https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41552508/article/details/100556943附上学习连接
以防万一还是搬出来吧
一、适用问题
莫队算法是一种离线算法,用分块去优化暴力,不包含修改的话,复杂度为 0的二分之三。
莫队的算法是不断扩大区间的。
三、普通莫队习题
1. [2009国家集训队] 小Z的袜子
题意: n nn 双颜色不同袜子,m mm 次询问,每次询问给出 [L,R] [L,R][L,R] 区间,询问在 [L,R] [L,R][L,R] 区间中随机抽出两双颜色相同的袜子的概率,输出最简分数形式 (A/B) (A/B)(A/B)。
我们所记录的是x双同色袜子的组合方案数所以我们除以他的区间内袜子的c(n,2)就是答案了
分析到这里,就可以发现这是一道普通莫队的裸题,我们添加与删除时只需加上或减去当前与该点颜色相同的袜子数,这样同时可以避免重复计算。
代码:
#include
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2*1e5+100;
using namespace std;
int a[N],pos[N],n,m,L,R;
ll ans[N][2],flag[N],Ans;
struct Node{
int l,r,id;
bool operator < (Node xx) const{
if(pos[l] == pos[xx.l]) return r < xx.r;
else return pos[l] < pos[xx.l];
}
}Q[N];
ll gcd(ll a,ll b) {return b == 0 ? a:gcd(b,a%b);}
void add(int x){
Ans += flag[a[x]];
flag[a[x]]++;
}
void del(int x){
flag[a[x]]--;
Ans -= flag[a[x]];
}
int main()
{
L = 1, R = 0;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
int sz = sqrt(n);
rep(i,1,n){
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
pos[i] = i/sz;
}
rep(i,1,m){
scanf("%d%d",&Q[i].l,&Q[i].r);
Q[i].id = i;
}
sort(Q+1,Q+1+m);
rep(i,1,m){
while(L < Q[i].l) del(L),L++;
while(L > Q[i].l) L--, add(L);
while(R < Q[i].r) R++, add(R);
while(R > Q[i].r) del(R), R--;
ll len = Q[i].r-Q[i].l+1;
ll tp = len*(len-1ll)/(ll)2;
ll g = gcd(Ans,tp);
ans[Q[i].id][0] = Ans/g;
ans[Q[i].id][1] = tp/g;
}
rep(i,1,m) printf("%lld/%lld\n",ans[i][0],ans[i][1]);
return 0;
}
2. 花神的嘲讽计划Ⅰ
题意: 初始序列长度为 n nn,m mm 组询问,每次询问给出一个 x xx、y yy,以及长度为 k kk 的连续序列。询问在区间 [x,y] [x,y][x,y] 中是否存在一段连续的长度为 k kk 的,与询问中给出的序列相同的一段序列。存在输出 No NoNo,不存在输出 Yes YesYes。(1≤n,m≤106) (1\leq n,m\leq 10^6)(1≤n,m≤10
6
)
思路: 这题可以观察到每次询问的连续序列长度都是固定为 k kk,因此不难想到用 hash hashhash 来解决这个问题。我们将每个位置后面连续的一段 k kk 哈希起来,然后每个位置就有了一个对应的 hash hashhash 值。我们将这些 hash hashhash 值离散化之后,用桶来记录区间端点移动时对答案的贡献。
代码:
#include
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2*1e6+100;
const ll mod = 1e11+7;
using namespace std;
int n,m,k,L,R,flag[N],tot,ans[N],pos[N],pp[N];
ll a[N],b[N],ha[N];
struct Node{
int l,r,id;
ll w;
bool operator < (Node xx) const {
if(pos[l] != pos[xx.l]) return pos[l] < pos[xx.l];
else return r < xx.r;
}
}q[N];
int find(ll x){
return lower_bound(b+1,b+1+tot,x)-b;
}
ll Hash(int pos){
ll tp = 0;
ll base = 1;
rep(i,pos,pos+k-1){
tp = (tp+a[i]*base)%mod;
if(tp < 0) tp = (tp+mod)%mod;
base = (base*(ll)133)%mod;
if(base < 0) base = (base+mod)%mod;
}
return tp;
}
void add(int x) {flag[pp[x]]++;}
