【算法编程】KMP、Manacher和BFPRT算法
一、KMP算法
1、算法背景
KMP 算法原本是用来解决包含问题的,具体问题如下:
- 给定一个主串
str1和模式串str2,要求找出str2在str1中出现的位置,此即串的模式匹配问题。
例如:
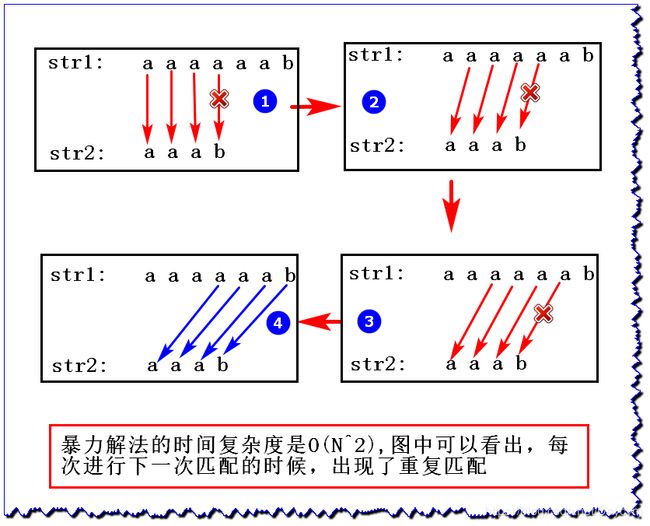
str1:aaaaaabstr2:aaab
暴力解决方法:
str1 从0的位置依次往下匹配 str2
- KMP算法的核心是利用匹配失败后的信息,尽量减少模式串与主串的匹配次数以达到快速匹配的目的
- 具体实现就是通过一个
next()函数实现,函数本身包含了模式串的局部匹配信息
2、预备概念
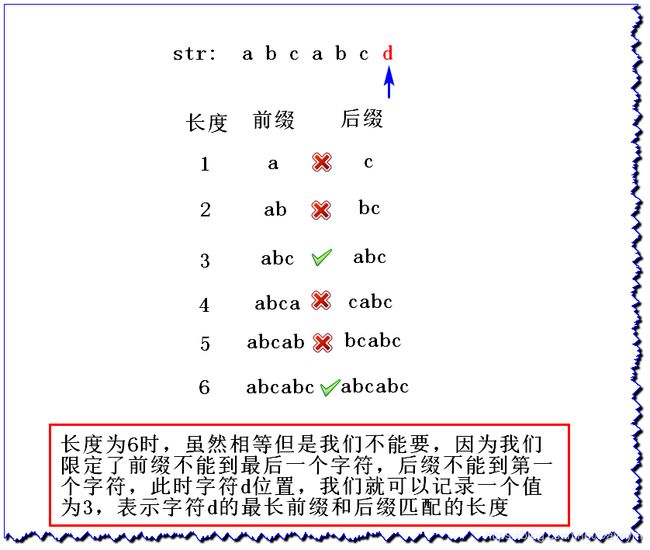
在介绍KMP之前我们先来了解一个概念,没有这个概念后面无法进行。在一个字符串中的一个字符之前的子串的最长前缀和后缀匹配的长度。
例如:
- str:
abcabcd - 求字符
d之前的最长前缀和后缀匹配的长度
前缀不能包含除字符d之外的最后一个字符,后缀不能包含第一个字符
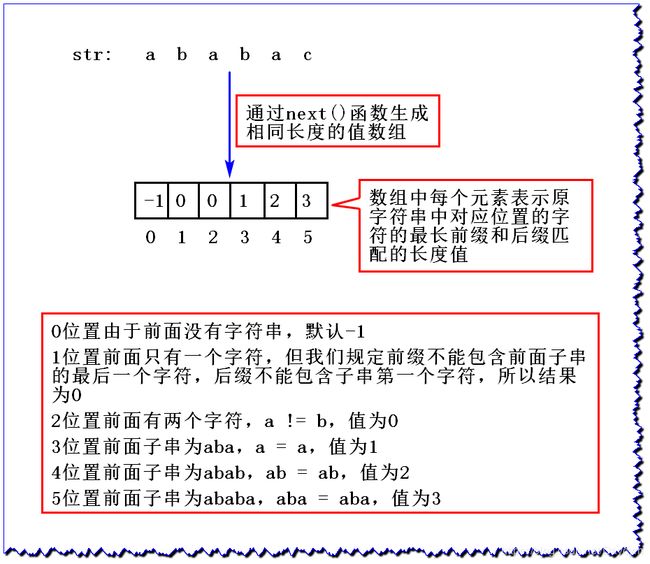
KMP 就是通过一个 next() 函数实现 str2 中每个字符对应的最长前缀和后缀匹配的长度
public static int[] getNext(char[] str2) {
if (str2.length == 1) { //如果str2长度为1,返回-1
return new int[] { -1 };
}
int[] next = new int[str2.length];
next[0] = -1; //位置0
next[1] = 0; //位置1
int i = 2; //当前来到的位置
int cn = 0; //前缀子串后一个字符
while (i < next.length) {
if (str2[i - 1] == str2[cn]) { //如果当前字符的前一个字符和前缀子串后一个字符相等
next[i++] = ++cn; //当前数组值+1,当前位置来到下一个位置,
} else if (cn > 0) { //cn就是图中X,Y,Z...位置
cn = next[cn];
} else {
next[i++] = 0; //否则值为0
}
}
return next;
}
3、KMP算法
4、Java代码
package day07;
public class Code01_KMP {
public static int kmp(String str1, String str2) {
if(str1 == null || str2 == null || str2.length() < 1 || str1.length() < str2.length()){
return -1;
}
char[] s = str1.toCharArray();
char[] m = str2.toCharArray();
int si = 0; //str1当前位置
int mi = 0; //str2当前位置
int[] next = getNext(m); //获取str2的最长前缀和后缀匹配的长度
while(si < s.length && mi < m.length) {
if(s[si] == m[mi]) { //如果相等,str1和str2同时跳下一个字符
si++;
mi++;
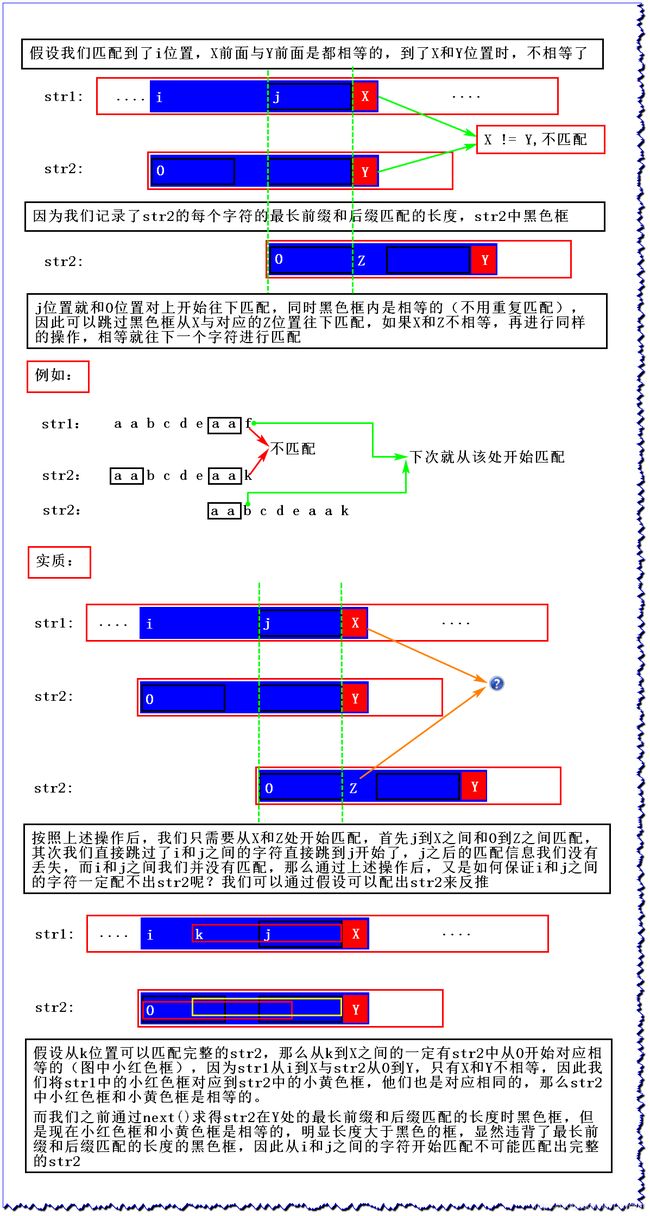
/**
* 不相等,str2往后推,str1中的j对应str2中的0位置,并从X和Z开始匹配
* 如果X和Z一直不匹配,str2就往后推,一直将0推到Z处都不相等,此时next[mi]为-1
* 说明一直到第一个字符都不匹配,那么此时str1往跳下一个字符再开始匹配
*/
}else if(next[mi] == -1) { //str2推到0位置了
si++;
}else { //str2没推到0,就更新mi位置,也就是Z的位置
mi = next[mi];
}
}
//如果mi到str2最后了,说明存在匹配的,返回si-mi即匹配子串的开始下标,否则返回-1
return mi == m.length ? si - mi : -1;
}
public static int[] getNext(char[] str2) {
if (str2.length == 1) { //如果str2长度为1,返回-1
return new int[] { -1 };
}
int[] next = new int[str2.length];
next[0] = -1; //位置0
next[1] = 0; //位置1
int i = 2; //当前来到的位置
int cn = 0; //前缀子串后一个字符
while (i < next.length) {
if (str2[i - 1] == str2[cn]) { //如果当前字符的前一个字符和前缀子串后一个字符相等
next[i++] = ++cn; //当前数组值+1,当前位置来到下一个位置,
} else if (cn > 0) { //cn就是图中X,Y,Z...位置
cn = next[cn];
} else {
next[i++] = 0; //否则值为0
}
}
return next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcabcababaccc";
String match = "ababa";
System.out.println(kmp(str, match));
}
}
5、KMP算法应用(1)
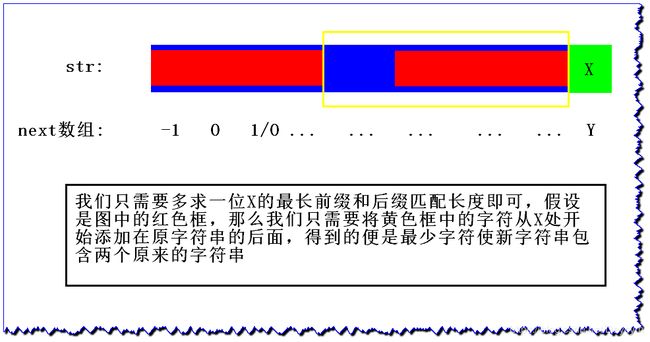
在给定的原字符串 str 后添加字符使得到的新字符串包含两个原字符串,要求添加的字符是最少的
例如:
str:abcabc- 添加
