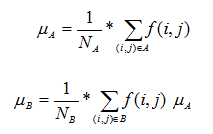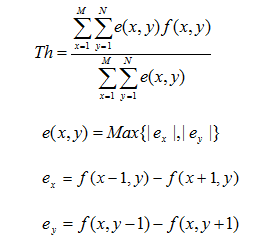图像基本变换---图像二值化(包含OSTU/迭代法/统计法/双峰法/P分位法/最大熵法)
OSTU法图像二值化
[算法说明]
Ostu法又叫做最大类间方差法,是一种常用的图像分割算法。基本算法思想是根据初始阈值把图像分为两类,然后计算两类之间的方差,更新阈值,重新计算类间方差,当满足类间方差最大时的阈值,即为所求最佳阈值,具体过程如下:
1,初始化一阈值Th,将图像f(x,y)分为A,B两类;
2,分别计算A,B两类像素集合的均值ua和ub,公式如下:
其中,Na和Nb分别表示集合A,B中的像素个数。
3,计算A,B两类的类间方差,公式如下:
4,将Th从0到255循环,分别计算A,B的类间方差,当类间方差最大时,对应的Th即为所求的最佳分割或二值化的阈值。
[函数代码]
///
/// Ostu method of image segmention.
///
/// The source image.
///
public static WriteableBitmap OstuThSegment(WriteableBitmap src) ////Ostu法阈值分割
{
if (src != null)
{
int w = src.PixelWidth;
int h = src.PixelHeight;
WriteableBitmap dstImage = new WriteableBitmap(w, h);
byte[] temp = src.PixelBuffer.ToArray();
byte[] tempMask = (byte[])temp.Clone();
//定义灰度图像信息存储变量
int[] srcData = new int[w * h];
//定义阈值变量
int Th = 0; ;
//定义背景和目标像素数目变量N1,N2,灰度变量U1,U2,灰度和变量Sum1,Sum2,临时缓存变量Temp
int N1 = 0, N2 = 0, Sum1 = 0, Sum2 = 0;
//定义背景和目标像素比例变量W1,W2,图像整体平均灰度变量U,方差变量g,对比阈值变量TT
double W1 = 0, W2 = 0, U1 = 0, U2 = 0, g = 0, TT = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < h; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++)
{
srcData[i + j * w] = (int)((double)tempMask[i * 4 + j * w * 4] * 0.114 + (double)tempMask[i * 4 + 1 + j * w * 4] * 0.587 + (double)tempMask[i * 4 + 2 + j * w * 4] * 0.299);
}
}
//寻找最大类间方差
for (int T = 0; T <= 255; T++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < srcData.Length; i++)
{
if (srcData[i] > T)
{
N2++;
Sum2 += srcData[i];
}
else
{
N1++;
Sum1 += srcData[i];
}
}
W1 = (double)(N1 / (N1 + N2));
W2 = (double)(1.0 - W1);
U1 = (N1 == 0 ? 0.0 : (Sum1 / N1));
U2 = (N2 == 0 ? 0.0 : (Sum2 / N2));
g = N1 * N2 * (U1 - U2) * (U1 - U2);
if (g > TT)
{
TT = g;
Th = T;
}
N1 = 0; N2 = 0;
Sum1 = 0; Sum2 = 0; W1 = 0.0; W2 = 0.0; U1 = 0.0; U2 = 0.0; g = 0.0;
}
for (int j = 0; j < h; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++)
{
temp[i * 4 + j * w * 4] = temp[i * 4 + 1 + j * w * 4] = temp[i * 4 + 2 + j * w * 4] = (byte)(srcData[i + j * w] < Th ? 0 : 255);
}
}
Stream sTemp = dstImage.PixelBuffer.AsStream();
sTemp.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
sTemp.Write(temp, 0, w * 4 * h);
return dstImage;
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
[图像效果]
Fig.1原图 Fig.2效果图
迭代法图像二值化
[算法说明]
迭代法图像二值化的算法思想是:首先,初始化一个阈值Th,然后按照某种策略通过迭代不断更新这一阈值,直到满足给定的约束条件为止,步骤如下:
1,对于一幅图像,假设当前像素为f(x,y),设定一阈值Th,跟据当前阈值,循环f(x,y),将图像分为两类像素的集合A,B;
2,分别计算A,B集合的像素均值ua和ub,公式如下:
其中,Na和Nb分别表示集合A,B中的像素个数。
3,更新阈值:
4,判断当前计算阈值与上次计算阈值的差值是否满足约束条件,即两次阈值差值小于一约束值T,若小于,则当前阈值Th即为所求最佳阈值,否则,转至步骤2。
[函数代码]
///
/// Iterative method of image segmention.
