Caffe制作LMDB数据并进行分类网络训练和测试
这是一篇caffe训练分类模型步骤说明博客、本次步骤不涉及caffe的编译讲解
- caffe制作LMDB数据集及求均值文件
- 生成train.txt和val.txt
- 制作LMDB数据集
- 生成binaryproto均值文件
- caffe训练网络模型
- train_val.prototxt
- solver.prototxt
- train_model.sh
- 进行网络模型训练
- 进行网络模型测试
- caffe自带的test工具
- pycaffe接口
本篇博客以某项比赛数据、ResNet-50模型为例,讲解了生成自己的train.txt和val.txt文本文件、制作LMDB数据集、生成均值文件、网络训练、网络测试以及使用pycaffe接口进行测试的详细流程。
数据集来源:某项比赛
模型:ResNet-50
系统:Linux-Ubuntu
caffe制作LMDB数据集及求均值文件
数据集分为train和val数据集,训练集180000张图片左右,验证集20000张图片左右,总共涉及对45种类型的分类,包括干旱地、棒球场等。
在用caffe进行网络模型训练前,最好先生成LMDB格式数据集,这会提高caffe读取数据的效率。当完成这部分工作后,会有两个文件夹和一个文件:训练集train_lmdb文件夹、验证集val_lmdb文件夹和binaryproto均值文件。
制作步骤分别为:生成train.txt和val.txt、制作LMDB数据集、生成均值文件
生成train.txt和val.txt
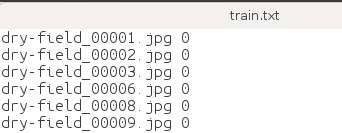
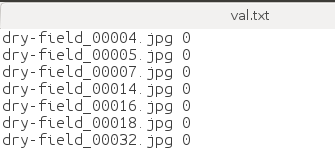
首先需要生成具有训练集和验证集图片名称和对应标签信息的txt文件,即train.txt和val.txt文本文件。
- python脚本如下:
import os
up_dir = 'E:/xxx/'
train_dirname = 'E:/xxx/val'
id_path = "E:/xxx/ClsName2id.txt"
class_name_list = os.listdir(train_dirname)
train_txt = open(os.path.join(up_dir, 'val.txt'), 'w') #修改val.txt为train.txt即可
id_txt = open(id_path, 'r', encoding='UTF-8')
for line in id_txt:
for class_name in class_name_list:
if line.split(':')[0] == class_name:
print(class_name)
image_list = os.listdir(os.path.join(train_dirname, class_name))
for image in image_list:
train_txt.write(image)
train_txt.write(' ')
train_txt.write(str(int(line.split(':')[2])-1))
train_txt.write('\n')
train_txt.close()
行数即为你训练集或验证集的图片数量
列有两列,第一列是图片名称,第二列是图片对应的标签。
在这里要特别注意一点,图片的标签值一定要从0开始,否则精度会下降很多。trust me, 我做过相应的实验,有时间会把实验结果放上来。
制作LMDB数据集
我使用的是caffe下的create_imagenet.sh文件,文件可以在caffe/examples/imagenet下找到。
打开后如下:
需要修改的地方以及怎样修改,我在相应行用中文进行了注释,按照说明进行修改即可,主要是路径和名称问题。
#!/usr/bin/env sh
# Create the imagenet lmdb inputs
# N.B. set the path to the imagenet train + val data dirsset -e
EXAMPLE=/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing # 生成的lmdb文件存放路径
DATA=/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing # train.txt和val.txt所在路径
TOOLS=/home1/xxx/caffeMS/build/tools # 改成自己的caffe路径
TRAIN_DATA_ROOT=/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing/train/ # 训练原始图片路径
VAL_DATA_ROOT=/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing/val/ # 验证原始图片路径
rm -rf $EXAMPLE/train_lmdb
rm -rf $EXAMPLE/val_lmdb
# Set RESIZE=true to resize the images to 256x256. Leave as false if images have
# already been resized using another tool.
RESIZE=true # 设为ture,会进行resize
if $RESIZE; then
RESIZE_HEIGHT=256
RESIZE_WIDTH=256
else
RESIZE_HEIGHT=0
RESIZE_WIDTH=0
fi
if [ ! -d "$TRAIN_DATA_ROOT" ]; then
echo "Error: TRAIN_DATA_ROOT is not a path to a directory: $TRAIN_DATA_ROOT"
echo "Set the TRAIN_DATA_ROOT variable in create_imagenet.sh to the path" \
"where the ImageNet training data is stored."
exit 1
fi
if [ ! -d "$VAL_DATA_ROOT" ]; then
echo "Error: VAL_DATA_ROOT is not a path to a directory: $VAL_DATA_ROOT"
echo "Set the VAL_DATA_ROOT variable in create_imagenet.sh to the path" \
"where the ImageNet validation data is stored."
exit 1
fi
echo "Creating train lmdb..."
