《UNIX环境高级编程》笔记--硬链接和符号链接
目录(?)[+]
1.硬链接
每个文件都会占用一个 inode ,文件内容由 inode 的记录来指向想要读取该文件,必须要经过目录记录的文件名来指向到正
确的 inode 号码才能读取。也就是说,其实文件名只与目录有关,但是文件内容则与 inode 有关。那么想一想, 有没有可能
有多个档名对应到同一个 inode 号码呢?有的!那就是 hard link 的由来。 所以简单的说:hard link 只是在某个目录下新增一
笔档名链接到某 inode 号码的关连记录而已。
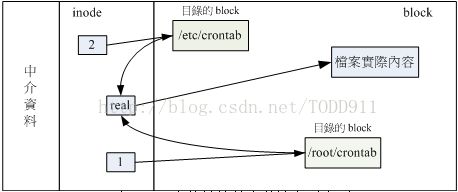
举个例子来说,假设我系统有个 /root/crontab 他是 /etc/crontab 的实体链接,也就是说这两个档名连结到同一个 inode , 自
然这两个文件名的所有相关信息都会一模一样(除了文件名之外)。实际的情况可以如下所示:
[root@www ~]# ln /etc/crontab . <==创建实体链接的命令
[root@www ~]# ll -i /etc/crontab /root/crontab
1912701 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 255 Jan 6 2007 /etc/crontab
1912701 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 255 Jan 6 2007 /root/crontab
你可以发现两个档名都连结到 1912701 这个 inode 号码,所以您瞧瞧,是否文件的权限/属性完全一样呢? 因为这两个『档名』
其实是一模一样的『文件』啦!而且你也会发现第二个字段由原本的 1 变成 2 了! 那个字段称为『连结』,这个字段的意义
为:『有多少个档名链接到这个 inode 号码』的意思。 如果将读取到正确数据的方式画成示意图,就类似如下画面:
上图的意思是,你可以透过 1 或 2 的目录之 inode 指定的 block 找到两个不同的档名,而不管使用哪个档名均可以指到 real 那个
inode 去读取到最终数据!那这样有什么好处呢?最大的好处就是『安全』!如同上图中, 如果你将任何一个『档名』删除,其
实 inode 与 block 都还是存在的! 此时你可以透过另一个『档名』来读取到正确的文件数据喔!此外,不论你使用哪个『档名』
来编辑, 最终的结果都会写入到相同的 inode 与 block 中,因此均能进行数据的修改!
一般来说,使用 hard link 配置链接文件时,磁盘的空间与 inode 的数目都不会改变! 我们还是由图 2.2.1 来看,由图中可以知道,
hard link 只是在某个目录下的 block 多写入一个关连数据而已,既不会添加 inode 也不会耗用 block 数量。
创建现有文件的硬链接是使用link函数。函数声明如下:
- <pre name="code" class="cpp">#include <unistd.h>
- int link(const char* existingpath, const char* newpath);</pre>
删除一个现有文件的硬链接是使用unlink函数,函数声明如下:
- #include <unistd.h>
- int unlink(const char* pathname);
实践:
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main(void){
- if(link("a","a2")<0){
- perror("unlink");
- }
- return 0;
- }
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll -i a
939363 -rw-rw-r-- 1 yan yan 0 Jul 10 07:55 a
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ./a.out
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll -i a a2
939363 -rw-rw-r-- 2 yan yan 0 Jul 10 07:55 a
939363 -rw-rw-r-- 2 yan yan 0 Jul 10 07:55 a2
如果link的是一个目录,结果会如何:
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main(void){
- if(link("test","test2")<0){
- perror("link");
- }
- return 0;
- }
运行结果:
drwxrwxr-x 2 yan yan 4096 Jul 10 07:58 test/
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ./a.out
link: Operation not permitted
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ su
Password:
root@yan-vm:/home/yan/apue# ./a.out
link: Operation not permitted
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main(void){
- if(unlink("a")<0){
- perror("unlink");
- }
- return 0;
- }
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll -i a a2
939363 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 0 Jul 10 08:09 a
939363 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 0 Jul 10 08:09 a2
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ./a.out
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll a
ls: cannot access a: No such file or directory
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll -i a2
939363 -rw-rw-r-- 1 yan yan 0 Jul 10 07:55 a2
如果unlink是一个目录会怎样?
