matlab三种图像二值化函数,详细,附代码(转)
代码链接:https://download.csdn.net/download/hupeng810/1511870
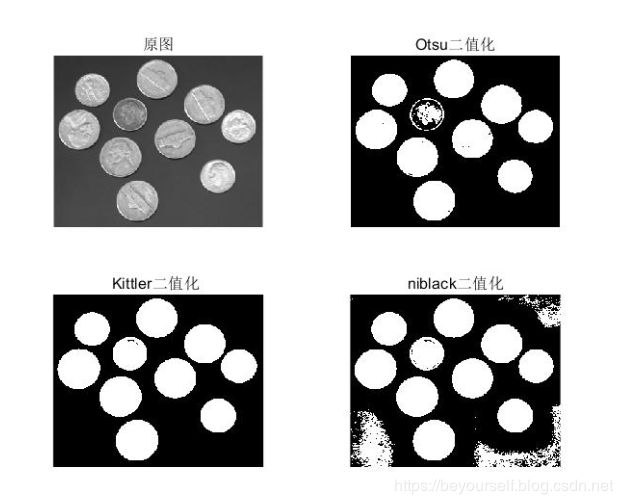
Ostu二值化:
thOTSU = graythresh(imag)
imagBWO = im2bw(imag, thOTSU)
function imagBW = otsu(imag)
function imagBW = otsu(imag)
% OTSU binarizes a gray scale image 'imag' into a binary image, with the
% noises removed.
% Input:
% imag: the gray scale image, with black foreground(0), and white
% background(255).
% Output:
% imagBW: the binary image of the gray scale image 'imag', with Otsu
% algorithm.
% Reference:
% Nobuyuki Otsu. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms.
% IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. 1979.SMC-9(1):62-66
imag = imag(:, :, 1);
[counts, x] = imhist(imag); % counts are the histogram. x is the intensity level.
GradeI = length(x); % the resolusion of the intensity. i.e. 256 for uint8.
varB = zeros(GradeI, 1); % Between-class Variance of binarized image.
prob = counts ./ sum(counts); % Probability distribution
meanT = 0; % Total mean level of the picture
for i = 0 : (GradeI-1)
meanT = meanT + i * prob(i+1);
end
varT = ((x-meanT).^2)' * prob;
% Initialization
w0 = prob(1); % Probability of the first class
miuK = 0; % First-order cumulative moments of the histogram up to the kth level.
varB(1) = 0;
% Between-class variance calculation
for i = 1 : (GradeI-1)
w0 = w0 + prob(i+1);
miuK = miuK + i * prob(i+1);
if (w0 == 0) || (w0 == 1)
varB(i+1) = 0;
else
varB(i+1) = (meanT * w0 - miuK) .^ 2 / (w0 * (1-w0));
end
end
maxvar = max(varB);
em = maxvar / varT % Effective measure
index = find(varB == maxvar);
index = mean(index);
th = (index-1)/(GradeI-1)
imagBW = im2bw(imag, th);
% thOTSU = graythresh(imag)
% imagBWO = im2bw(imag, thOTSU);
Kittler二值化:
function imagBW = kittlerMet(imag)
% KITTLERMET binarizes a gray scale image 'imag' into a binary image
% Input:
% imag: the gray scale image, with black foreground(0), and white
% background(255).
% Output:
% imagBW: the binary image of the gray scale image 'imag', with kittler's
% minimum error thresholding algorithm.
% Reference:
% J. Kittler and J. Illingworth. Minimum Error Thresholding. Pattern
% Recognition. 1986. 19(1):41-47
MAXD = 100000;
imag = imag(:,:,1);
[counts, x] = imhist(imag); % counts are the histogram. x is the intensity level.
GradeI = length(x); % the resolusion of the intensity. i.e. 256 for uint8.
J_t = zeros(GradeI, 1); % criterion function
prob = counts ./ sum(counts); % Probability distribution
meanT = x' * prob; % Total mean level of the picture
% Initialization
w0 = prob(1); % Probability of the first class
miuK = 0; % First-order cumulative moments of the histogram up to the kth level.