abc,得到新的字符串abcabcabc且里面包含两个原字符串,abcabc
当然
abcabcabcabc满足包含两个原字符串,但是添加的字符不是最少的
abcabc,最后一个字符后的位置的最长前缀和后缀匹配长度为3,那么我们只需要截取下标3到最后位置的字符即是答案,abc组成新的字符串abcabcabc
Java代码:
package day07;
public class Code02_KMP_ShortestHaveTwice {
public static String shortestHaveTwice(String str) {
if(str == null || str.length() == 0){
return "";
}
char[] charStr = str.toCharArray();
if(charStr.length == 1) { //长度为1,重复即可
return str + str;
}
if(charStr.length == 2) { //长度为2,如果前两个字符相等就加一个字符,如果不等,就重复
return charStr[0] == charStr[1] ? (str + String.valueOf(charStr[0])) : (str + str);
}
int endNext = endNextLength(charStr); //计算next数组,多了一位
return str + str.substring(endNext); //原字符串加截取字符串
}
public static int endNextLength(char[] charStr) {
int next[] = new int[charStr.length + 1];
next[0] = -1; //第一个字符的next数组值
next[1] = 0; //第二个字符的next数组值
int pos = 2; //当前位置
int cn = 0; //前缀后一个字符
while(pos < next.length) {
if(charStr[pos - 1] == charStr[cn]) {
next[pos++] = ++cn;
}else if(cn > 0) {
cn = next[cn];
}else {
next[pos++] = 0;
}
}
return next[next.length - 1];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String test1 = "a";
System.out.println(shortestHaveTwice(test1));
String test2 = "aa";
System.out.println(shortestHaveTwice(test2));
String test3 = "ab";
System.out.println(shortestHaveTwice(test3));
String test4 = "abcdabcd";
System.out.println(shortestHaveTwice(test4));
String test5 = "abracadabra";
System.out.println(shortestHaveTwice(test5));
}
}
5、KMP算法应用(2)
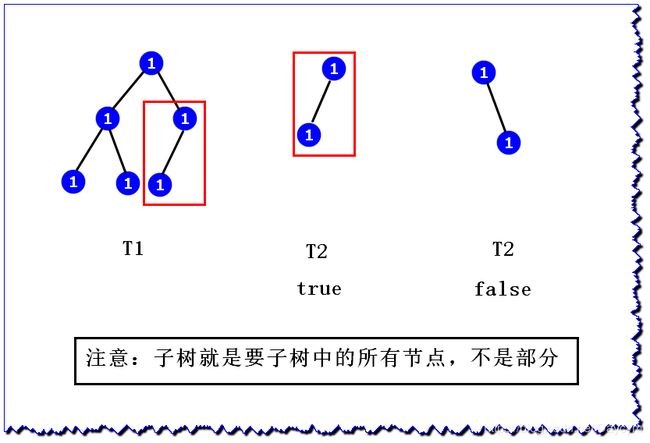
给定两个树 T1 和 T2,求 T1 中是否有一棵子树和 T2 一样,一样返回 true ,否则返回 false
例如:
解题思路:
- 将两个数都进行前序序列化,如上图中两课树
- T1->S1:
1_1_1_#_#_1_#_#_1_1_#_#_#_ - T2->S2:
1_1_#_#_#_ - 我们只需要判断
T1中是否包含T2子串即可,包含返回true,否则返回false
Java代码:
package day07;
public class Code03_KMP_T1SubtreeEqualsT2 {
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
//主函数
public static boolean isSubtree(Node t1, Node t2) {
String t1Str = serialByPre(t1); //序列化
String t2Str = serialByPre(t2); //序列化
return getIndexOf(t1Str, t2Str) != -1;
}
//前序序列化
public static String serialByPre(Node head) {
if(head == null) {
return "#!";
}
String res = head.value + "!";
res += serialByPre(head.left);
res += serialByPre(head.right);
return res;
}
//KMP,查找子串开始位置
public static int getIndexOf(String s, String m) {
if(s == null || m == null || m.length() < 1 || s.length() < m.length()) {
return -1;
}
char[] ss = s.toCharArray();
char[] ms = m.toCharArray();
int[] nextArr = getNextArray(ms);
int index = 0;
int mi = 0;
while(index < ss.length && mi < ms.length){
if(ss[index] == ms[mi]) {
index++;
mi++;
}else if(nextArr[mi] == -1) {
index++;
}else {
mi = nextArr[mi];
}