unlink: Is a directory
看来无法使用unlink删除目录。
只有当硬链接计数达到0时,该文件的内容才可被删除;只要有进程打开了该文件,其内容也不能删除。关闭一个文件时,内核
首先检查打开该文件的进程数,如果达到0,然后再检查其硬链接数,如果也是0,则删除该文件内容。
下面是unlink的一种应用,确保程序创建的临时文件不会被遗留下来。
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- int main(void){
- int fd;
- char buf[10];
- if((fd = open("tempfile",O_RDWR)) <0){
- perror("open");
- return -1;
- }
- if(unlink("tempfile") < 0){
- perror("unlink");
- return -1;
- }
- printf("unlink ok\n");
- int readnum = read(fd,buf,10);
- printf("read num:%d,read content:%s\n",readnum,buf);
- sleep(15);
- printf("done\n");
- return 0;
- }
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ cat tempfile
123
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ./a.out
unlink ok
read num:4,read content:123
^Z
[2]+ Stopped ./a.out
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll tempfile
ls: cannot access tempfile: No such file or directory
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ fg
./a.out
done
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll tempfile
ls: cannot access tempfile: No such file or directory
进程用open或者creat创建一个文件,然后立即调用unlink,因为该文件仍旧是打开的,所以不会将其内容删除,只有当进程
关闭该文件或者终止时,该文件才会被删除。
删除一个文件可以使用remove函数,函数声明如下:
- #include <stdio.h>
- int remove(const char* pathname);
实践:
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main(void){
- if(remove("a")<0){
- perror("remove");
- }
- return 0;
- }
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll a
-rw-rw-r-- 1 yan yan 0 Jul 10 09:44 a
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ./a.out
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll a
ls: cannot access a: No such file or directory
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ mkdir a
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll
total 80
drwxrwxr-x 4 yan yan 4096 Jul 10 09:44 ./
drwx---rwx 25 yan yan 4096 Jul 10 09:42 ../
drwxrwxr-x 2 yan yan 4096 Jul 10 09:44 a/
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ./a.out
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll
total 76
drwxrwxr-x 3 yan yan 4096 Jul 10 09:44 ./
drwx---rwx 25 yan yan 4096 Jul 10 09:42 ../
不像unlink函数,remove函数可以删除目录。
2.符号链接
- #include <unistd.h>
- int symlink(const char* actualpath, const char* sympath);
如果成功返回0,出错返回-1。
实践:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- int main(void){
- if(symlink("a","link2a") < 0){
- perror("symlink");
- return -1;
- }
- return 0;
- }
如果link2a不存在:
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll link2a
ls: cannot access link2a: No such file or directory
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ./a.out
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll link2a a
-rw-rw-r-- 1 yan yan 0 Jul 10 10:04 a
lrwxrwxrwx 1 yan yan 1 Jul 10 10:06 link2a -> a
如果link2a已经存在:
lrwxrwxrwx 1 yan yan 1 Jul 10 10:06 link2a -> a
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ./a.out
symlink: File exists
readlink函数读取符号链接本身,并读该链接中的名字,函数声明如下:
- #include <unistd.h>
- ssize_t readlink(const char* restrict pathname, char* restrict buf, size_t bufsize);
如果成功返回读到的字节,出错则返回-1.
实践:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- int main(void){
- char buf[256];
- if(readlink("symblicfile",buf,256)<0){
- perror("readlink");
- return -1;
- }
- printf("%s\n",buf);
- return 0;
- }
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ll symblicfile
lrwxrwxrwx 1 yan yan 7 Jul 10 07:21 symblicfile -> desfile
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ./a.out
desfile稾s
为什么会有乱码呢?原因是,buf中返回的字符串不会以null结尾,所以需要自己来添加:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <string.h>
- int main(void){
- char buf[256];
- memset(buf,0,256);
- if(readlink("symblicfile",buf,256)<0){
- perror("readlink");
- return -1;
- }
- buf[255] = 0;
- printf("%s\n",buf);
- return 0;
- }
yan@yan-vm:~/apue$ ./a.out
desfile