hdu4421 ZOJ 3656——Bit Magic
Problem Description
Yesterday, my teacher taught me about bit operators: and (&), or (|), xor (^). I generated a number table a[N], and wrote a program to calculate the matrix table b[N][N] using three kinds of bit operator. I thought my achievement would get teacher's attention.
The key function is the code showed below.
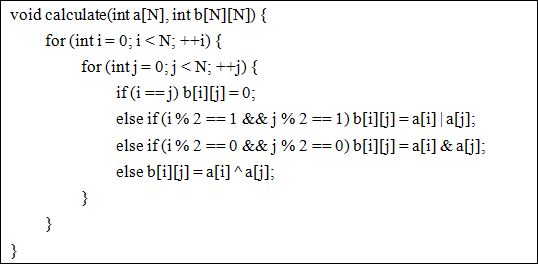
There is no doubt that my teacher raised lots of interests in my work and was surprised to my talented programming skills. After deeply thinking, he came up with another problem: if we have the matrix table b[N][N] at first, can you check whether corresponding number table a[N] exists?
The key function is the code showed below.
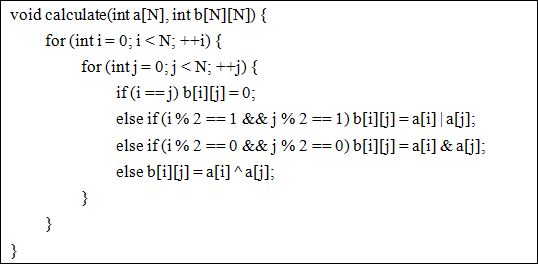
There is no doubt that my teacher raised lots of interests in my work and was surprised to my talented programming skills. After deeply thinking, he came up with another problem: if we have the matrix table b[N][N] at first, can you check whether corresponding number table a[N] exists?
Input
There are multiple test cases.
For each test case, the first line contains an integer N, indicating the size of the matrix. (1 <= N <= 500).
The next N lines, each line contains N integers, the jth integer in ith line indicating the element b[i][j] of matrix. (0 <= b[i][j] <= 2 31 - 1)
For each test case, the first line contains an integer N, indicating the size of the matrix. (1 <= N <= 500).
The next N lines, each line contains N integers, the jth integer in ith line indicating the element b[i][j] of matrix. (0 <= b[i][j] <= 2 31 - 1)
Output
For each test case, output "YES" if corresponding number table a[N] exists; otherwise output "NO".
Sample Input
2 0 4 4 0 3 0 1 24 1 0 86 24 86 0
Sample Output
YES NO
Source
2012 Asia ChangChun Regional Contest
Recommend
怎么样,是不是很像POJ的3678,但是这里值可不止0 1两种取法哦,本弱看了题解才知道,要对b[][]的每一位2sat,如果所有的位都有解,那么才有解,OTL OTL ORZ
怎么样,是不是很像POJ的3678,但是这里值可不止0 1两种取法哦,本弱看了题解才知道,要对b[][]的每一位2sat,如果所有的位都有解,那么才有解,OTL OTL ORZ
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
const int N =1050;
struct node
{
int from;
int to;
int next;
}edge[N*N],redge[N*N];
int head[N],rhead[N];
bool instack[N];
int DFN[N],block[N],color[N],in_deg[N],low[N],Stack[N],cfl[N];
int index,tot,sccnum,Top,rtot,n,m;
int b[505][505];
void addedge(int from,int to)
{
edge[tot].from=from;
edge[tot].to=to;
edge[tot].next=head[from];
head[from]=tot++;
}
/*void raddedge(int from,int to)
{
redge[rtot].from=from;
redge[rtot].to=to;
redge[rtot].next=rhead[from];
rhead[from]=rtot++;
}*/
void tarjan(int u)
{
DFN[u]=low[u]=++index;
instack[u]=1;
Stack[Top++]=u;
for (int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next)
{
int v=edge[i].to;
if (DFN[v]==-1)
{
tarjan(v);
if(low[u]>low[v])
low[u]=low[v];
}
else if (instack[v] && low[u]>DFN[v])
low[u]=DFN[v];
}
if (DFN[u]==low[u])
{
int v;
sccnum++;
do
{
Top--;
v=Stack[Top];
block[v]=sccnum;
instack[v]=0;
}
while (v!=u);
}
}
/*void topo_sort()
{
queue<int>qu;
memset(color,0,sizeof(color));
for (int i=1;i<=sccnum;i++)
if (in_deg[i]==0)
qu.push(i);
while (!qu.empty())
{
int u=qu.front();
qu.pop();
if (!color[u])
{
color[u]=1;
color[cfl[u]]=-1;
}
for (int i=rhead[u];i!=-1;i=redge[i].next)
{
int v=redge[i].to;
in_deg[v]--;
if (!in_deg[v])
qu.push(v);
}
}
}*/
bool judge()
{
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if (block[i]==block[i+n])
return false;
//cfl[block[2*i]]=block[2*i+1];
//cfl[block[2*i+1]]=block[2*i];
}
return true;
}
void init()
{
memset(block,-1,sizeof(block));
memset(DFN,-1,sizeof(DFN));
memset(instack,0,sizeof(instack));
index=sccnum=Top=0;
}
/*void r_build()
{
memset(in_deg,0,sizeof(in_deg));
memset(rhead,-1,sizeof(rhead));
rtot=0;
for (int i=0;i<tot;i++)
{
int u=edge[i].from;
int v=edge[i].to;
if (block[u]!=block[v])
{
raddedge(block[v],block[u]);
in_deg[block[u]]++;
}
}
}*/
/*void solve()
{
build();
init();
for (int i=1;i<=2*n;i++)
if (DFN[i]==-1)
tarjan(i);
if (!judge())
printf("bad luck\n");
else
{
bool flag=false;
r_build();
topo_sort();
}*/
int main()
{
while (~scanf("%d",&n))
{
bool flag=false;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
scanf("%d",&b[i][j]);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=i;j<n;j++)
{
if(i==j && b[i][j])
{
flag=true;
break;
}
if(b[i][j]!=b[j][i])
{
flag=true;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
{
printf("NO\n");
continue;
}
for(int k=0;k<32;k++)
{
init();
tot=0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(i%2 && j%2)//或运算
{
if(b[i][j] & (1<<k))//b那一位上的值 1
{
addedge(i,j+n);
addedge(j,i+n);
}
else
{
addedge(i+n,i);
addedge(j+n,j);
addedge(i,j);
addedge(j,i);
}
}
else if(i%2==0 && j%2==0)//与
{
if(b[i][j] & (1<<k))
{
addedge(i,i+n);
addedge(j,j+n);
addedge(i+n,j+n);
addedge(j+n,i+n);
}
else
{
addedge(i+n,j);
addedge(j+n,i);
}
}
else //XOR
{
if(b[i][j] & (1<<k))
{
addedge(i,j+n);
addedge(j,i+n);
addedge(i+n,j);
addedge(j+n,i);
}
else
{
addedge(i,j);
addedge(j,i);
addedge(i+n,j+n);
addedge(j+n,i+n);
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<2*n;i++)
if(DFN[i]==-1)
tarjan(i);
if(!judge())
{
flag=true;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
printf("NO\n");
else
printf("YES\n");
}
return 0;
}