}
return mi == ms.length ? index - mi : -1;
}
//获取next数组
public static int[] getNextArray(char[] ms) {
if (ms.length == 1) {
return new int[] { -1 };
}
int[] nextArr = new int[ms.length];
nextArr[0] = -1;
nextArr[1] = 0;
int pos = 2;
int cn = 0;
while (pos < nextArr.length) {
if (ms[pos - 1] == ms[cn]) {
nextArr[pos++] = ++cn;
} else if (cn > 0) {
cn = nextArr[cn];
} else {
nextArr[pos++] = 0;
}
}
return nextArr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node t1 = new Node(1);
t1.left = new Node(2);
t1.right = new Node(3);
t1.left.left = new Node(4);
t1.left.right = new Node(5);
t1.right.left = new Node(6);
t1.right.right = new Node(7);
t1.left.left.right = new Node(8);
t1.left.right.left = new Node(9);
Node t2 = new Node(2);
t2.left = new Node(4);
t2.left.right = new Node(8);
t2.right = new Node(5);
t2.right.left = new Node(9);
System.out.println(isSubtree(t1, t2));
}
}
二、Manacher算法
Manacher算法,又叫“马拉车”算法,可以在时间复杂度为O(n)的情况下求解一个字符串的最长回文子串长度的问题。
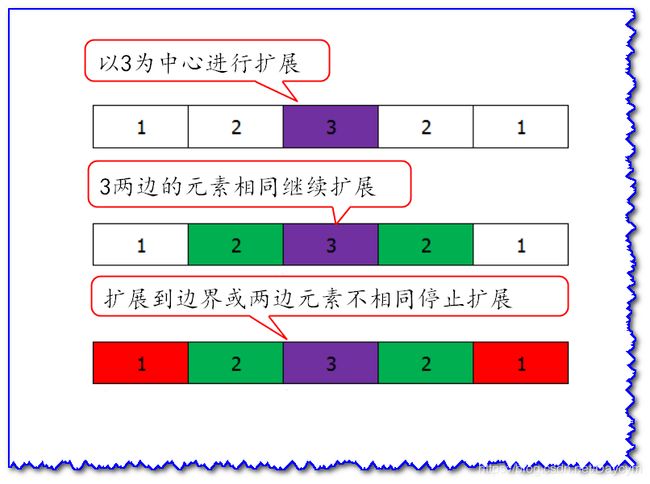
1、中心扩展法求解最长回文子串
中心扩展法的思想是,遍历到数组的某一个元素时,以这个元素为中心,向两边进行扩展,如果两边的元素相同则继续扩展,否则停止扩展。算法复杂度为 O ( N 2 ) O(N^2) O(N2)。
如下图:当遍历到3时
但是单个字符扩展存在缺陷,当字符串长度为偶数时,例如:1221
1,2,2,1是一个回文串,然而找不到对称中心,这样以一个元素为中心向两边扩展就不好用了
- 1、分别以单个字符和相邻两个字符为中心扩展(下面代码使用的是此方法)
- 2、对1,2,2,1进行填充,比如说用#进行填充得到:#,1,#,2,#,2,#,1,#
Java代码:
class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if(s == null || s.length() < 1)
return "";
int start = 0;
int end = 0;
//中心扩展法,依次遍历中心点
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
//求扩展中心的长度
int len1 = expandLen(s, i, i); //以每个字符为中心
int len2 = expandLen(s, i, i+1); //以每相邻两字符作为中心
int len = Math.max(len1, len2);
if(len > end - start){
start = i - (len - 1) / 2;
end = i + len / 2;
}
}
return s.substring(start, end+1);
}
public int expandLen(String s, int L, int R){
int left = L;
int right = R;
while(left >= 0 && right < s.length() && s.charAt(left) == s.charAt(right)){
left--;
right++;
}
return right - left - 1;
}
}
2、Manacher算法
直接通过例子来说明:
Manacher算法的核心思想,就是利用前面遍历的时候产生的回文子串
如上图:
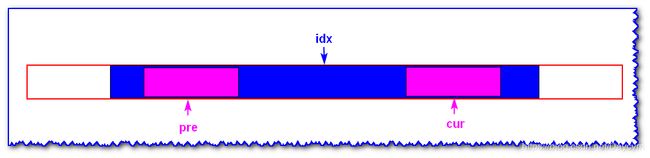
- i d x idx idx 表示为蓝色回文子串的对称轴(已知)
- 现在求以 c u r cur cur 为对称轴的回文子串(未知)
- p r e pre pre 为以 i d x idx idx 为对称轴, c u r cur cur 的对称位置(遍历到 c u r cur cur, p r e pre pre就已知了)
情况一: i ′ i' i′ 的回文子串超出 i d x idx idx 的回文子串的左边界
已知 i d x idx idx 为蓝色块子串的中心轴,现在求以i为中心轴的回文子串
- i i i 处于以 i d x idx idx 为中心轴的回文子串中, i ′ i' i′ 为 i i i 关于 i d x idx idx 的对称点,且以 i ′ i' i′ 为中心轴的回文子串已知(橘黄色块)
- 其中 i i i 指向 c c c, i ′ i' i′ 指向 b b b, i d x idx idx 指向 e e e(小写字符为变量,大写字母为具体字符)
- 那么由 e e e 为中心的回文子串中得知, b = c b=c b=c
- 又因为 i d x idx idx 的回文不包括 a a a 和 d d d,所以 a ! = d a !=d a!=d( a = d a=d a=d 时,以 i d x idx idx 的回文子串还要扩展下去)
