简单LSTM代码讲解
仅供本人参考,错了概不负责
part1
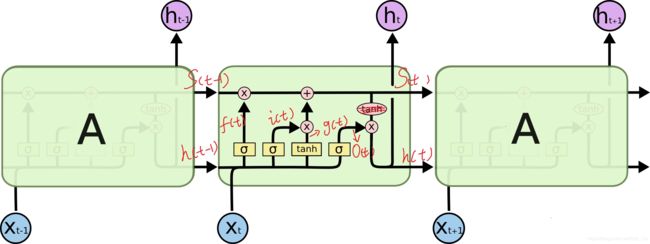
图源:https://www.zhihu.com/question/41949741/answer/309529532
我们在使用tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell时,有一个要自己设置的参数 num_units,先讲讲这玩意是啥?
这四个小黄块,有一定了解的同学都知道[ht-1, Xt]输入后,经过四个黄块和St-1,又得到了ht和St,所以必然[ht-1, Xt]经过黄块后,维度和原ht-1一样。这个num_units就是ht-1维度,那几个小黄块就是线性映射后再结激活函数。
查看BasicLSTMCell源码:
def build(self, inputs_shape):
if inputs_shape[-1] is None:
raise ValueError("Expected inputs.shape[-1] to be known, saw shape: %s"
% inputs_shape)
input_depth = inputs_shape[-1]
h_depth = self._num_units
self._kernel = self.add_variable(
_WEIGHTS_VARIABLE_NAME,
shape=[input_depth + h_depth, 4 * self._num_units])
self._bias = self.add_variable(
_BIAS_VARIABLE_NAME,
shape=[4 * self._num_units],
initializer=init_ops.zeros_initializer(dtype=self.dtype))
build函数中初始化了[input_depth + h_depth, 4 * self._num_units]形状的变量,
输入:其中
input_depth代表Xt输入的维度,h_depth也就是_num_units代表ht-1的维度;
输出:4*self._num_units为4个小黄块的维度W
并且源码并没有定义任何时间步长有关的参数,说明cell参数在不同time_step都是共享的。
part2
知道了tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell是个什么东西之后,我们来讲讲:
搭建LSTM
创建cell之后有至少两种方式创建rnn
tf.nn.dynamic_rnn
batch_size = 5
time_step = 7
depth = 30
num_units = 20
inputs = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([batch_size, time_step, depth]))
cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(num_units)
outputs, output_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, inputs, dtype=tf.float32)
# outputs1 [batch_size, time_step, num_units]
# output_state [2, batch_size, num_units]
-inputs形状为[batch_size, time_step, depth]
-outputs形状为[batch_size, time_step, num_units],每个time_step的h信息总和
当要取最后一次time_step的信息,需要tf.transpose(outputs, [1,0,2])[-1]来获得
-output_state形状为[2, batch_size, num_units],这个2,结合lstm的图
一个是
Ct(part1的St,我喜欢叫Ct),一个是ht(即最后一个时刻t的信息)
如果初始化的是GRUCell,显然就[batch_size, num_units], 没错,这个还是part1中的那个参数
tf.nn.static_rnn
inputs = tf.unstack(inputs, axis=1)
cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(20)
outputs1, output_state_fw1 = tf.nn.static_rnn(cell, inputs, dtype=tf.float32)
-inputs形状为[time_step, batch_size, depth]
-outputs形状为[time_step, batch_size, num_units],每个time_step的h信息总和
当要取最后一次time_step的信息,需要outputs[-1]来获得
-output_state_fw形状为[2, batch_size, num_units],这个2,和上面一样
tf.nn.dynamic_rnn和tf.nn.static_rnn最本质的区别还是在于每个batch中的time_step是否可以变化,tf.nn.dynamic_rnn可变;tf.nn.static_rnn所有batch的time_step都要一样.
https://www.zhihu.com/question/52200883/answer/153694449
这里更推荐tf.nn.dynamic_rnn
- 不用
tf封装的rnn,自己实现展开
这种方式在一些时候有用,如time_step很小时,for展开即可,用的少不详细讲解.
