目录
- Proto文件
- 序列化
- 二进制文件解析
- 反序列化
- 参考
博客:blog.shinelee.me | 博客园 | CSDN
这篇文章中,我们将定义一个相对复杂的数据结构,直接分析其序列化后的二进制文件。
Proto文件
编写addressbook.proto文件,在官方例子上略作修改,增加了float字段,以分析浮点数的存储方式。
syntax = "proto2";
package tutorial;
message Person {
required string name = 1;
required int32 id = 2;
optional string email = 3;
enum PhoneType {
MOBILE = 0;
HOME = 1;
WORK = 2;
}
message PhoneNumber {
required string number = 1;
optional PhoneType type = 2 [default = HOME];
}
repeated PhoneNumber phones = 4;
repeated float weight_recent_months = 100 [packed = true];
}
message AddressBook {
repeated Person people = 1;
}生成编解码文件,addressbook.pb.cc和addressbook.pb.h。
protoc.exe addressbook.proto --cpp_out=.序列化
编写如下代码,将address_book对象序列化,保存到二进制文件address_book.bin。
int main()
{
tutorial::AddressBook address_book;
tutorial::Person* person = address_book.add_people();
person->set_id(1);
person->set_name("Jack");
person->set_email("[email protected]");
tutorial::Person::PhoneNumber* phone_number = person->add_phones();
phone_number->set_number("123456");
phone_number->set_type(tutorial::Person::HOME);
phone_number = person->add_phones();
phone_number->set_number("234567");
phone_number->set_type(tutorial::Person::MOBILE);
person->add_weight_recent_months(50);
person->add_weight_recent_months(52);
person->add_weight_recent_months(54);
fstream fw("./address_book.bin", ios::out | ios::binary);
address_book.SerializePartialToOstream(&fw);
fw.close();
return 0;
}二进制文件address_book.bin一共有62个字节,内容如下:
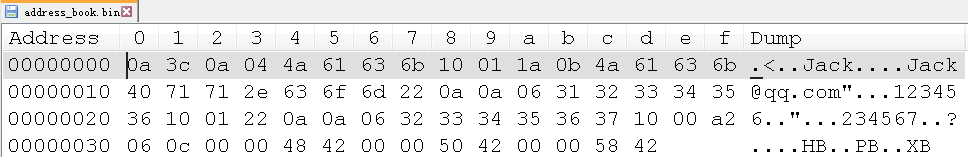
二进制文件解析
由前面的文章,每个field的key = (field_number << 3) | wire_type都通过varint表示。
message Addressbook的第一个字段为Person people,Person也是一个message,下面逐个字节地进行解析。
0a // (1 << 3) + 2,1为people的field_bumber,2为embedded message对应的wire type
3c // 0x3c = 60,表示接下来60个字节为Person people的数据
// 下面进入到 message Person
0a // (1 << 3) + 2,Person的第一个字段name field_number=1,2为string对应的wire type
04 // name字段的字符串长度为4
4a 61 63 6b // "Jack" 的ascii编码
10 // (2 << 3) + 0,字段id field_number=2,0为int32对应的wire type
01 // id为1
1a // (3 << 3) + 2,字段email field_number=3,2为string对应的wire type
0b // 0x0b = 11 email字段的字符串长度为11
4a 61 63 6b 40 71 71 2e 63 6f 6d // "[email protected]"
//第1个PhoneNumber,嵌套message
22 // (4 << 3) + 2,,phones字段,field_number=4,2为embedded message对应的wire type
0a // 接下来10个字节为PhoneNumber的数据
0a // (1 << 3) + 2, message PhoneNumber的第一个字段number,2为string对应的wire type
06 // number字段的字符串长度为6
31 32 33 34 35 36 // "123456"
10 // (2 << 3) + 0,PhoneType type字段,0为enum对应的wire type
01 // HOME,enum被视为整数
// 第2个PhoneNumber,嵌套message
22 0a 0a 06 32 33 34 35 36 37 10 00 //信息解读同上,最后的00为MOBILE
a2 06 // 1010 0010 0000 0110 varint方式,weight_recent_months的key
// 010 0010 000 0110 → 000 0110 0100 010 little-endian存储
// (100 << 3) + 2,100为weight_recent_months的field number
// 2为 packed repeated field的wire type
0c // 后面12个字节为packed float的数据,每4个字节一个
00 00 48 42 // float 50
00 00 50 42 // float 52
00 00 58 42 // float 54需要注意的是,repeated后面接的字段如果是个message,比如上面的PhoneNumber,有几个PhoneNumber,编码时其key就会出现几次;如果接的是数值型的字段,且以packed = true压缩存储时,只会出现1个key,如果不以压缩方式存储,其key也会出现多次,在proto3中,默认以压缩方式进行存储,proto2中则需要显式地声明。
至此,二进制文件已经分析完毕,现在再去看解码代码,就so easy了。
反序列化
这里只贴上message Person对应的解码代码,可以看到其中遇到嵌套message PhoneNumber时,会去调用PhoneNumber的解码代码。
bool Person::MergePartialFromCodedStream(