- 又因为 i d x idx idx 左到 b b b 和 i d x idx idx右到 c c c 相等的,且 a ! = d a!=d a!=d,所以以 c c c 为中心轴的回文半径只有 i d x 右 − l o c a t i o n ( c ) idx右-location(c) idx右−location(c)
- 若 a a a 关于以 b b b 为中心的回文的对称点为 a ′ a' a′。 a ′ a' a′ 以 e e e 为中心轴的回文的对称点为 a ′ ′ a'' a′′,那么 a = a ′ = a ′ ′ ! = d a=a'=a''!=d a=a′=a′′!=d
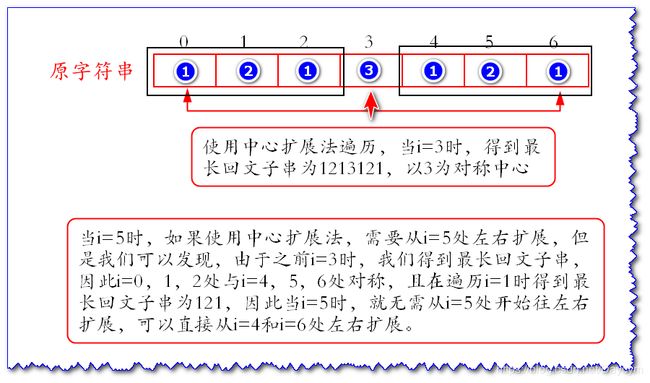
举例说明:
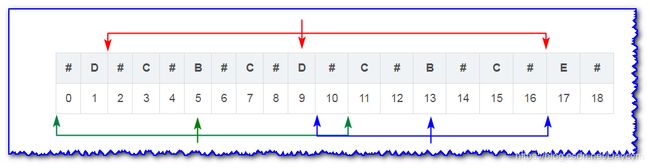
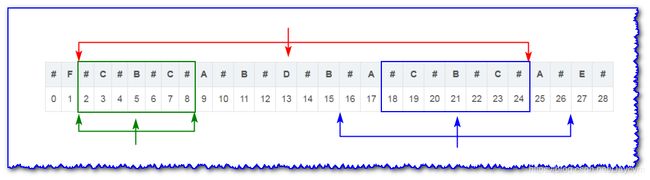
- 当遍历到13号B时,以9号D为中心轴的回文子串从2号到16号(由于前面已经遍历过,已知),长度为 16 − 2 + 1 = 15 16-2+1=15 16−2+1=15
- 以5号B为中心轴的回文子串从0号到10号(已知),长度为 10 − 0 + 1 = 11 10-0+1=11 10−0+1=11
- 13号B关于9号D的对称点为5号B,现在要求以13号B为对称轴的回文子串
1号D和17号E不相等,现在只要盘判定以13号B为中心轴的回文子串是否包含17号
- 如果包括17号E,那么它关于13号B对称的点就是9号D,而9号D关于5号B的对称点就是1号D
- 根据对称性可知,17号E应该等于9号D等于1号D,很显然不相等
所以以13号B为中心轴的回文子串不包括17号E,又根据以5号B和9号D为中心轴的回文子串可知:
- 2号#到5号B等于8号#到5号B
- 10号#到13号B等于16号#到13号B
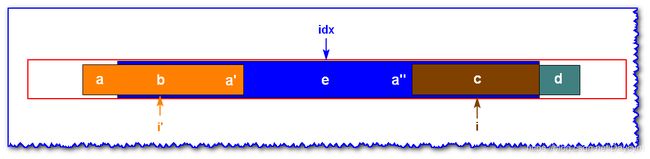
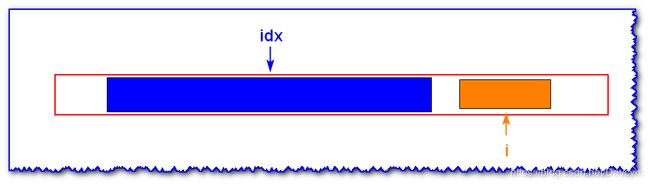
情况二: i ′ i' i′ 的回文子串 i d x idx idx 的回文子串包含
已知 i i i 关于 i d x idx idx 为中心轴的对称点 i ′ i' i′ 的最大回文子串如上图
- 因为 i ′ i' i′ 的回文子串不包括 a , b a,b a,b 则 a ! = b a!=b a!=b
- 又因为 a , d a,d a,d 和 b , c b,c b,c 分别关于 i d x idx idx对称,记 b = c , a = d b=c,a=d b=c,a=d ,所以 c ! = d c!=d c!=d
- 又因为在 c c c 和 d d d 之间是回文,原因在于 c c c 和 d d d 之间的字符关于 i d x idx idx 的 a a a 和 b b b 之间对称,且 a a a 和 b b b 之间是回文串,所以, c c c 和 d d d 之间也是回文串。所以 i i i 的回文子串的长度和 i ′ i' i′ 相同
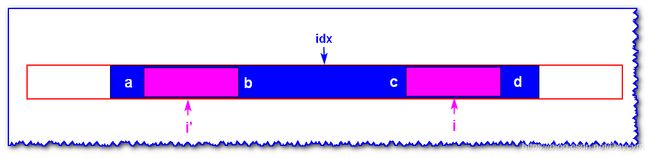
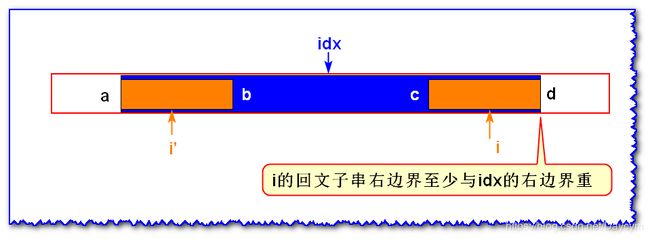
情况三: i ′ i' i′ 的回文子串的左边界与 i d x idx idx 的回文子串的左边界重合
由 i d x idx idx 为中心轴的回文子串可知, b = c , a ! = d b=c,a!=d b=c,a!=d,且 i ′ i' i′ 的回文长度在 a a a 到 b b b 之间(不包括 a , b a,b a,b)
那么 i i i 的回文子串的长度至少如上图所示
- 若 c = d c=d c=d 时,关于 i i i 为中心轴的回文还是可以扩展的
- 若 c ! = d c!=d c!=d 则刚好是上图所示的。
举例说明(c=d时):
i i i 关于 i d x idx idx 的对称点 i ′ i' i′ 的最长回文子串如上图,且 i ′ i' i′ 的回文左边界与 i d x idx idx 重合,所以 i i i 为中心的回文需要从蓝色框边界开始在往左右两边试着扩展
情况四: i ′ i' i′ 的回文子串没有被 i d x idx idx 的回文子串包含
此时,我们没有任何信息可以利用,只能以 i i i 为中心轴,向左右两边扩展。找出它的最长回文子串。
Java代码:
package day07;
public class Code04_Manacher {
//求最长回文子串
public static String longestPalindrome(String s) {
int n = s.length();
if (n <= 1) return s ;
StringBuilder strb = new StringBuilder();
strb.append("#");
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
strb.append(s.charAt(i));
strb.append("#");
}
int len = strb.length();
int[] radius = new int[len];
int idx = 0; //表示上一次回文子串的中心轴下标
int rad = 1; //idx能够包含最大的范围的下一个字符下标
int j = 0;
int maxIdx = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
//情况四
if(i >= rad){
int count = 1;
while((i - count) >=0
&& (i + count) < strb.length()