void del(int x) {flag[pp[x]]--;}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k);
rep(i,1,n) scanf("%lld",&a[i]);
rep(i,1,m){
int xx,yy; scanf("%d%d",&xx,&yy);
q[i].l = xx, q[i].r = yy, q[i].id = i;
q[i].r = q[i].r-k+1;
ll tp = 0;
ll base = 1;
rep(j,1,k){
ll hp; scanf("%lld",&hp);
tp = (tp+hp*base)%mod;
if(tp < 0) tp = (tp+mod)%mod;
base = (base*(ll)133)%mod;
if(base < 0) base = (base+mod)%mod;
}
q[i].w = tp;
b[++tot] = tp;
}
rep(i,1,n-k+1){
ll tp = Hash(i);
ha[i] = tp;
b[++tot] = tp;
}
sort(b+1,b+1+tot);
tot = unique(b+1,b+1+tot)-b-1;
rep(i,1,n-k+1){
pp[i] = find(ha[i]);
}
int sz = sqrt(n);
rep(i,1,n) pos[i] = i/sz;
sort(q+1,q+1+m);
L = 1, R = 0;
rep(i,1,m){
while(L < q[i].l) del(L), L++;
while(L > q[i].l) L--, add(L);
while(R < q[i].r) R++, add(R);
while(R > q[i].r) del(R), R--;
int pos = find(q[i].w);
if(flag[pos]) ans[q[i].id] = 1;
else ans[q[i].id] = 0;
}
rep(i,1,m){
if(ans[i]) printf("No\n");
else printf("Yes\n");
}
return 0;
}
3. XOR and Favorite Number
思路: 既然是某一区间的异或和,不难想到先求一个异或前缀和,然后对于一个 j jj 来说,就是询问区间 [l,r] 中有多少个 i i 满足 sum[i−1] ^ sum[j]=k。
问题拆解到这一步,剩下的问题就比较明了了,直接上莫队,然后用桶维护每一个数的异或前缀和即可。
代码:
#include
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2*1e6+100;
using namespace std;
int a[N],pos[N],n,m,k,L,R;
ll ans[N],flag[N],Ans;
struct Node{
int l,r,id;
bool operator < (Node xx) const{
if(pos[l] == pos[xx.l]) return r < xx.r;
else return pos[l] < pos[xx.l];
}
}Q[N];
void add(int x){
Ans += flag[a[x]^k];
flag[a[x]]++;
}
void del(int x){
flag[a[x]]--;
Ans -= flag[a[x]^k];
}
int main()
{
L = 1, R = 0;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k);
int sz = sqrt(n);
rep(i,1,n){
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
a[i] = a[i]^a[i-1];
pos[i] = i/sz;
}
rep(i,1,m){
scanf("%d%d",&Q[i].l,&Q[i].r);
Q[i].id = i;
}
sort(Q+1,Q+1+m);
flag[0] = 1;
rep(i,1,m){
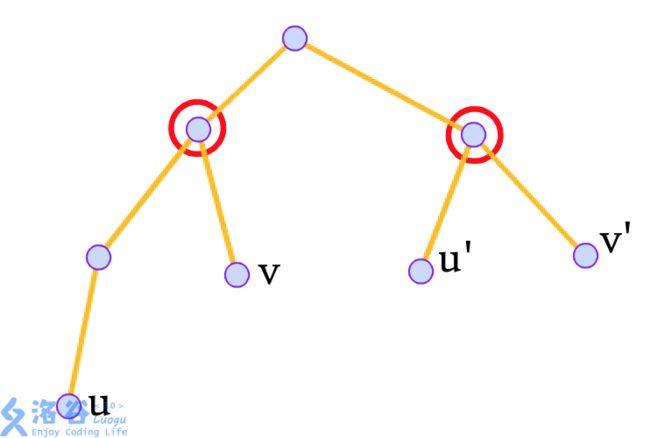
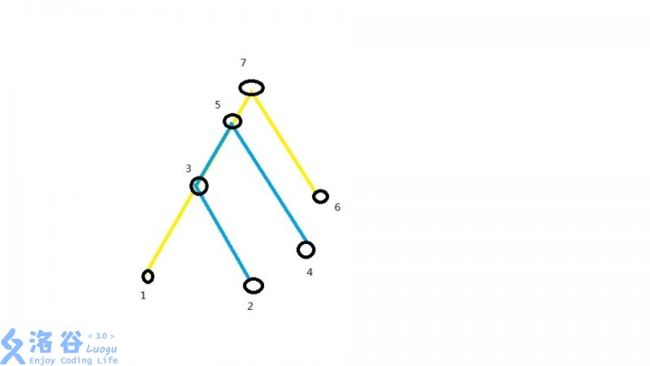
while(L while(L>Q[i].l) L--, add(L-1); while(R while(R>Q[i].r) del(R), R--; ans[Q[i].id] = Ans; } rep(i,1,m) printf("%lld\n",ans[i]); return 0; } 4. 问区间里有多少对i,j满足i 由于 n nn 和 m mm 的范围比较小,可以考虑使用莫队分块算法,在加入和删除的地方使用树状数组统计答案即可。 