///
/// The source image.
///
public static WriteableBitmap IterativeThSegment(WriteableBitmap src) ////迭代法阈值分割
{
if (src != null)
{
int w = src.PixelWidth;
int h = src.PixelHeight;
WriteableBitmap dstImage = new WriteableBitmap(w, h);
byte[] temp = src.PixelBuffer.ToArray();
byte[] tempMask = (byte[])temp.Clone();
//定义灰度图像信息存储变量
int[] srcData = new int[w * h];
//定义背景和目标像素个数变量C1,C2,总体灰度和变量sum
int C1 = 0, C2 = 0, sum = 0;
//定义背景和目标的灰度和变量G1,G2,前后两次灰度均值变量t0,t
double G1 = 0, G2 = 0, t0 = 256, t = 0;
//定义阈值变量
int Th = 0;
//定义循环控制变量
bool s = true;
for(int j=0;j { for(int i=0;i { srcData[i + j * w] = (int)((double)tempMask[i * 4 + j * w * 4] * 0.114 + (double)tempMask[i * 4 + 1 + j * w * 4] * 0.587 + (double)tempMask[i * 4 + 2 + j * w * 4]*0.299); sum += srcData[i + j * w]; } } //初始化阈值 Th = sum / (w*h); while (s) { for (int i = 0; i < srcData.Length; i++) { if (srcData[i] < Th) { C1++; G1 += srcData[i]; } else { C2++; G2 += srcData[i]; } } t = (double)((G1 / C1 + G2 / C2) / 2); if (Math.Abs(t - t0) < 1) { s = false; for (int j = 0; j < h; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) { temp[i * 4 + j * w * 4] = temp[i * 4 + 1 + j * w * 4] = temp[i * 4 + 2 + j * w * 4] = (byte)(srcData[i + j * w] < Th ? 0 : 255); } } } else { t0 = t; C1 = 0; C2 = 0; G1 = 0; G2 = 0; //更新阈值 Th = (int)t; } } Stream sTemp = dstImage.PixelBuffer.AsStream(); sTemp.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin); sTemp.Write(temp, 0, w * 4 * h); return dstImage; } else { return null; } } [图像效果] Fig.1原图 Fig.2效果图 [算法说明] 简单统计法图像二值化就是基于统计原理获取图像阈值进行二值图像分割。假设图像为f(x,y),阈值为Th,则计算公式如下: [函数代码] /// /// Statistical method of image segmention. /// /// The source image. /// public static WriteableBitmap StatisticalThSegment(WriteableBitmap src) ////Ostu法阈值分割 { if (src != null) { int w = src.PixelWidth; int h = src.PixelHeight; WriteableBitmap dstImage = new WriteableBitmap(w, h); byte[] temp = src.PixelBuffer.ToArray(); byte[] tempMask = (byte[])temp.Clone(); //定义灰度图像信息存储变量 int[] srcData = new int[w * h]; int eX = 0; int eY = 0; int sumEF = 0; int sumE = 0; int eMax = 0; //定义阈值变量 int Th = 0; for (int j = 0; j < h; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) { srcData[i + j * w] = (int)((double)tempMask[i * 4 + j * w * 4] * 0.114 + (double)tempMask[i * 4 + 1 + j * w * 4] * 0.587 + (double)tempMask[i * 4 + 2 + j * w * 4] * 0.299); } } for (int j = 1; j < h - 1; j++) { for (int i = 1; i < w - 1; i++) { eX = srcData[i - 1 + j * w] - srcData[i + 1 + j * w]; eY = srcData[i + (j - 1) * w] - srcData[i + (j + 1) * w]; eMax = Math.Max(eX, eY); sumE += eMax; sumEF += eMax * srcData[i + j * w]; } } Th = (int)(sumEF / sumE); for (int j = 0; j < h; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) { temp[i * 4 + j * w * 4] = temp[i * 4 + 1 + j * w * 4] = temp[i * 4 + 2 + j * w * 4] = (byte)(srcData[i + j * w] < Th ? 0 : 255); } } Stream sTemp = dstImage.PixelBuffer.AsStream(); sTemp.