d: update
cocos2d: update
cocos2d: update
自定义调度器(scheduler)
游戏开发中,在某些情况下我们可能不需要频繁的进行逻辑检测,这样可以提高游戏性能。所以Cocos2d-x还提供了自定义调度器,可以实现以一定的时间间隔连续调用某个函数。
由于引擎的调度机制,自定义时间间隔必须大于两帧的间隔,否则两帧内的多次调用会被合并成一次调用。所以自定义时间间隔应在0.1秒以上。
同样,取消该调度器可以用unschedule(SEL_SCHEDULEselector, float delay)。
以下代码用来测试该调度器:
HelloWorldScene.h
void updateCustom(float dt);
HelloWorldScene.cpp
boolHelloWorld::init()
{
...
schedule(schedule_selector(HelloWorld::updateCustom), 1.0f, kRepeatForever, 0);
returntrue;
}
voidHelloWorld::updateCustom(float dt)
{
log("Custom");
}
在控制台你会看到每隔1秒输出以下信息
cocos2d: Custom
cocos2d: Custom
cocos2d: Custom
cocos2d: Custom
cocos2d: Custom
我们来看下scheduler(SEL_SCHEDULEselector, float interval, unsigned int repeat, float delay)函数里面的参数:
1. 第一个参数selector即为你要添加的事件函数
2. 第二个参数interval为事件触发时间间隔
3. 第三个参数repeat为触发一次事件后还会触发的次数,默认值为kRepeatForever,表示无限触发次数
4. 第四个参数delay表示第一次触发之前的延时
单次调度器(schedulerOnce)
游戏中某些场合,你只想进行一次逻辑检测,Cocos2d-x同样提供了单次调度器。
该调度器只会触发一次,用unschedule(SEL_SCHEDULEselector, float delay)来取消该触发器。
以下代码用来测试该调度器:
HelloWorldScene.h
void updateOnce(float dt);
HelloWorldScene.cpp
boolHelloWorld::init()
{
...
scheduleOnce(schedule_selector(HelloWorld::updateOnce), 0.1f);
returntrue;
}
voidHelloWorld::updateOnce(float dt)
{
log("Once");
}
这次在控制台你只会看到一次输出
cocos2d: Once