&& strb.charAt(i - count) == strb.charAt(i + count)){
count++;
}
radius[i] = count - 1;
if((i + radius[i]) >= rad){
idx = i;
rad = i + count;
}
maxIdx = (radius[i] > radius[maxIdx] ? i : maxIdx);
}else if(i < rad){
j = 2*idx - i; //i关于idx的对称点j
int idx_radius = idx - radius[idx]; //idx回文子串的左边界下标
int j_radius = j - radius[j];//j的回文子串的左边界下标
if(j_radius > idx_radius){ //情况二
radius[i] = radius[j]; //i的回文子串和其关于idx对称点的回文子串长度一样
}else if(j_radius < idx_radius){//情况一
radius[i] = idx + radius[idx] - i;//idx的右边界下标-i下标
}else{ //情况三
radius[i] = idx + radius[idx] - i;//至少
int count2 = 1;
//相等时,继续扩展
while((i + radius[i] + count2) < len
&& (i - radius[i] - count2) >= 0
&& strb.charAt(i + radius[i] + count2) == strb.charAt(i - radius[i] - count2)){
count2++;
}
//不等时
radius[i] += (count2 - 1);
//更新最长回文子串中心和右边界下一个字符下标
if(i + radius[i] >= rad){
idx = i;
rad = i + count2;
}
}
//更新最长回文子串的中心
maxIdx = (radius[i] > radius[maxIdx] ? i : maxIdx);
}
}
StringBuilder ret = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = maxIdx-radius[maxIdx]+1; i <= maxIdx + radius[maxIdx]; i+=2){
ret.append(strb.charAt(i));
}
return ret.toString();
}
//求最长回文子串长度(代码优化)
public static int maxLcpsLength(String str) {
if(str == null || str.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
char[] charArr = manacherString(str); //每个字符前后加#
int[] pArr = new int[charArr.length]; //回文半径数组
int index = -1;
int pR = -1;
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i != charArr.length; i++) {
//i在回文右边界里面,我们起码有一部分不用验的区域,否则只有自己不用验
pArr[i] = pR > i ? Math.min(pArr[2 * index - i], pR - i) : 1;
//跳过不用验的区域,我们让它往后扩一下
while (i + pArr[i] < charArr.length && i - pArr[i] > -1) {
if (charArr[i + pArr[i]] == charArr[i - pArr[i]]) //如果相等,半径加1
pArr[i]++;
else { //否则跳出
break;
}
}
if (i + pArr[i] > pR) { //如果回文半径超过右边界
pR = i + pArr[i]; //更新回文半径
index = i;
}
max = Math.max(max, pArr[i]); //取较大值
}
return max - 1;
}
public static char[] manacherString(String str) {
char[] charArr = str.toCharArray();
char[] res = new char[str.length() * 2 + 1];
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0; i != res.length; i++) {
res[i] = (i & 1) == 0 ? '#' : charArr[index++]; //奇数位置设为#,偶数为原字符
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abc1234321ab";
System.out.println(longestPalindrome(str));
System.out.println(maxLcpsLength(str));
}
}
3、Manacher算法应用
给定一个字符串,只能往字符串后添加字符,如何让字符串添加后整体为回文串,且添加的字符最少
解题思路:
- 求得包含原字符串最后一个字符的最长回文子串
- 然后将原字符串中前面的字符逆序过来,就是答案
例如:
- str:
abc12321 - 字符1的最长回文子串是
12321,剩下abc逆序过来,cba就是答案
在具体的计算中,Manacher算法在计算3的回文子串的时候,它的右边界正好到最后一个字符,停止计算
Java代码:
package day07;
public class Code05_Manacher_ShortestEnd {
