OpenCV4.0进阶(8)图像积分图算法
知识点:
1、概述:
在卷积操作中,如果我们想快速计算得到卷积窗口中所有元素的和或平方和,我们该怎么操作?
图像积分图算法就是一种快速计算图像区域和与平方和的算法,由Crow在1984年首次提出,目的是为了在多尺度透视投影中提高渲染速度。
目前,图像积分图在图像特征提取HAAR/SURF、二值图像分析、图像相似相关性NCC计算、图像卷积快速计算等方面均有应用,是图像处理中的经典算法之一。
2、核心思想:
通过建立每个图像自己的积分图查找表,在图像积分处理计算阶段根据预先建立的积分图查找表,直接查找从而实现对均值卷积线性时间计算,做到了卷积执行的时间与半径窗口大小的无关联。
3、图像积分图建立:
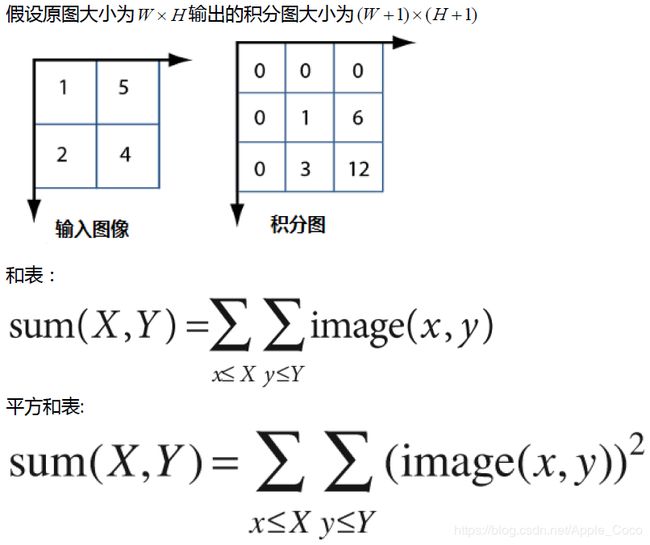
在积分图 (Integral Image - ii) 中任意位置处的值 ii(x, y) ,表示输入图像中该像素点左上角所有像素之和(包括该像素点)。文字描述太抽象?看下图解释(图片来源于贾志刚老师的OpenCV研习社,微信知识星球)
积分图中的1就是输入图像左上角的像素1、积分图中的6等于输入图像1+5两处像素点的像素值之和,同理,3=1+2,12=1+5+2+4。
这里积分图为什么会比输入图像多一行和多一列呢?是因为方便我们在积分图中直接通过下标取值来计算。
4、图像积分图查找:
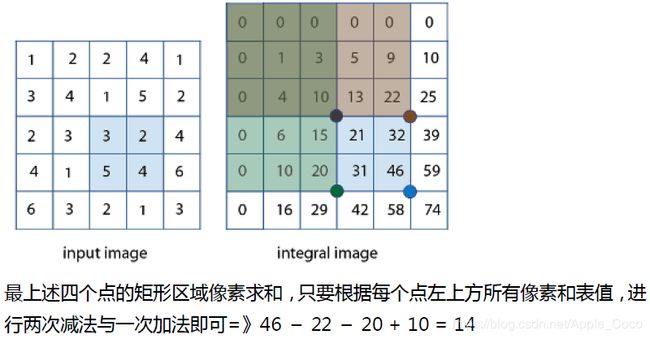
如下图所示,想快速计算3+2+5+4的和,我们该怎么做?
5、相关API:
/** @overload */
void integral( InputArray src, OutputArray sum, int sdepth = -1 );/** @overload */
void integral( InputArray src, OutputArray sum,
OutputArray sqsum, int sdepth = -1, int sqdepth = -1 );void integral( InputArray src, OutputArray sum,
OutputArray sqsum, OutputArray tilted,
int sdepth = -1, int sqdepth = -1 );前两个都是第三个的重载函数,编译器会根据你给定参数的个数和类型的不同调用不同的函数。
- src:input image as W * H, 8-bit or floating-point (32f or 64f).
- sum:integral image as (W + 1) * (H + 1), 32-bit integer or floating-point (32f or 64f).
- sqsum:integral image for squared pixel values; it is (W+1) * (H+1), double-precision floating-point (64f) array.
- tilted:对旋转45度的图像进行倾斜积分;它是(W+1) * (H+1)数组,数据类型与sum相同。
- sdepth:desired depth of the integral and the tilted integral images, CV_32S, CV_32F, or CV_64F.
- sqdepth:desired depth of the integral image of squared pixel values, CV_32F or CV_64F.
代码演示:
#ifndef DAY28
#define DAY28
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void blur_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum);
int getblockSum(Mat &sum, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int i);
void day28() {
Mat src = imread("G:/opencvTest/flower.jpg");
if (src.empty()) {
printf("could not load image...\n");
return;
}
namedWindow("input", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("input", src);
namedWindow("output", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
// 计算积分图
Mat sum, sqrsum;
integral(src, sum, sqrsum, CV_32S, CV_32F);
cout << "src.size: " << src.size() << endl;
cout << "sum.size: " << sum.size() << endl;
// 积分图应用,利用积分图实现均值模糊
blur_demo(src, sum);
waitKey();
}
// 积分图应用,利用积分图实现均值模糊
void blur_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum) {
int w = image.cols;
int h = image.rows;
int ch = image.channels();
Mat result = Mat::zeros(image.size(), image.type());
int x2 = 0, y2 = 0;
int x1 = 0, y1 = 0;
int ksize = 5; // 定义卷积窗口大小为5
int radius = ksize / 2; // 定义卷积窗口半径
int cx = 0, cy = 0; // 定义卷积窗口中心点坐标
for (int row = 0; row < h + radius; row++) {
// 越界保护
y2 = (row + 1) > h ? h : (row + 1);
y1 = (row - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (row - ksize);
for (int col = 0; col < w + radius; col++) {
// 越界保护
x2 = (col + 1) > w ? w : (col + 1);
x1 = (col - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (col - ksize);
cx = (col - radius) < 0 ? 0 : col - radius;
cy = (row - radius) < 0 ? 0 : row - radius;
int num = (x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1);
// 遍历BGR3通道
for (int i = 0; i < ch; i++) {
// 查找积分图和表,计算卷积
int s = getblockSum(sum, x1, y1, x2, y2, i);
result.at(cy, cx)[i] = saturate_cast(s / num);
}
}
}
imshow("output", result);
}
// 查找积分图和表
int getblockSum(Mat &sum, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int i) {
int tl = sum.at(y1, x1)[i];
int tr = sum.at(y2, x1)[i];
int bl = sum.at(y1, x2)[i];
int br = sum.at(y2, x2)[i];
int s = (br - bl - tr + tl);
return s;
}
#endif // !DAY28