J_t(1) = MAXD;
n = GradeI-1;
for i = 1 : n
w0 = w0 + prob(i+1);
miuK = miuK + i * prob(i+1); % first-order cumulative moment
if (w0 < eps) || (w0 > 1-eps)
J_t(i+1) = MAXD; % T = i
else
miu1 = miuK / w0;
miu2 = (meanT-miuK) / (1-w0);
var1 = (((0 : i)'-miu1).^2)' * prob(1 : i+1);
var1 = var1 / w0; % variance
var2 = (((i+1 : n)'-miu2).^2)' * prob(i+2 : n+1);
var2 = var2 / (1-w0);
if var1 > eps && var2 > eps % in case of var1=0 or var2 =0
J_t(i+1) = 1+w0 * log(var1)+(1-w0) * log(var2)-2*w0*log(w0)-2*(1-w0)*log(1-w0);
else
J_t(i+1) = MAXD;
end
end
end
minJ = min(J_t);
index = find(J_t == minJ);
th = mean(index);
th = (th-1)/n
imagBW = im2bw(imag, th);
% figure, imshow(imagBW), title('kittler binary');
niblack二值化:
function imagBW = niblack(imag)
% NIBLACK binarizes a gray scale image 'imag' to a binary image, using
% Niblack algorithm. The noises of the gray scale image are removed.
% Input:
% imag: the gray scale image, with black foreground(0), and white
% background(255).
% Output:
% imagBW: the binary image of the gray scale image 'imag', with
% Niblack algorithm.
% Reference:
% Wayne Niblack. An Introduction to Digital Image Processing. pp: 115.
% 1986. Prentice/Hall International. ISBN: 013 480674 3
tic;
k = -0.2; % the first manual parameter
b = 80; % the second manual parameter, about the width of the square neighborhood
choice = 1; % 1 for pixel-to-pixel computation, 2 for pixel averaging within the square neighborhood for fast computation.
imag = imag( :, :, 1);
[Hei, Wid] = size(imag);
imag = padarray(imag, [b b], 'symmetric', 'both'); % Pad image array
Hei_pad = Hei + 2 * b;
Wid_pad = Wid + 2 * b;
imagBW = false(Hei_pad, Wid_pad);
switch choice
case 1
for i = 1+b : Hei+b
for j = 1+b : Wid+b
upR = i-floor(b/2-1/2);
dnR = i+floor(b/2);
lfC = j-floor(b/2-1/2);
rtC = j+floor(b/2);
m_ij = mean(mean(imag(upR : dnR, lfC : rtC)));
sigma_squared = double(imag(upR : dnR, lfC : rtC)) - m_ij;
sigma_squared = mean(mean(sigma_squared .^2));
sigma = sqrt(sigma_squared);
th_ij = m_ij + k * sigma;
if double(imag(i,j)) > th_ij
imagBW(i,j) = 1;
end
end
end
case 2
for i = 1+b : b : Hei+b
for j = 1+b : b : Wid+b
upR = i-floor(b/2-1/2);
dnR = i+floor(b/2);
lfC = j-floor(b/2-1/2);
rtC = j+floor(b/2);
m_ij = mean(mean(imag(upR : dnR, lfC : rtC)));
sigma_squared = double(imag(upR : dnR, lfC : rtC)) - repmat(m_ij, (dnR-upR+1), (rtC-lfC+1));
sigma_squared = sigma_squared .^ 2;
sigma_squared = mean(mean(sigma_squared));
sigma = sqrt(sigma_squared);
th_ij = m_ij + k * sigma;
imagBW(upR : dnR, lfC : rtC) = double(imag(upR : dnR, lfC : rtC)) > th_ij;
end
end
otherwise
display('Wrong Choice!');
end
imagBW = imagBW(1+b : Hei+b, 1+b : Wid+b);
% figure, imshow(imagBW), title('Binarized Image');
toc;