TOMCAT原理以及处理HTTP请求的过程、ContextPath ServletPath
一、TOMCAT
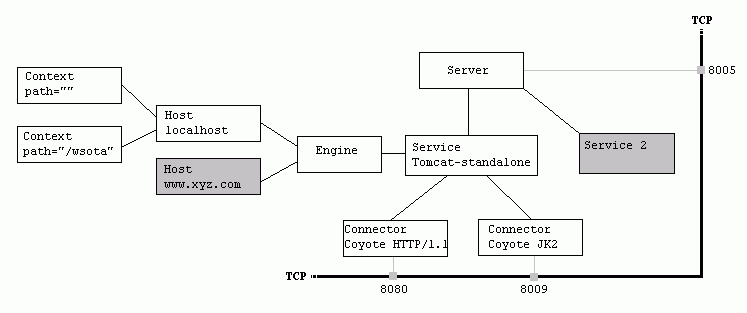
1 - Tomcat Server的组成部分
Tomcat服务器是由一系列可配置的组件构成的,其中核心组件是Catalina Servlet容器,它是所有其他Tomcat组件的顶层容器。Tomcat各组件之间的层次关系如图1-20所示。
-Server
---Service
------Connector
------Engine
---------Context
图1-20 Tomcat组件之间的层次结构
我们下面简单介绍一下各组件在Tomcat服务器中的作用。
(1)Server
Server表示整个的Catalina Servlet容器。Tomcat提供了Server接口的一个默认实现,这通常不需要用户自己去实现。在Server容器中,可以包含一个或多个Service组件。
1.2 - Service
A Service element represents the combination of one or more Connector components that share a single Engine
Service是这样一个集合:它由一个或者多个Connector组成,以及一个Engine,负责处理所有Connector所获得的客户请求
1.3 - Connector
一个Connector将在某个指定端口上侦听客户请求,并将获得的请求交给Engine来处理,从Engine处获得回应并返回客户
TOMCAT有两个典型的Connector,一个直接侦听来自browser的http请求,一个侦听来自其它WebServer的请求
Coyote Http/1.1 Connector 在端口8080处侦听来自客户browser的http请求
Coyote JK2 Connector 在端口8009处侦听来自其它WebServer(Apache)的servlet/jsp代理请求
1.4 - Engine
The Engine element represents the entire request processing machinery associated with a particular Service
It receives and processes all requests from one or more Connectors
and returns the completed response to the Connector for ultimate transmission back to the client
Engine下可以配置多个虚拟主机Virtual Host,每个虚拟主机都有一个域名
当Engine获得一个请求时,它把该请求匹配到某个Host上,然后把该请求交给该Host来处理
Engine有一个默认虚拟主机,当请求无法匹配到任何一个Host上的时候,将交给该默认Host来处理
1.5 - Host
代表一个Virtual Host,虚拟主机,每个虚拟主机和某个网络域名Domain Name相匹配
每个虚拟主机下都可以部署(deploy)一个或者多个Web App,每个Web App对应于一个Context,有一个Context path
当Host获得一个请求时,将把该请求匹配到某个Context上,然后把该请求交给该Context来处理
匹配的方法是“最长匹配”,所以一个path==""的Context将成为该Host的默认Context
所有无法和其它Context的路径名匹配的请求都将最终和该默认Context匹配
1.6 - Context
一个Context对应于一个Web Application,一个Web Application由一个或者多个Servlet组成
Context在创建的时候将根据配置文件$CATALINA_HOME/conf/web.xml和$WEBAPP_HOME/WEB-INF/web.xml载入Servlet类
当Context获得请求时,将在自己的映射表(mapping table)中寻找相匹配的Servlet类
如果找到,则执行该类,获得请求的回应,并返回
假设来自客户的请求为:
http://localhost:8080/wsota/wsota_index.jsp
1) 请求被发送到本机端口8080,被在那里侦听的Coyote HTTP/1.1 Connector获得
2) Connector把该请求交给它所在的Service的Engine来处理,并等待来自Engine的回应
3) Engine获得请求localhost/wsota/wsota_index.jsp,匹配它所拥有的所有虚拟主机Host
4) Engine匹配到名为localhost的Host(即使匹配不到也把请求交给该Host处理,因为该Host被定义为该Engine的默认主机)
5) localhost Host获得请求/wsota/wsota_index.jsp,匹配它所拥有的所有Context
6) Host匹配到路径为/wsota的Context(如果匹配不到就把该请求交给路径名为""的Context去处理)
7) path="/wsota"的Context获得请求/wsota_index.jsp,在它的mapping table中寻找对应的servlet
8) Context匹配到URL PATTERN为*.jsp的servlet,对应于JspServlet类
9) 构造HttpServletRequest对象和HttpServletResponse对象,作为参数调用JspServlet的doGet或doPost方法
10)Context把执行完了之后的HttpServletResponse对象返回给Host
11)Host把HttpServletResponse对象返回给Engine
12)Engine把HttpServletResponse对象返回给Connector
13)Connector把HttpServletResponse对象返回给客户browser
二、Context Path、Servlet Path、Path info
|-- Context Path --|-- Servlet Path -|--Path Info--|
http://www.myserver.com /mywebapp /helloServlet /hello
|-------- Request URI ----------------------------|
Remember the following three points:
1. Request URI = context path + servlet path + path info.
2. Context paths and servlet paths start with a / but do not end with it.
3. HttpServletRequest provides three methods getContextPath(),
getServletPath() and getPathInfo() to retrieve the context path,
the servlet path, and the path info, respectively, associated with a request.
Identifying the servlet path
To match a request URI with a servlet, the servlet container follows a simple algorithm.
Once it identifies the context path, if any, it evaluates the remaining part of the
request URI with the servlet mappings specified in the deployment descriptor, in the
following order. If it finds a match at any step, it does not take the next step.
1 The container tries to match the request URI to a servlet mapping. If it finds a
match, the complete request URI (except the context path) is the servlet path. In
this case, the path info is null.
2 It tries to recursively match the longest path by stepping down the request URI
path tree a directory at a time, using the / character as a path separator, and determining
if there is a match with a servlet. If there is a match, the matching part
of the request URI is the servlet path and the remaining part is the path info.
3 If the last node of the request URI contains an extension (.jsp, for example),
the servlet container tries to match it to a servlet that handles requests for the
specified extension. In this case, the complete request URI is the servlet path
and the path info is null.
4 If the container is still unable to find a match, it will forward the request to the
default servlet. If there is no default servlet, it will send an error message indicating
the servlet was not found.
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>RedServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/red/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>RedServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/red/red/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>RedBlueServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/red/blue/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>BlueServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/blue/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>GreenServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/green</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ColorServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.col</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
Request URI Servlet Used Servlet Path Path Info
/colorapp/red RedServlet /red null
/colorapp/red/ RedServlet /red /
/colorapp/red/aaa RedServlet /red /aaa
/colorapp/red/blue/aa RedBlueServlet /red/blue /aa
/colorapp/red/red/aaa RedServlet /red/red /aaa
/colorapp/aa.col ColorServlet /aa.col null
/colorapp/hello/aa.col ColorServlet /hello/aa.col null
/colorapp/red/aa.col RedServlet /red /aa.col
/colorapp/blue NONE(Error message)
/colorapp/hello/blue/ NONE(Error message)
/colorapp/blue/mydir NONE(Error message)
/colorapp/blue/dir/aa.col ColorServlet /blue/dir/aa.col null
/colorapp/green GreenServlet /green null