GLOG_logtostderr=1 $TOOLS/convert_imageset \
--resize_height=$RESIZE_HEIGHT \
--resize_width=$RESIZE_WIDTH \
--shuffle \
$TRAIN_DATA_ROOT \
$DATA/train.txt \ # 训练文本名字
$EXAMPLE/train_lmdb # lmdb训练数据集数据集名字
echo "Creating val lmdb..."
GLOG_logtostderr=1 $TOOLS/convert_imageset \
--resize_height=$RESIZE_HEIGHT \
--resize_width=$RESIZE_WIDTH \
--shuffle \
$VAL_DATA_ROOT \
$DATA/val.txt \ # 测试文本名字
$EXAMPLE/val_lmdb # lmdb验证集数据集名字
echo "Done."
成功后,会生成两个文件夹train_lmdb和val_lmdb,这两个文件夹就是我们LMDB格式数据集。

生成binaryproto均值文件
生成均值文件使用的是make_imagenet_mean.sh,和create_imagenet.sh文件一样,也可以在caffe/examples/imagenet路径下找到。
主要是对train_lmdb。
#!/usr/bin/env sh
# Compute the mean image from the imagenet training lmdb
# N.B. this is available in data/ilsvrc12
EXAMPLE=/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing # train_lmdb文件夹所在路径
DATA=/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing # 生成的binaryproto路径
TOOLS=/home1/xxx/caffeMS/build/tools # 设置为自己的caffe路径
rm -f $DATA/rs_imagenet_mean.binaryproto
$TOOLS/compute_image_mean $EXAMPLE/train_lmdb \
$DATA/rs_imagenet_mean.binaryproto # 均值文件名字
echo "Done."
caffe训练网络模型
进行模型训练需要train_val.prototxt、solver.prototxt以及train_model.sh三个文件。
train_val.prototxt
train_val.prototxt中定义了网络模型的结构、数据输入部分和loss部分。
我所使用的是ResNet-50网络模型。
因为模型有两千多行,在这里我只放出开头读入数据部分和结尾训练loss部分,当然这两部分也是一般我们需要修改的地方。
开头输入数据部分:
name: "ResNet-50"
layer {
name: "data"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
include {
phase: TRAIN # 训练时输入数据设置
}
transform_param {
crop_size: 224 # 从原始图片中随机裁剪出224x224大小的图片区域
mirror: true # 镜像设为true,提高样本数量
mean_file: "/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing/rs_imagenet_mean.binaryproto" # 均值文件所在路径
}
data_param {
source: "/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing/train_lmdb/" # train_ldmb路径
batch_size: 25 #*iter_size # batch_size,根据你显卡内存大小进行选择
backend: LMDB # 数据来源要改成LMDB
}
}
layer {
name: "data"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
include {
phase: TEST # 测试时输入数据设置
}
transform_param {
crop_size: 224 # 测试时从中心裁剪出224x224大小区域进行测试
mirror: false # 镜像设为flase
mean_file: "/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing/rs_imagenet_mean.binaryproto" # 均值文件所在路径
}
data_param {
source: "/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing/val_lmdb/" # val_lmdb路径
batch_size: 10 #not *iter_size # batch_size,根据你显卡内存大小进行选择
backend: LMDB # 数据来源要改成LMDB
}
}
结尾loss部分:
layer {
name: "loss1/loss1"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss" # 采用SoftmaxWithLoss
bottom: "my-classifier"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss1/loss1"
loss_weight: 0.3 # 训练输出的loss所占的权重
}
layer {
name: "test/loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss" # 采用SoftmaxWithLoss
bottom: "my-classifier"
bottom: "label"
top: "test/loss"
include {
phase: TEST # 验证时的loss参与训练权重参数的更新
}
}
layer {
name: "accuracy"
type: "Accuracy" # 测试时的精度输出
bottom: "my-classifier"
bottom: "label"
top: "accuracy"
include {
phase: TEST
}
}
solver.prototxt
solver.prototxt中定义了loss优化器、模型保存路径、最大迭代次数、基础学习率、学习率衰减策略、模型运算是GPU还是CPU等超参数。
# the definition of neural network model
net: "train_val.prototxt" # 网络结构路径
# test_iter is related to batch_size in test layer, test_iter * batch_size = the number of test data
test_iter: 2000 # 测试次数
