Map排序
Map排序的方式有很多种,这里记录下自己总结的两种比较常用的方式:按键排序(sort by key), 按值排序(sort by value)。
按键排序(sort by key)
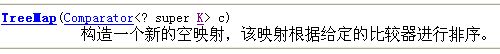
jdk内置的Java.util包下的TreeMap<K,V>既可满足此类需求,原理很简单,其重载的构造器之一
有一个参数,该参数接受一个比较器,比较器定义比较规则,比较规则就是作用于TreeMap<K,V>的键,据此可实现按键排序。
public Map<String, String> sortMapByKey(Map<String, String> oriMap) {
if (oriMap == null || oriMap.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Map<String, String> sortedMap = new TreeMap<String, String>(new Comparator<String>() {
public int compare(String key1, String key2) {
int intKey1 = 0, intKey2 = 0;
try {
intKey1 = getInt(key1);
intKey2 = getInt(key2);
} catch (Exception e) {
intKey1 = 0;
intKey2 = 0;
}
return intKey1 - intKey2;
}});
sortedMap.putAll(oriMap);
return sortedMap;
}
private int getInt(String str) {
int i = 0;
try {
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("^\\d+");
Matcher m = p.matcher(str);
if (m.find()) {
i = Integer.valueOf(m.group());
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return i;
}
按值排序(sort by value)
按值排序就相对麻烦些了,貌似没有直接可用的数据结构能处理类似需求,需要我们自己转换一下。
Map本身按值排序是很有意义的,很多场合下都会遇到类似需求,可以认为其值是定义的某种规则或者权重。
public Map<String, String> sortMapByValue(Map<String, String> oriMap) {
Map<String, String> sortedMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
if (oriMap != null && !oriMap.isEmpty()) {
List<Map.Entry<String, String>> entryList = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, String>>(oriMap.entrySet());
Collections.sort(entryList,
new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, String>>() {
public int compare(Entry<String, String> entry1,
Entry<String, String> entry2) {
int value1 = 0, value2 = 0;
try {
value1 = getInt(entry1.getValue());
value2 = getInt(entry2.getValue());
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
value1 = 0;
value2 = 0;
}
return value2 - value1;
}
});
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iter = entryList.iterator();
Map.Entry<String, String> tmpEntry = null;
while (iter.hasNext()) {
tmpEntry = iter.next();
sortedMap.put(tmpEntry.getKey(), tmpEntry.getValue());
}
}
return sortedMap;
}
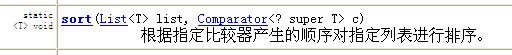
本例中先将待排序oriMap中的所有元素置于一个列表中,接着使用java.util.Collections的一个静态方法
来排序列表,同样是用比较器定义比较规则。排序后的列表中的元素再依次被装入Map,需要注意的一点是为了肯定的保证Map中元素与排序后的List中的元素的顺序一致,使用了LinkedHashMap数据类型,虽然该类型不常见,但是在一些特殊场合下还是非常有用的。