public static char[] manacherString(String str) {
char[] charArr = str.toCharArray();
char[] res = new char[str.length() * 2 + 1];
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i != res.length; i++) {
res[i] = (i & 1) == 0 ? '#' : charArr[index++];
}
return res;
}
public static String shortestEnd(String str) {
if (str == null || str.length() == 0) {
return null;
}
char[] charArr = manacherString(str);
int[] pArr = new int[charArr.length];
int index = -1;
int pR = -1;
int maxContainsEnd = -1;
for (int i = 0; i != charArr.length; i++) {
pArr[i] = pR > i ? Math.min(pArr[2 * index - i], pR - i) : 1;
while (i + pArr[i] < charArr.length && i - pArr[i] > -1) {
if (charArr[i + pArr[i]] == charArr[i - pArr[i]])
pArr[i]++;
else {
break;
}
}
if (i + pArr[i] > pR) {
pR = i + pArr[i];
index = i;
}
//回文子串的右边界到字符串的最后位置,停止计算
if (pR == charArr.length) {
maxContainsEnd = pArr[i];
break;
}
}
char[] res = new char[str.length() - maxContainsEnd + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
res[res.length - 1 - i] = charArr[i * 2 + 1];
}
return String.valueOf(res);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcd123321";
System.out.println(shortestEnd(str));
}
}
三、BFPRT算法
BFPRT算法解决的是在一个无序数组中找到第K大或第K小的数。当然这个问题可以先排序,时间复杂度为 O ( N ∗ l o g N ) O(N*logN) O(N∗logN),用BFPRT算法的时间复杂度为 O(N)
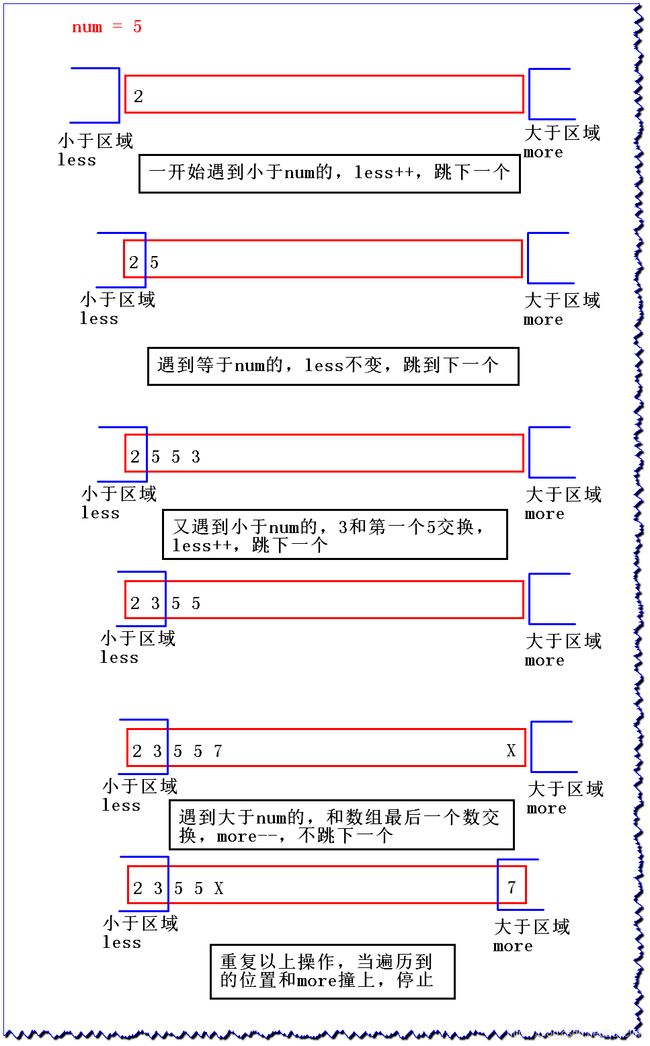
在介绍BFPRT算法之前我们先来了解荷兰国旗问题:
给定一个数组arr,和一个数num,请把小于num的数放在数组的左边,等于num的数放在数组的中间,大于num的数放在数组的右边。
要求额外空间复杂度O(1),时间复杂度O(N)
Java代码:
package day07;
public class Code06_NetherlandsFlag {
public static int[] netherlandsFlag(int[] arr, int l, int r, int num) {
int less = l - 1;
int more = r + 1;
while(l < more) {
if(arr[l] < num) {
swap(arr, ++less, l++);
}else if(arr[l] > num) {
swap(arr, --more, l);
}else {
l++;
}
}
return new int[] {less + 1, more -1};
}
public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
// for test
public static int[] generateArray() {
int[] arr = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 3);
}
return arr;
}
// for test
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] test = generateArray();
printArray(test);
int[] res = netherlandsFlag(test, 0, test.length - 1, 1);
printArray(test);
System.out.println(res[0]);
System.out.println(res[1]);
}
}
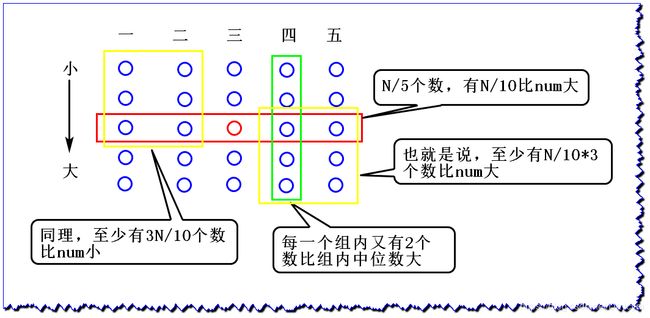
通过荷兰国旗问题将数组分为三部分:小于、等于和大于
在选择划分值num,BFPRT算法是如何进行的呢?
- (1)求 B F P R T ( a r r , k ) BFPRT(arr,k) BFPRT(arr,k) ,先对数组进行分组,相连的5个数一组,
0~4,5~9,10~14,15~19,...最后不够的单独成一组 - (2)对每组的5个数进行排序,跨组之间不排序,每组 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) 的复杂度,一共差不多 N 5 \frac{N}{5} 5N 组,此步骤时间复杂度 O ( N ) O(N) O(N)