Bi-LSTM搭建:
当然至少也分tf.nn.static_bidirectional_rnn和tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn()
tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn()
batch_size = 5
time_step = 7
depth = 30
num_units = 20
inputs = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([batch_size, max_time, depth])
fw_cells = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(num_units) # 前向LSTM层
bw_cells = tf.nn.rnn_cell.GRUCell(num_units) # 后向LSTM层
outputs, (output_state_fw, output_state_bw) = tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(fw_cells, bw_cells, inputs, dtype=tf.float32)
# outputs [2, batch_size, time_step, num_units]
# output_state_fw [2, batch_size, num_units]
# output_state_bw [batch_size, num_units]
outputs和(output_state_fw, output_state_bw)以tuple方式返回
-inputs形状为[batch_size, time_step, depth]
-outputs形状为[2, batch_size, time_step, num_units],2表示fw和bw两个的输出,以tuple方式组合,使用时要output = tf.concat(output, -1)成[batch_size, time_step, 2*num_units],当要取最后一次time_step的信息,需要tf.transpose(outputs, [1,0,2])[-1]来获得
-output_state_fw形状为[2, batch_size, num_units],这个2,结合lstm的图,为fw的Ct和ht
-output_state_bw形状为[batch_size, num_units],和fw时不同,需要注意,只有bw的ht
tf.nn.static_bidirectional_rnn
inputs = tf.unstack(inputs, axis=1)
fw_cells = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(20) # LSTM层
bw_cells = tf.nn.rnn_cell.GRUCell(20) # 后向LSTM层
output, output_state_fw, output_state_bw = tf.nn.static_bidirectional_rnn(fw_cells, bw_cells, inputs, dtype=tf.float32)
# outputs [time_step, batch_size, num_units]
# output_state_fw [2, batch_size, num_units]
# output_state_bw [batch_size, num_units]
-inputs形状为[time_step, batch_size, depth]
-outputs形状为[time_step, batch_size, 2*num_units],每个time_step的h信息总和
当要取最后一次time_step的信息,需要outputs[-1]来获得
-output_state_fw形状为[2, batch_size, num_units],这个2,结合lstm的图,为fw的Ct和ht
-output_state_bw形状为[batch_size, num_units],和fw时不同,需要注意,只有bw的ht
多层的LSTM搭建:
tf.nn.dynamic_rnn
units = [10,20,30]
fw_cells = [tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(unit) for unit in units] # LSTM层
cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell(fw_cells, state_is_tuple=True)
outputs, output_state_fw = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, inputs, dtype=tf.float32)
-outputs形状为[time_step, batch_size, fw_num_units]
-output_state_fw形状为[lstm_layer_nums, 2 , batch_size, fw_num_units] (2同上)
其他的和tf.nn.dynamic_rnn一样,需要
tf.transpose(outputs, [1,0,2])[-1]获得最后一层,不同的就是tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell创建了多层而已
注意:当 fw_cells, bw_cells传入的多个layer的 num_units不同时,打印这部分信息会报错(显然)
fw_cells是多个cell组成的list
tf.nn.static_rnn同理
多层的Bi-Lstm搭建:
推荐使用(contrib),肯定的tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn也可以。
tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn
batch_size = 5
time_step = 7
depth = 64
inputs = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([batch_size, time_step, depth]))
units = [20,20,20]
fw_cells = [tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(unit) for unit in units] # LSTM层
bw_cells = [tf.nn.rnn_cell.GRUCell(unit) for unit in units] # 后向LSTM层
fw_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell(fw_cells, state_is_tuple=True)
bw_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell(bw_cells, state_is_tuple=True)
output, (output_state_fw, output_state_bw) = tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(fw_cell, bw_cell, inputs, dtype=tf.float32)
# outputs [2, batch_size, time_step, units[-1]]
# output_state_fw [2, batch_size, num_units]
# output_state_bw [batch_size, num_units]
似乎只是把之前讲的都叠加了而已,
outputs的最后一维为最后一层的lstm的num_units
注意:同理,当 fw_cells, bw_cells传入的多个layer的 num_units不同时,打印这部分信息会报错(显然)
tf.nn.static_bidirectional_rnn
inputs = tf.unstack(inputs, axis=1) #unstack的不能给dynamic_rnn当输入,服了。。。
units = [20,20,20]
fw_cells = [tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(unit) for unit in units] # LSTM层
bw_cells = [tf.nn.rnn_cell.GRUCell(unit) for unit in units] # 后向LSTM层
fw_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell(fw_cells, state_is_tuple=True)
bw_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell(bw_cells, state_is_tuple=True)
output, output_state_fw, output_state_bw = tf.nn.static_bidirectional_rnn(fw_cell, bw_cell, inputs, dtype=tf.float32)
# outputs [time_step, batch_size, fw_units[-1]+bw_units[-1]]
# output_state_fw [2, batch_size, fw_num_units]
# output_state_bw [batch_size, bw_num_units]
outputs最后一维为 前向最后一维+后向最后一维
其他的和前文讲的无差别
注意:同理,当 fw_cells, bw_cells传入的多个layer的 num_units不同时,打印这部分信息会报错(显然)
tf.contrib.rnn.stack_bidirectional_rnn
博主推荐使用的省去了部分操作
inputs = tf.unstack(inputs, axis=1) #unstack的不能给dynamic_rnn当输入,服了。。。
fw_units = [20,20,20]
bw_units = [20,20,20]
fw_cells = [tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(unit) for unit in fw_units] # 前向LSTM层
bw_cells = [tf.nn.rnn_cell.GRUCell(unit) for unit in bw_units] # 后向LSTM层
outputs, output_state_fw, output_state_bw = tf.contrib.rnn.stack_bidirectional_rnn(fw_cells, bw_cells, inputs, dtype=tf.float32)
# outputs [time_step, batch_size, fw_units[-1]+bw_units[-1]]
# output_state_fw [2, batch_size, fw_num_units]
# output_state_bw [batch_size, bw_num_units]
-inputs形状为[time_step, batch_size, depth]
-outputs形状为[time_step, batch_size, fw_num_units + bw_num_units]
-output_state_fw形状为[bi-lstm_layer_nums, 2 , batch_size, fw_num_units ] (2同上)
-output_state_bw形状为[bi-lstm_layer_nums, batch_size, bw_num_units ]
注意:同理,当 fw_cells, bw_cells传入的多个layer的 num_units不同时,打印这部分信息会报错(显然)
fw_cells是多个cell组成的list;同理于bw_cells