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin); sTemp.Write(temp, 0, w * 4 * h); return dstImage; } else { return null; } } [图像效果] Fig.1原图 Fig.2效果图 [算法说明] 双峰法图像分割是一种简单的分割算法,双峰法图像二值化就是根据双峰法得到的阈值进行二值化。假如一张图像的直方图如下所示: Fig.1双峰法示意图 在直方图中我们可以明显的看到两个山峰状的图像分布,山峰的顶点我们记为Hmax1和Hmax2,他们对应的灰度值分别为T1和T2,那么双峰法图像分割的思想就是找到图像两个山峰之间的谷地最低值,即在[T1,T2]的灰度范围内寻找阈值T,使其满足对应的像素数目最少,表现在图像上就是高度最低,用T对图像进行分割或二值化。 [函数代码] /// /// Peaks histogram method of image segmention. /// /// The source image. /// public static WriteableBitmap PeakshistogramThSegment(WriteableBitmap src) ////双峰法阈值分割 { if (src != null) { int w = src.PixelWidth; int h = src.PixelHeight; WriteableBitmap dstImage = new WriteableBitmap(w, h); byte[] temp = src.PixelBuffer.ToArray(); byte[] tempMask = (byte[])temp.Clone(); //定义灰度图像信息存储变量 int[] srcData = new int[w * h]; //定义直方图存取变量 int[] histValues = new int[256]; //定义双峰位置变量h1,h2,对应的灰度变量t1,t2,谷底灰度变量t int h1 = 0, h2 = 0, t1 = 0, t2 = 0, t = 255; //定义阈值变量 int Th = 0; for (int j = 0; j < h; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) { srcData[i + j * w] = (int)((double)tempMask[i * 4 + j * w * 4] * 0.114 + (double)tempMask[i * 4 + 1 + j * w * 4] * 0.587 + (double)tempMask[i * 4 + 2 + j * w * 4] * 0.299); histValues[srcData[i + j * w]]++; } } for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) { if (i < 129) { if (histValues[i] > t1) { h1 = i; t1 = histValues[i]; } } else { if (histValues[i] > t2) { h2 = i; t2 = histValues[i]; } } } for (int n = h1; n <= h2; n++) { if (histValues[n] < t) { Th = n; t = histValues[n]; } } for (int j = 0; j < h; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) { temp[i * 4 + j * w * 4] = temp[i * 4 + 1 + j * w * 4] = temp[i * 4 + 2 + j * w * 4] = (byte)(srcData[i + j * w] < Th ? 0 : 255); } } Stream sTemp = dstImage.PixelBuffer.AsStream(); sTemp.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin); sTemp.Write(temp, 0, w * 4 * h); return dstImage; } else { return null; } } [图像效果] Fig.2原图 Fig.3效果图 [算法说明] 所谓P分位法图像分割,就是在知道图像中目标所占的比率Ratio时,循环不同的灰度值对图像进行分割,并计算对应的目标所占的比率,如果该比率与Ratio的差值足够小,那么该阈值就是所求的最佳分割阈值。 算法过程如下: 1,已知目标图像所占比率P; 2,设定一阈值Th,它将图像分割为两部分,目标部分A和背景部分B,统计两部分所包含的像素数目分别为Na和Nb; 3,将Th从1-254迭代,每改变一次Th ,计算一次Na,Nb,根据Na,Nb计算目标所占的比率P,公式如下: 4,计算当前阈值对应的分割比率与已知比率的差值,若小于某阈值则停止迭代,否则,转至3继续进行,公式如下: 其中T为某一小数。 [函数代码] /// /// P-Parameter method of image segmention. /// /// The source image. /// The ratio of object, from 0 to 1. /// public static WriteableBitmap PParameterThSegment(WriteableBitmap src,double P) ////P参数法阈值分割 { if (src != null) { int w = src.PixelWidth; int h = src.PixelHeight; WriteableBitmap dstImage = new WriteableBitmap(w, h); byte[] temp = src.PixelBuffer.ToArray(); byte[] tempMask = (byte[])temp.Clone(); //定义灰度图像信息存储变量 int[] srcData = new int[w * h]; //定义背景和目标像素个数变量 int C1 = 0, C2 = 0; //定义阈值变量 int Th = 0; for (int j = 0; j < h; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) { srcData[i + j * w] = (int)((double)tempMask[i * 4 + j * w * 4] * 0.114 + (double)tempMask[i * 4 + 1 + j * w * 4] * 0.587 + (double)tempMask[i * 4 + 2 + j * w * 4] * 0.299); } } for (int T = 0; T <= 255; T++) { for (int i = 0; i < srcData.Length; i++) { if (srcData[i] > T) { C1++; } else { C2++; } } double t = Math.Abs((double)((double)C1 / ((double)C1 + (double)C2)) - P); if (t < 0.01) { Th = T; break; } C1 = 0; C2 = 0; } for (int j = 0; j < h; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) { temp[i * 4 + j * w * 4] = temp[i * 4 + 1 + j * w * 4] = temp[i * 4 + 2 + j * w * 4] = (byte)(srcData[i + j * w] < Th ? 0 : 255); } } Stream sTemp = dstImage.PixelBuffer.AsStream(); sTemp.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin); sTemp.Write(temp, 0, w * 4 * h); return dstImage; } else { return null; } } [图像效果] Fig.1原图 Fig.2效果图(P=0.8) [算法说明] 一维最大熵法图像分割就是利用图像的灰度分布密度函数定义图像的信息熵,通过优化一定的熵准则得到熵最大时对应的阈值,从而进行图像分割的方法。 算法过程: 1,对于一幅灰度图像,灰度范围为[0,L-1],求取图像的最小灰度级min,最大灰度级max; 2,按照如下熵的公式求取灰度t对应的熵值; 其中,pi表示灰度级i出现的概率。 3,计算t从最小灰度min到最大灰度max之间不同灰度级所对应的熵值E(t),求取E(t)最大时所对应的灰度级t,该灰度级即为所求的阈值Th。 [函数代码] /// /// Entropy max method of image segmention. /// /// The source iamge. /// public static WriteableBitmap EntropymaxThSegment(WriteableBitmap src) ////一维熵最大法阈值分割 { if (src != null) { int w = src.PixelWidth; int h = src.PixelHeight; WriteableBitmap dstImage = new WriteableBitmap(w, h); byte[] temp = src.PixelBuffer.ToArray(); byte[] tempMask = (byte[])temp.Clone(); //定义灰度图像信息存储变量 int[] srcData = new int[w * h]; //定义阈值变量 int Th = 0; //定义直方图存储变量 int[] histogram = new int[256]; //定义熵值变量 double Ht = 0.0; double Hl = 0.0; double sigma = 0.0; //定义灰度最值变量 int max = 0; int min = 255; //定义临时变量 double t = 0.0, pt = 0.0, tempMax = 0.0; int tempV = 0; for (int j = 0; j < h; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) { tempV = (int)((double)tempMask[i * 4 + j * w * 4] * 0.114 + (double)tempMask[i * 4 + 1 + j * w * 4] * 0.587 + (double)tempMask[i * 4 + 2 + j * w * 4] * 0.299); srcData[i + j * w] = tempV; histogram[tempV]++; if (tempV > max) { max = tempV; } if (tempV < min) { min = tempV; } } } for (int i = min; i < max; i++) { t = (double)((double)histogram[i] / (double)(w * h)); if (t > 0.00000001) { Hl += -t * Math.Log10(t); } else continue; } for (int i = min; i < max; i++) { t = (double)((double)histogram[i] / (double)(w * h)); pt += t; if (t > 0.00000001) { Ht += -t * Math.Log10(t); sigma = Math.Log10(pt * (1 - pt)) * Ht / pt + (Hl - Ht) / (1 - pt); if (sigma > tempMax) { tempMax = (int)sigma; Th = i; } } else continue; } for (int j = 0; j < h; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) { temp[i * 4 + j * w * 4] = temp[i * 4 + 1 + j * w * 4] = temp[i * 4 + 2 + j * w * 4] = (byte)(srcData[i + j * w] < Th ? 0 : 255); } } Stream sTemp = dstImage.PixelBuffer.AsStream(); sTemp.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin); sTemp.Write(temp, 0, w * 4 * h); return dstImage; } else { return null; } } [图像效果] Fig.1原图 Fig.2效果图 demo下载:http://www.zealfilter.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=15&extra=page%3D2简单统计法图像二值化
双峰法图像二值化
P分位法图像二值化
一维最大熵法图像二值化