【杭电oj】1325 - Is It A Tree?(树,并查集)
Is It A Tree?
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 19420 Accepted Submission(s): 4349
Problem Description
A tree is a well-known data structure that is either empty (null, void, nothing) or is a set of one or more nodes connected by directed edges between nodes satisfying the following properties.
There is exactly one node, called the root, to which no directed edges point.
Every node except the root has exactly one edge pointing to it.
There is a unique sequence of directed edges from the root to each node.
For example, consider the illustrations below, in which nodes are represented by circles and edges are represented by lines with arrowheads. The first two of these are trees, but the last is not.
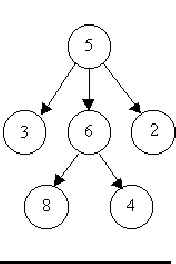
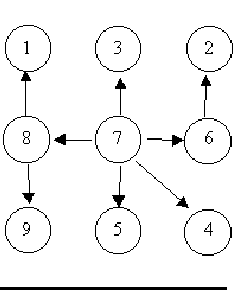
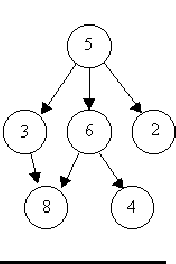
In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not.
There is exactly one node, called the root, to which no directed edges point.
Every node except the root has exactly one edge pointing to it.
There is a unique sequence of directed edges from the root to each node.
For example, consider the illustrations below, in which nodes are represented by circles and edges are represented by lines with arrowheads. The first two of these are trees, but the last is not.



In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not.
Input
The input will consist of a sequence of descriptions (test cases) followed by a pair of negative integers. Each test case will consist of a sequence of edge descriptions followed by a pair of zeroes Each edge description will consist of a pair of integers; the first integer identifies the node from which the edge begins, and the second integer identifies the node to which the edge is directed. Node numbers will always be greater than zero.
Output
For each test case display the line ``Case k is a tree." or the line ``Case k is not a tree.", where k corresponds to the test case number (they are sequentially numbered starting with 1).
Sample Input
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4 5 6 0 0 8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5 7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0 3 8 6 8 6 4 5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0 -1 -1
Sample Output
Case 1 is a tree. Case 2 is a tree. Case 3 is not a tree.
Source
North Central North America 1997
考察树的概念:空树或一个根节点、有向无环、除根结点外每个结点入度都为1。
我的代码考虑了根节点的个数、是否构成环、节点入度三个方面。
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX 100000
int a[MAX+5],k[MAX+5],n[MAX+5];
int find(int x)
{
if (x!=a[x])
a[x]=find(a[x]);
return a[x]; //寻找根并进行路径压缩
}
void join(int x,int y)
{
int fx,fy;
fx=find (x);
fy=find (y);
if (fx!=fy)
a[fy]=fx;
}
int main()
{
int x,y;
int flag; //是否有多个根
int circle; //是否构成环
int num=1;
while (1)
{
flag=0;
circle=0;
memset(k,0,sizeof(k));
memset(n,0,sizeof(n));
for (int i=1;i<=MAX;i++)
a[i]=i;
while (scanf ("%d %d",&x,&y))
{
if (x<0)
break;
if (x==0)
break;
k[x]=1;
k[y]=1;
if (find(x)==find(y))
circle=1; //若输入的两个数根已经相同,则构成环
else if (find (y)!=y)
circle=1; //入度不为1
else
join(x,y);
}
if (x<0)
break;
for (int i=1;i<=MAX;i++)
{
if (k[i])
n[find(a[i])]++;
}
for (int i=1;i<=MAX;i++)
{
if (n[i]>0)
flag++;
}
printf ("Case %d ",num++);
if (flag>1)
printf ("is not a tree.\n");
else if (circle)
printf ("is not a tree.\n");
else
printf ("is a tree.\n");
}
return 0;
}
但是写完以后又看到了一个更简单的代码,边数为节点个数-1,这样考虑相当于考虑了根结点的个数,然而在时间上更占优势。
他的代码如下:
//一开始一直超时,因为不是-1 -1结束,而是负数结束
//和1272的不同:这个加了方向
//判断是不是树,只要节点等于边+1;同时每个节点的入度小于2;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int f[100005];
int main()
{
int a,b,flag,i,j;
int t=1;
while(1)
{
j=0;
i=0;
flag=0;
memset(f,0,sizeof(f));
while(scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)&&a&&b)
{
if(a<0||b<0)
return 0;
if(f[b]-1==1)
flag=1;
if(f[a]==0)
j++;
if(f[b]==0)
j++;
f[a]=1;f[b]=2;i++;
}
if(flag==0&&j==i+1)
printf("Case %d is a tree.\n",t++);
else printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n",t++);
}
}