代码: #include #define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof a); #define rep(i,a,b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++) #define per(i,a,b) for(int i = a; i >= b; i--) #define __ ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0) typedef long long ll; typedef double db; const int N = 27000+100; const db EPS = 1e-9; using namespace std; void dbg() {cout << "\n";} template #define logs(x...) {cout << #x << " -> "; dbg(x);} int n,m,k,a[N],b[3*N],tot,L,R,pos[N],now[N][3]; struct Node{ int l,r,id; bool operator < (Node xx) const { if(pos[l] == pos[xx.l]) return r < xx.r; else return pos[l] < pos[xx.l]; } }q[N]; ll c[3*N],ans[N],Ans; inline int lowbit(int x) {return x&(~x+1);} inline void update(int x,ll v) {for(;x<=tot;x+=lowbit(x)) c[x]+=v;} inline ll ask(int x){ ll tp = 0; while(x) tp += c[x], x -= lowbit(x); return tp; } int find(int x){ return lower_bound(b+1,b+1+tot,x)-b; } void add(int x){ int p1 = now[x][1], p2 = now[x][2]; Ans += ask(p1)-ask(p2); update(now[x][0],1); } void del(int x){ update(now[x][0],-1); int p1 = now[x][1], p2 = now[x][2]; Ans -= ask(p1)-ask(p2); } int main() { L = 1, R = 0; scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k); int sz = sqrt(n); rep(i,1,n){ scanf("%d",&a[i]); b[++tot] = a[i]; b[++tot] = a[i]+k; b[++tot] = a[i]-k-1; pos[i] = i/sz; } sort(b+1,b+1+tot); tot = unique(b+1,b+1+tot)-b-1; rep(i,1,n){ now[i][0] = find(a[i]); now[i][1] = find(a[i]+k); now[i][2] = find(a[i]-k-1); } rep(i,1,m){ scanf("%d%d",&q[i].l,&q[i].r); q[i].id = i; } sort(q+1,q+1+m); rep(i,1,m){ while(L < q[i].l){ del(L); L++; } while(L > q[i].l){ L--; add(L); } while(R < q[i].r){ R++; add(R); } while(R > q[i].r){ del(R); R--; } ans[q[i].id] = Ans; } rep(i,1,m) printf("%lld\n",ans[i]); return 0; } 5莫队求组合数前缀和 求C(n,0)+C(n,1)+C(n,2)+.....+C(n,m); 设S(n,m)=C(n,0)+C(n,1)+C(n,2)+.....+C(n,m); 第一个式子易得,第二个式子:杨辉三角的c n,m=c(n-1,m)+c(n-1,m-1),利用这个我们来推出s(n,m)就有上面那样公式 那么就是这一行等于上一行的都用了2次,只有第最后一个用了一次 所以减去c(n-1,m) 当我们按上述步骤把uu移到u'u′,vv移到v'v′时,奇怪的事情出现了: 还有就是我们在看下图 我们当前处理出来的是询问(1,6)的答案,也就是这条黄色路径 我们下一个要求的是蓝色路径(2,4)的答案 这种情况下我们发现,其实每次增加的就是lca(1,2)到2,以及lca(4,6)到4的那些节点 同时lca(1,2)到1,以及lca(4,6)到6的路径上的节点要去掉 诶? 那岂不是可以求出两个lca,然后把这两对点路径上除了lca的点的状态都反过来就可以了? 是的就是这样,上代码 普通莫队最重要的辨别点在于可以 O(1) 的增加或删除节点,而回滚莫队的关键点在于只能 O(1) O(1)O(1) 的增加或者删除节点,增加或删除只能二者选其一。 例如 历史研究这道题(增加节点的) 考虑一般莫队,复杂度是 那怎么办呢,要是l是每次递减的就好了,人为制造扩大区间把缩小区间弄掉 如果r在块外,l在块内, 例如 ---|---L------|-----R----- 这样,r每次递增那就不管他和原来的莫队一样就行 l每次设置在下一块的开始位置,如下图 ---|---L------|-----R----- ---|---L-----|^-----r----- ^是l的位置 这样每次l都是向块内移动的r每次都是向右移动的,就保证了区间的递增性 如果L和R都是在同一个块内怎么办,, for暴力计算!!!! 观察l,每次移动到应该查询的位置(L),然后计算完答案后,再移动回去(下一块的开始位置) 这样,就是回滚莫队 了,可以明显看到l是滚来~滚去~的 这道题和上面的增加区间相反,这道题是减少区间,你想想那个mex,肯定是区间减少可以o(1)更新答案,增大反而不行嘛 所以 不难发现,对于这个问题来说,删除节点可以 O(1) O(1)O(1) 的更新答案,但是增加节点后答案的变化难以确定,因此考虑采用删除节点形式的回滚莫队来解决这个问题。 