poj1456(贪心)
Supermarket
| Time Limit: 2000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 7856 | Accepted: 3343 |
Description
A supermarket has a set Prod of products on sale. It earns a profit px for each product x∈Prod sold by a deadline dx that is measured as an integral number of time units starting from the moment the sale begins. Each product takes precisely one unit of time for being sold. A selling schedule is an ordered subset of products Sell ≤ Prod such that the selling of each product x∈Sell, according to the ordering of Sell, completes before the deadline dx or just when dx expires. The profit of the selling schedule is Profit(Sell)=Σ
x∈Sellpx. An optimal selling schedule is a schedule with a maximum profit.
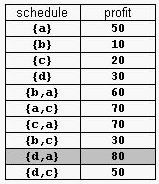
For example, consider the products Prod={a,b,c,d} with (pa,da)=(50,2), (pb,db)=(10,1), (pc,dc)=(20,2), and (pd,dd)=(30,1). The possible selling schedules are listed in table 1. For instance, the schedule Sell={d,a} shows that the selling of product d starts at time 0 and ends at time 1, while the selling of product a starts at time 1 and ends at time 2. Each of these products is sold by its deadline. Sell is the optimal schedule and its profit is 80.
Write a program that reads sets of products from an input text file and computes the profit of an optimal selling schedule for each set of products.
For example, consider the products Prod={a,b,c,d} with (pa,da)=(50,2), (pb,db)=(10,1), (pc,dc)=(20,2), and (pd,dd)=(30,1). The possible selling schedules are listed in table 1. For instance, the schedule Sell={d,a} shows that the selling of product d starts at time 0 and ends at time 1, while the selling of product a starts at time 1 and ends at time 2. Each of these products is sold by its deadline. Sell is the optimal schedule and its profit is 80.

Write a program that reads sets of products from an input text file and computes the profit of an optimal selling schedule for each set of products.
Input
A set of products starts with an integer 0 <= n <= 10000, which is the number of products in the set, and continues with n pairs pi di of integers, 1 <= pi <= 10000 and 1 <= di <= 10000, that designate the profit and the selling deadline of the i-th product. White spaces can occur freely in input. Input data terminate with an end of file and are guaranteed correct.
Output
For each set of products, the program prints on the standard output the profit of an optimal selling schedule for the set. Each result is printed from the beginning of a separate line.
Sample Input
4 50 2 10 1 20 2 30 1 7 20 1 2 1 10 3 100 2 8 2 5 20 50 10
Sample Output
80 185
Hint
The sample input contains two product sets. The first set encodes the products from table 1. The second set is for 7 products. The profit of an optimal schedule for these products is 185.
本题要求在规定截止期限内卖出商品的最大值,我想动态规划可做但不方便,贪心即可简单解决。
现将商品按Pi从大到小排序,保证在规定期限内每次都能选择到最大值,从而保证在总的期限内获益最大。
每个商品都在规定期限内的最大时间内卖,就可保证最终值最大,这就是贪心策略。
1.本体数据不大0 <= n <= 10000,1 <= di <= 10000,用个双重循环+hash表都不会超时的
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int MAX=10000+10;
struct product
{
int pi,di;
}Product[MAX];
bool visited[MAX];
bool cmp(product a,product b)
{
return a.pi>b.pi;
}
int main()
{
int i,n,j;
int ans;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d%d",&Product[i].pi,&Product[i].di);
memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited));
sort(Product,Product+n,cmp);
ans=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=Product[i].di;j>0;j--)
{
if(!visited[j])
{
ans+=Product[i].pi;
visited[j]=true;
break;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
2.n*pi最多可得10000*10000,运算量还是有点大的,可以运用并查集来优化加速。每次找到最大商品后,通过其期限值找到当前可以卖的最大时间,即满足贪心策略。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
using namespace std;
const int MAX=10000+10;
struct product
{
int pi,di;
}Product[MAX];
bool visited[MAX];
int par[MAX];
bool cmp(product a,product b)
{
return a.pi>b.pi;
}
int Get_par(int a)
//查找a的父亲节点并压缩路径
{
if(par[a]==a)
return par[a];
//注意语句的顺序
int pa=par[a];
par[a]=Get_par(par[a]);
return par[a];
}
int main()
{
int n,i,ans;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d%d",&Product[i].pi,&Product[i].di);
sort(Product,Product+n,cmp);
for(i=0;i<MAX;i++)
par[i]=i;
ans=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int pa=Get_par(Product[i].di);
if(pa>0)
{
ans+=Product[i].pi;
par[pa]=pa-1;
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}