- (3)取每个组的中位数构成新的数组,长度为 N 5 \frac{N}{5} 5N, k ′ = 长 度 / 2 + 1 k'=长度/2+1 k′=长度/2+1
- (4)递归调用BFPRT算法,传入(3)中的新数组, B F P R T ( 新 数 组 , k ′ ) BFPRT(新数组,k') BFPRT(新数组,k′),即求新数组的第 k ′ k' k′ 小的数
- (5)根据num划分
那么为什么要选这样的num值呢?
BFPRT算法复杂度(了解):
T ( N ) = T ( N 5 ) + T ( 7 N 10 ) + O ( N ) T(N)=T(\frac{N}{5})+T(\frac{7N}{10})+O(N) T(N)=T(5N)+T(107N)+O(N)
时间复杂度是 O ( N ) O(N) O(N)
Java代码:
package day07;
public class Code07_BFPRT_GetKMinNum {
//主函数
public static int[] getKMinNum(int[] arr, int k) {
//越界返回原数组
if(k < 1 || k > arr.length) {
return arr;
}
int minKth = getKthMinNum(arr, k); //获取第k小的数
int[] res = new int[k]; //结果数组,用于存储前k个小的数
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0; i != arr.length; i++) {
if(arr[i] < minKth) { //小于minKth,存入res数组
res[index++] = arr[i];
}
}
for(;index != res.length; index++) { //加入第k小的数
res[index] = minKth;
}
return res;
}
public static int getKthMinNum(int[] arr, int k) {
int[] copyArr = copyArray(arr); //数组拷贝
return bfprt(copyArr, 0, copyArr.length - 1, k - 1);
}
public static int[] copyArray(int[] arr) {
int[] res = new int[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i != res.length; i++) {
res[i] = arr[i];
}
return res;
}
public static int bfprt(int[] arr, int begin, int end, int k) {
if (begin == end) {
return arr[begin];
}
int num = medianOfMedians(arr, begin, end); //求用于划分的num值
int[] pivotRange = partition(arr, begin, end, num); //按num划分小于,等于,大于区域,返回等于区域的左右下标
if (k >= pivotRange[0] && k <= pivotRange[1]) { //第k小的数在等于区域,直接返回等于区域的值
return arr[k];
} else if (k < pivotRange[0]) { //第k小的数在小于区域,用小于区域继续递归
return bfprt(arr, begin, pivotRange[0] - 1, k);
} else {
return bfprt(arr, pivotRange[1] + 1, end, k); //第k小的数在大于区域,用大于区域继续递归
}
}
public static int medianOfMedians(int[] arr, int begin, int end) {
int num = end - begin + 1; //数的个数
int offset = num % 5 == 0 ? 0 : 1; //最后一组是否正好5个数
int[] mArr = new int[num / 5 + offset]; //组数组,用于存每组的中位数
for (int i = 0; i < mArr.length; i++) {
int beginI = begin + i * 5; //每个数组的起始下标
int endI = beginI + 4; //结束下标
mArr[i] = getMedian(arr, beginI, Math.min(end, endI)); //获取中位数存入组数组
}
return bfprt(mArr, 0, mArr.length - 1, mArr.length / 2); //中位数数组递归调用bfprt
}
//获取中位数
public static int getMedian(int[] arr, int begin, int end) {
insertionSort(arr, begin, end); //组内排序,插入排序
int sum = end + begin;
int mid = (sum / 2) + (sum % 2);
return arr[mid]; //返回中位数
}
//插入排序
public static void insertionSort(int[] arr, int begin, int end) {
for (int i = begin + 1; i != end + 1; i++) {
for (int j = i; j != begin; j--) {
if (arr[j - 1] > arr[j]) {
swap(arr, j - 1, j);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
//划分区域