删除节点的回滚莫队,就是区间长度不断缩小的情况。因此我们需要对每个查询的左端点所在块编号进行升序,对每个查询的右端点进行降序,这样可以保证右端点是不断递减的。 然后对于左右端点在同一个块中的情况,我们依然是暴力求取答案。而对于不在同一块中的情况,我们需要每次查询结束后都将左端点移动到查询左端点所在的块的左边界上,这样才能保证区间长度在不断缩小。 除了上述这些回滚莫队的共性点之外,我们还需要关注一些特性点。对于这个问题,我们需要在最开始将左右边界分别设置为 1 11 和 n ,这样的目的是保证区间长度是不断递减的。然后求取答案时,我们需要维护两部分答案,一部分是区间 [l,r]中完全包含左端点所在块的部分的答案,另一部分即为当前查询的结果。 保存第一部分答案的目的在于增加节点是不能 O(1) O(1)O(1) 维护答案的,因此左端点递增之后答案就会变化而且不能恢复,所以如果不保存第一部分的答案是不能直接继承到下一个查询的,具体细节看代码就能够理解。 Chika and Friendly Pairs
Harvest of Apples
![]()
#include
#include
#include
#include
using
namespace
std;
const
int
mod=1e9+7;
#define ll long long
const
int
maxn=1e5+7;
ll jiecheng[maxn],inv[maxn];
ll ans[maxn];
int
block;
ll qsm(ll a,ll b)
{
ll ans=1;
while
(b){
if
(b&1)
ans=ans*a%mod;
a=a*a%mod;
b>>=1;
}
return
ans;
}
void
init()
{
jiecheng[1] = 1;
for
(
int
i = 2; i < maxn; i++)
jiecheng[i] = jiecheng[i-1] * i % mod;
for
(
int
i = 1; i < maxn; i++)
inv[i] = qsm(jiecheng[i], mod-2);
}
struct
node{
int
l,r;
int
i;
}modui[maxn];
bool
cmp(node a,node b)
{
if
(a.l/block==b.l/block)
return
a.r
return
a.l}
ll C(ll n,ll m)
{
if
(m == 0 || m == n)
return
1;
ll ans=1;
ans=(jiecheng[n]*inv[m])%mod*inv[n-m];
ans=ans%mod;
return
ans;
}
int
main()
{
init();
block = sqrt(maxn);
int
t;
scanf(
"%d"
,&t);
for
(
int
i=0;i
{
scanf(
"%d%d"
,&modui[i].l,&modui[i].r);
modui[i].i=i;
}
sort(modui,modui+t,cmp);
int
l=1,r=0;
int
sum=1;
for
(
int
i = 0; i < t; i++)
{
while
(l < modui[i].l) sum = (2 * sum - C(l++, r) + mod) % mod;
while
(l > modui[i].l) sum = ((sum + C(--l, r))*inv[2]) % mod;
while
(r < modui[i].r) sum = (sum + C(l, ++r)) % mod;
while
(r > modui[i].r) sum = (sum - C(l, r--) + mod) % mod;
ans[modui[i].i] = sum;
}
for
(
int
i=0;i
{
printf(
"%lld\n"
,ans[i]);
}
return
0;
}
~~~待修改莫队
1. Machine Learning
思路: 这个问题唯一的操作难点在于 mex mexmex 函数的求取,其实我们可以像求取 SG SGSG 函数的 mex mexmex 一样,直接暴力求取即可。然后其余部分就是常规的带修改莫队的操作了。#include
祖先,也就是被圈红的那两个点都被标记了两次,也就是说标记状态没有改变。
那这好办,最后再更新一下这两个节点,轻松解决问题。#include
回滚莫队!!!
首先先说回滚莫队用来解决什么问题,
————————————————![]() ,但是这题要求区间最值,那,要维护区间最值的话,只能是再套个其他的数据结构,复杂度就变成了
,但是这题要求区间最值,那,要维护区间最值的话,只能是再套个其他的数据结构,复杂度就变成了![]() ,没法再优化。我们可以想到一个区间更新最大值如果他的区间是扩大的,那我们可以o(1)更新这个最大值对吧例如一个区间找到最大值是x,现在扩大区间我们只需要把x和新元素进行比较就行,但是缩小的话我们就没办法了
,没法再优化。我们可以想到一个区间更新最大值如果他的区间是扩大的,那我们可以o(1)更新这个最大值对吧例如一个区间找到最大值是x,现在扩大区间我们只需要把x和新元素进行比较就行,但是缩小的话我们就没办法了#include
Rmq Problem / mex(删除节点的)
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「Gene_INNOCENT」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41552508/article/details/100556943#include