# carry out test once every 5 training iterations
test_interval: 50 # 每多少次进行一次测试
# exclude test phase when test_initialization = false
# test_initialization: false
# display information once every 10 training iterations
display: 10 # 训练多少次显示一次
average_loss: 40
# the initial learning rate
base_lr: 0.0000001 # 基础学习率
lr_policy: "poly" # 学习率更新策略
stepsize: 1000 # 每1000次学习率更新一次
gamma: 0.96 # 学习率更新的超参
# The max number of iterations
max_iter: 50000 # 最大迭代次数
power: 1.0 # 学习率更新超参
momentum: 0.9 # 动量设置
# weight decay item, in case of overfitting
weight_decay: 0.0002 # 正则化设置
# save once every 50 training iterations
snapshot: 400 # 训练多少次保存一次模型
# save path
snapshot_prefix: "snapshot/resnet_50_ft" # 训练模型保存路径
solver_mode: GPU # 采用GPU训练,也可改为CPU
train_model.sh
train_model.sh是命令文件,其中会设置预训练模型路径、solver.prototxt路径、log日志保存路径等参数。
#!/usr/bin/env sh
TOOLS=/home1/xxx/caffeMS/build/tools
GLOG_logtostderr=0 GLOG_log_dir=./ft_log/ $TOOLS/caffe train --solver=solver.prototxt --weights=/home1/jsk/RemoteSensing/ResNet/ResNet-50/snapshot/resnet_50__iter_100000.caffemodel -gpu 0 #加入 -gpu 选项
TOOLS改为自己的caffe路径
GLOG_log_dir改为自己要保存的日志文件路径
–solver表示solver.prototxt文件路径
–weights表示预训练模型所在路径
-gpu 0表示采用编号为0的显卡进行训练
进行网络模型训练
打开linux终端命令窗口:
输入
sudo sh train_model.sh
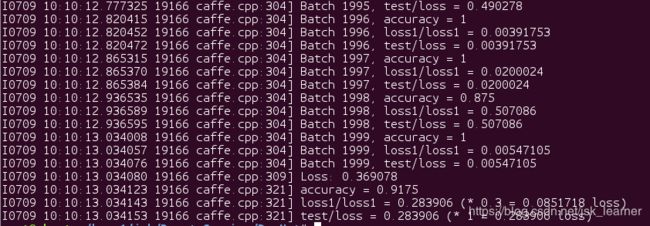
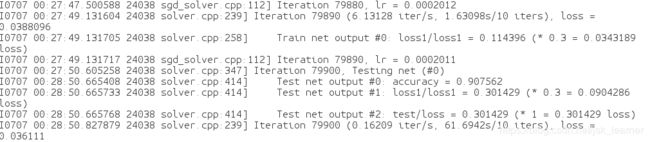
网络模型训练就开始了,出现如下图所示,表示你前期工作没有错误。

日志文件被保存在,我的就是./ft_log/下

打开后,内容如图:
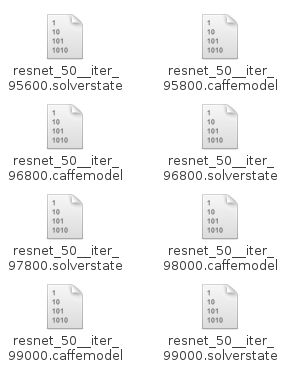
训练模型保存在,我的是snapshot路径下
进行网络模型测试
网络模型测试,可以使用caffe自带的test工具,或者使用matcaffe或pycaffe接口进行模型测试。
下面我将讲解caffe自带的test工具和利用pycaffe进行模型测试两种方法
caffe自带的test工具
创建一个脚本命令文件,test_model.sh,内容如下:
/home1/xxx/caffeMS/build/tools/caffe test --model=/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing/ResNet/ResNet-50/train_val.prototxt --weights=/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing/ResNet/ResNet-50/snapshot/resnet_50__iter_100000.caffemodel --iterations 2000 -gpu 0
打开linux终端命令窗口:
sudo sh test_model.sh
即可
pycaffe接口
代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf-8
import sys
#caffe_root='/home1/xxx/caffeMS/' #修改成你的Caffe项目路径
#sys.path.append(caffe_root+'python')
import caffe
sys.path.insert(0,'/home1/xxx/caffeMS/python')
caffe.set_mode_gpu() #设置为GPU运行
import os
import numpy as np
# 修改成你的deploy.prototxt文件路径
model_def = '/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing/ResNet/ResNet-50/deploy.prototxt'
model_weights = '/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing/ResNet/ResNet-50/snapshot/resnet_50__iter_100000.caffemodel'
# 修改成你的caffemodel文件的路径
net = caffe.Net(model_def, # defines the structure of the model
model_weights, # contains the trained weights
caffe.TEST) # use test mode (e.g., don't perform dropout)
#这是一个由mean.binaryproto文件生成mean.npy文件的函数
def convert_mean(binMean,npyMean):
blob = caffe.proto.caffe_pb2.BlobProto()
bin_mean = open(binMean, 'rb' ).read()
blob.ParseFromString(bin_mean)
arr = np.array( caffe.io.blobproto_to_array(blob) )
npy_mean = arr[0]
np.save(npyMean, npy_mean )
binMean='/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing/rs_imagenet_mean.binaryproto'
#修改成你的mean.binaryproto文件的路径
npyMean='rs_imagenet_mean.npy'