::google::protobuf::io::CodedInputStream* input) {
#define DO_(EXPRESSION) if (!PROTOBUF_PREDICT_TRUE(EXPRESSION)) goto failure
::google::protobuf::uint32 tag;
// @@protoc_insertion_point(parse_start:tutorial.Person)
for (;;) {
::std::pair<::google::protobuf::uint32, bool> p = input->ReadTagWithCutoffNoLastTag(16383u);
tag = p.first;
if (!p.second) goto handle_unusual;
switch (::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormatLite::GetTagFieldNumber(tag)) {
// required string name = 1;
case 1: {
if (static_cast< ::google::protobuf::uint8>(tag) == (10 & 0xFF)) {
DO_(::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormatLite::ReadString(
input, this->mutable_name()));
::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormat::VerifyUTF8StringNamedField(
this->name().data(), static_cast(this->name().length()),
::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormat::PARSE,
"tutorial.Person.name");
} else {
goto handle_unusual;
}
break;
}
// required int32 id = 2;
case 2: {
if (static_cast< ::google::protobuf::uint8>(tag) == (16 & 0xFF)) {
HasBitSetters::set_has_id(this);
DO_((::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormatLite::ReadPrimitive<
::google::protobuf::int32, ::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormatLite::TYPE_INT32>(
input, &id_)));
} else {
goto handle_unusual;
}
break;
}
// optional string email = 3;
case 3: {
if (static_cast< ::google::protobuf::uint8>(tag) == (26 & 0xFF)) {
DO_(::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormatLite::ReadString(
input, this->mutable_email()));
::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormat::VerifyUTF8StringNamedField(
this->email().data(), static_cast(this->email().length()),
::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormat::PARSE,
"tutorial.Person.email");
} else {
goto handle_unusual;
}
break;
}
// repeated .tutorial.Person.PhoneNumber phones = 4;
case 4: {
if (static_cast< ::google::protobuf::uint8>(tag) == (34 & 0xFF)) {
DO_(::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormatLite::ReadMessage(
input, add_phones()));
} else {
goto handle_unusual;
}
break;
}
// repeated float weight_recent_months = 100 [packed = true];
case 100: {
if (static_cast< ::google::protobuf::uint8>(tag) == (802 & 0xFF)) {
DO_((::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormatLite::ReadPackedPrimitive<
float, ::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormatLite::TYPE_FLOAT>(
input, this->mutable_weight_recent_months())));
} else if (static_cast< ::google::protobuf::uint8>(tag) == (805 & 0xFF)) {
DO_((::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormatLite::ReadRepeatedPrimitiveNoInline<
float, ::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormatLite::TYPE_FLOAT>(
2, 802u, input, this->mutable_weight_recent_months())));
} else {
goto handle_unusual;
}
break;
}
default: {
handle_unusual:
if (tag == 0) {
goto success;
}
DO_(::google::protobuf::internal::WireFormat::SkipField(
input, tag, _internal_metadata_.mutable_unknown_fields()));
break;
}
}
}
success:
// @@protoc_insertion_point(parse_success:tutorial.Person)
return true;
failure:
// @@protoc_insertion_point(parse_failure:tutorial.Person)
return false;
#undef DO_
} 以上。
参考
- Protocol Buffer Basics: C++