public static int[] partition(int[] arr, int begin, int end, int pivotValue) {
int less = begin - 1;
int cur = begin;
int more = end + 1;
while (cur != more) {
if (arr[cur] < pivotValue) {
swap(arr, ++less, cur++);
} else if (arr[cur] > pivotValue) {
swap(arr, cur, --more);
} else {
cur++;
}
}
int[] range = new int[2];
range[0] = less + 1;
range[1] = more - 1;
return range;
}
//交换
public static void swap(int[] arr, int index1, int index2) {
int tmp = arr[index1];
arr[index1] = arr[index2];
arr[index2] = tmp;
}
//打印数组
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i != arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 6, 9, 4, 3, 1, 2, 2, 5, 6, 1, 3, 5, 9, 7, 2, 5, 6, 1, 9 };
// sorted : { 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 7, 9, 9, 9 }
printArray(getKMinNum(arr, 10));
}
}
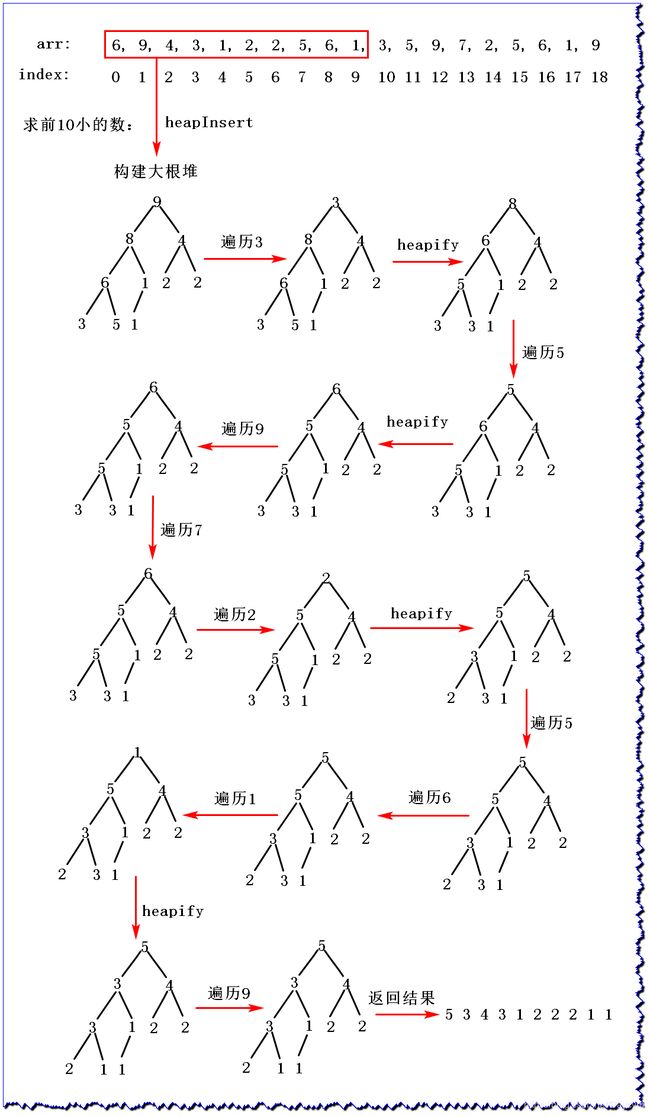
本题还可以使用堆来实现,不过时间复杂度为 O ( N l o g K ) O(NlogK) O(NlogK)
package day07;
public class Code08_Heap_GetKMinNum {
public static int[] getKMinNum(int[] arr, int k) {
//边界
if (k < 1 || k > arr.length) {
return arr;
}
int[] kHeap = new int[k]; //新建长度为k的数组
for (int i = 0; i != k; i++) { //前k个数建立大根堆
heapInsert(kHeap, arr[i], i);
}
for (int i = k; i != arr.length; i++) { //从k位置开始遍历数组
if (arr[i] < kHeap[0]) { //如果当前遍历小于堆顶,进行下沉操作
kHeap[0] = arr[i];
heapify(kHeap, 0, k);
}
}
return kHeap; //返回数组
}
//大根堆
public static void heapInsert(int[] arr, int value, int index) {
arr[index] = value;
while (index != 0) {
int parent = (index - 1) / 2; //父节点
if (arr[parent] < arr[index]) {
swap(arr, parent, index);
index = parent;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
//堆下沉操作
public static void heapify(int[] arr, int index, int heapSize) {
int left = index * 2 + 1; //当前节点的左节点
int right = index * 2 + 2; //当前节点的右节点
int largest = index; //较大的下标
while (left < heapSize) { //没到边界
if (arr[left] > arr[index]) { //如果左大于当前
largest = left; //更新较大下标
}
if (right < heapSize && arr[right] > arr[largest]) { //右大于刚才的较大值
largest = right; //较大下标更新为右
}
if (largest != index) { //如果较大的数不是当前数,进行交换
swap(arr, largest, index);
} else {
break;
}
index = largest; //当前遍历到较大数位置
left = index * 2 + 1; //更新left
right = index * 2 + 2; //更新right
}
}
public static void swap(int[] arr, int index1, int index2) {
int tmp = arr[index1];
arr[index1] = arr[index2];
arr[index2] = tmp;
}
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i != arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 6, 9, 4, 3, 1, 2, 2, 5, 6, 1, 3, 5, 9, 7, 2, 5, 6, 1, 9 };
// sorted : { 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 7, 9, 9, 9 }
printArray(getKMinNum(arr, 10));
}
}