#你想把生成的mean.npy文件放在哪个路径下
convert_mean(binMean,npyMean)
transformer = caffe.io.Transformer({'data': net.blobs['data'].data.shape})
transformer.set_transpose('data', (2,0,1)) # 通道变换,例如从(530,800,3) 变成 (3,530,800)
transformer.set_mean('data', np.load(npyMean).mean(1).mean(1))
#如果你在训练模型的时候没有对输入做mean操作,那么这边也不需要
transformer.set_raw_scale('data', 255) # rescale from [0, 1] to [0, 255]
transformer.set_channel_swap('data', (2, 1, 0)) # swap channels from RGB to BGR
with open('/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing/val.txt') as image_list:
# 修改成你要测试的txt文件的路径,这个txt文件的内容一般是:每行表示图像的路径,
#然后空格,然后是标签,也就是说每行都是两列
with open('rs_prediction_resize_center.txt','w') as result:
# 如果你想把预测的结果写到一个txt文件中,那么把这个路径修改成你想保存这个txt文件的路径
count_right=0
count_all=0
while 1:
list_name=image_list.readline()
if list_name == '\n' or list_name == '': #如果txt文件都读完了则跳出循环
break
image_type=list_name[0:-3].split('.')[-1]
if image_type == 'gif': #这里我对gif个数的图像直接跳过
continue
#print('image_type' + image_type)
#print '*******'+ list_name.split(' ')[1]
img_name = list_name.split(' ')[0]
image = caffe.io.load_image(os.path.join('/home1/xxx/RemoteSensing/val_resize/',img_name))
# 这里要添加你的图像所在的路径,根据你的list_name灵活调整,总之就是图像路径
#imshow(image)
output_prob = np.zeros((1, 45))
image_shape = np.array(image.shape)
crop_dims = (224,224)
crop_dims = np.array(crop_dims)
range_ = image_shape[0] - crop_dims[0]
#for k in range(0, range_ + 1, crop_dims[0]/4) + range(range_, 1, -crop_dims[0]/4):
#for m in range(0, range_ + 1, crop_dims[1]/4) + range(range_, 1, -crop_dims[1]/4):
#crop_img = image[m:m+crop_dims[0],k:k+crop_dims[1],:]
#transformed_image = transformer.preprocess('data', crop_img)
# 用转换后的图像代替net.blob中的data
#net.blobs['data'].data[...] = transformed_image
#net.blobs['data'].reshape(1, 3, 224, 224)
### perform classification
#output = net.forward()
# 读取预测结果和真实label
#output_prob += net.blobs['prob'].data[0]
crop_img = image[(image_shape[0]-crop_dims[0]) / 2:(image_shape[0]-crop_dims[0]) / 2 + crop_dims[0],(image_shape[1]-crop_dims[1]) / 2:(image_shape[1]-crop_dims[1]) / 2 + crop_dims[1],:]
transformed_image = transformer.preprocess('data', crop_img)
# 用转换后的图像代替net.blob中的data
net.blobs['data'].data[...] = transformed_image
net.blobs['data'].reshape(1, 3, 224, 224)
### perform classification
output = net.forward()
# 读取预测结果和真实label
output_prob += net.blobs['prob'].data[0]
true_label = int(list_name.split(' ')[1])
# 如果预测结果和真实label一样,则count_right+1
if(output_prob.argmax()==true_label):
count_right=count_right+1
count_all=count_all+1
# 保存预测结果,这个可选
result.writelines(list_name.split(' ')[0] + ' ' + str(int(list_name.split(' ')[1])) +' '+str(output_prob.argmax())+'\n')
#可以每预测完100个样本就打印一些,这样好知道预测的进度,尤其是要预测几万或更多样本的时候,否则你还以为代码卡死了
if(count_all%100==0):
#print(list_name.split('\n')[0])
print(count_all)
# 打印总的预测结果
print('Accuracy: '+ str(float(count_right)/float(count_all)))
print('count_all: ' + str(count_all))
print('count_right: ' + str(count_right))
print('count_wrong: ' + str(count_all-count_right))
其可以生成一个预测文件,有三列
第一列是图片名称
第二列是是图片的真实标签(groundtruth)
第三列是图片的预测值
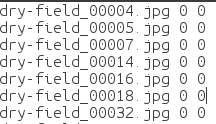
同时打印出模型预测的精度:

至此,我们已完成在caffe下从制作数据集到网络训练再到测试的全部过程。
希望能帮助到各位。谢谢。
2019.7.10