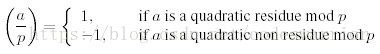Jacobi symbol(二次剩余+欧拉准则)
Jacobi symbol
Consider a prime number p and an integer a !≡ 0 (mod p). Then a is called a quadratic residue mod p if there is an integer x such that x 2 ≡ a (mod p), and a quadratic non residue otherwise. Lagrange introduced the following notation, called the Legendre symbol, L (a,p):
For the calculation of these symbol there are the following rules, valid only for distinct odd prime numbers p, q and integers a, b not divisible by p:
The Jacobi symbol, J (a, n) ,is a generalization of the Legendre symbol ,L (a, p).It defines as :
1. J (a, n) is only defined when n is an odd.
2. J (0, n) = 0.
3. If n is a prime number, J (a, n) = L(a, n).
4. If n is not a prime number, J (a, n) = J (a, p1) J (a, p2)… J (a, pm), p1…pm is the prime factor of n. Input
Two integer a and n, 2 < a< =10 6,2 < n < =10 6,n is an odd number.
Output
Output J (a,n)
Sample Input
3 5
3 9
3 13
Sample Output
-1
0
1
题意:
求J(a,n)
分析:二次剩余,欧拉准则!
在数论中,特别在同余理论裏,一个整数 X X 对另一个整数 p p 的二次剩余(英语:Quadratic residue)指 X X 的平方 X2 X 2 除以 p p 得到的余数。
当对于某个 d及某个X,式子X2≡d(modp)成立时,称“d是模p d 及 某 个 X , 式 子 X 2 ≡ d ( mod p ) 成 立 时 , 称 “ d 是 模 p 的二次剩余”
当对于某个 d及某个X,X2≡d(modp)不成立时,称“d是模p d 及 某 个 X , X 2 ≡ d ( mod p ) 不 成 立 时 , 称 “ d 是 模 p 的二次非剩余”
欧拉准则:
若p是奇质数且p不能整除d,则:
d是模p的二次剩余当且仅当:
dp−12≡1(modp) d p − 1 2 ≡ 1 ( mod p )d是模p的非二次剩余当且仅当:
dp−12≡−1(modp) d p − 1 2 ≡ − 1 ( mod p )以勒让德符号表示,即为:
dp−12≡(dp)(modp) d p − 1 2 ≡ ( d p ) ( mod p )
算是个求一个数是否是二次剩余的模板吧
code:
#include