模拟退火算法Python实现
作者:金良([email protected]) csdn博客:http://blog.csdn.net/u012176591
import numpy as np
coordinates = np.array([[565.0,575.0],[25.0,185.0],[345.0,750.0],[945.0,685.0],[845.0,655.0],
[880.0,660.0],[25.0,230.0],[525.0,1000.0],[580.0,1175.0],[650.0,1130.0],
[1605.0,620.0],[1220.0,580.0],[1465.0,200.0],[1530.0, 5.0],[845.0,680.0],
[725.0,370.0],[145.0,665.0],[415.0,635.0],[510.0,875.0],[560.0,365.0],
[300.0,465.0],[520.0,585.0],[480.0,415.0],[835.0,625.0],[975.0,580.0],
[1215.0,245.0],[1320.0,315.0],[1250.0,400.0],[660.0,180.0],[410.0,250.0],
[420.0,555.0],[575.0,665.0],[1150.0,1160.0],[700.0,580.0],[685.0,595.0],
[685.0,610.0],[770.0,610.0],[795.0,645.0],[720.0,635.0],[760.0,650.0],
[475.0,960.0],[95.0,260.0],[875.0,920.0],[700.0,500.0],[555.0,815.0],
[830.0,485.0],[1170.0, 65.0],[830.0,610.0],[605.0,625.0],[595.0,360.0],
[1340.0,725.0],[1740.0,245.0]])
def getdistmat(coordinates):
num = coordinates.shape[0]
distmat = np.zeros((52,52))
for i in range(num):
for j in range(i,num):
distmat[i][j] = distmat[j][i]=np.linalg.norm(coordinates[i]-coordinates[j])
return distmat
def initpara():
alpha = 0.99
t = (1,100)
markovlen = 10000
return alpha,t,markovlen
num = coordinates.shape[0]
distmat = getdistmat(coordinates)
solutionnew = np.arange(num)
valuenew = np.max
solutioncurrent = solutionnew.copy()
valuecurrent = np.max
solutionbest = solutionnew.copy()
valuebest = np.max
alpha,t2,markovlen = initpara()
t = t2[1]
result = [] #记录迭代过程中的最优解
while t > t2[0]:
for i in np.arange(markovlen):
#下面的两交换和三角换是两种扰动方式,用于产生新解
if np.random.rand() > 0.5:# 两交换
# np.random.rand()产生[0, 1)区间的均匀随机数
while True:#产生两个不同的随机数
loc1 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand()*(num-1)))
loc2 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand()*(num-1)))
if loc1 != loc2:
break
solutionnew[loc1],solutionnew[loc2] = solutionnew[loc2],solutionnew[loc1]
else: #三交换
while True:
loc1 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand()*(num-1)))
loc2 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand()*(num-1)))
loc3 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand()*(num-1)))
if((loc1 != loc2)&(loc2 != loc3)&(loc1 != loc3)):
break
# 下面的三个判断语句使得loc1<loc2<loc3
if loc1 > loc2:
loc1,loc2 = loc2,loc1
if loc2 > loc3:
loc2,loc3 = loc3,loc2
if loc1 > loc2:
loc1,loc2 = loc2,loc1
#下面的三行代码将[loc1,loc2)区间的数据插入到loc3之后
tmplist = solutionnew[loc1:loc2].copy()
solutionnew[loc1:loc3-loc2+1+loc1] = solutionnew[loc2:loc3+1].copy()
solutionnew[loc3-loc2+1+loc1:loc3+1] = tmplist.copy()
valuenew = 0
for i in range(num-1):
valuenew += distmat[solutionnew[i]][solutionnew[i+1]]
valuenew += distmat[solutionnew[0]][solutionnew[51]]
if valuenew < valuecurrent: #接受该解
#更新solutioncurrent 和solutionbest
valuecurrent = valuenew
solutioncurrent = solutionnew.copy()
if valuenew < valuebest:
valuebest = valuenew
solutionbest = solutionnew.copy()
else:#按一定的概率接受该解
if np.random.rand() < np.exp(-(valuenew-valuecurrent)/t):
valuecurrent = valuenew
solutioncurrent = solutionnew.copy()
else:
solutionnew = solutioncurrent.copy()
t = alpha*t
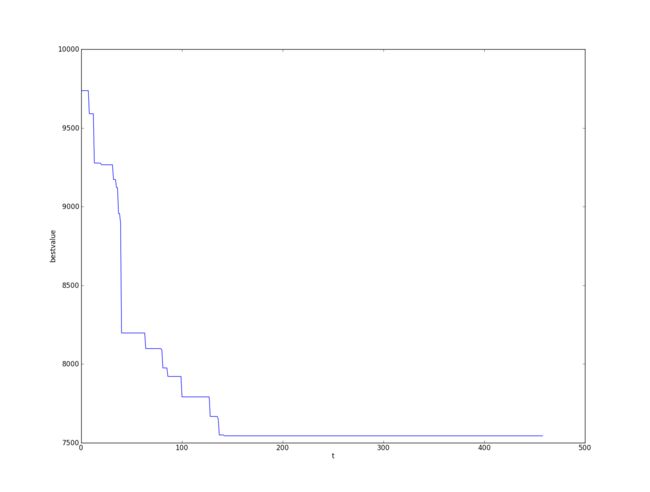
result.append(valuebest)
print t #程序运行时间较长,打印t来监视程序进展速度
plot(np.array(result))
ylabel("bestvalue")
xlabel("t")