(一)SLAM拓扑地图(地图的生成和显示)
首先,SLAM中的拓扑地图是什么?
拓扑地图由节点和边组成。
如下图:

那么如何生成这种拓扑地图呢?
本文主要目的是生成一个简单的拓扑地图,并在g2o_viewer 中显示。
1.拓扑地图的生成
1.1安装g2o_viewer
参考我的上一篇博客
http://blog.csdn.net/ktigerhero3/article/details/75457432
1.2生成拓扑地图
本文参考g2o包中的create_sphere.cpp来生成拓扑地图的节点和边。
并参考下面博文中的示例
http://blog.csdn.net/heyijia0327/article/details/47686523#reply
生成的拓扑地图结构如下

具体实现如下:
(1)使用cmake加载g2o库函数
新建createmap工程
CmakeLists.txt如下
注意将g2o安装包中的cmake_modules文件夹拷贝到当前工程目录中。
project(createmap)
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
LIST(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake_modules)
message("CMAKE_MODULE_PATH"${CMAKE_MODULE_PATH})
find_package(Eigen3 REQUIRED)
find_package(CSparse REQUIRED)
find_package(G2O REQUIRED)
IF(G2O_FOUND)
include_directories(${G2O_INCLUDE_DIR})
message("G2O lib is found:"${G2O_INCLUDE_DIR})
ENDIF(G2O_FOUND)
message("EIGEN3 lib is found:"${EIGEN_INCLUDE_DIR})
IF(EIGEN3_FOUND)
include_directories(${EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR})
message("Eigen3_INCLUDE_DIR"${EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR}})
ENDIF(EIGEN3_FOUND)
include_directories(${CSPARSE_INCLUDE_DIR})
SET(G2O_LIBS g2o_cli g2o_ext_freeglut_minimal g2o_simulator
g2o_solver_slam2d_linear g2o_types_icp g2o_types_slam2d g2o_core
g2o_interface g2o_solver_csparse g2o_solver_structure_only g2o_types_sba
g2o_types_slam3d g2o_csparse_extension g2o_opengl_helper g2o_solver_dense
g2o_stuff g2o_types_sclam2d g2o_parser g2o_solver_pcg g2o_types_data g2o_types_sim3 cxsparse )
aux_source_directory(. SRC_LIST)
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} ${SRC_LIST})
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} ${G2O_LIBS} )(2)使用代码生成节点和边(保存为*.g2o文件)
#include //CommandArgs arg;
//arg.param("o", outFilename, "-", "output filename");
string vertexTag = Factory::instance()->tag(vertices[0]);
string edgeTag = Factory::instance()->tag(edges[0]);
//ostream& fout = outFilename != "./out.g2o" ? fileOutputStream : cout;
ostream& fout=fileOutputStream;
for (size_t i = 0; i < vertices.size(); ++i) {
VertexSE3* v = vertices[i];
fout << vertexTag << " " << v->id() << " ";
v->write(fout);
fout << endl;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < edges.size(); ++i) {
EdgeSE3* e = edges[i];
VertexSE3* from = static_cast(e->vertex(0));
VertexSE3* to = static_cast(e->vertex(1));
fout << edgeTag << " " << from->id() << " " << to->id() << " ";
e->write(fout);
fout << endl;
}
return 0;
} 编译运行,发现再当前文件夹下生成
ori.g2o文件
内容如下
VERTEX_SE3:QUAT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
VERTEX_SE3:QUAT 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
VERTEX_SE3:QUAT 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
VERTEX_SE3:QUAT 3 0 0 0.2 0 0 0 1
EDGE_SE3:QUAT 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1
EDGE_SE3:QUAT 1 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1
EDGE_SE3:QUAT 2 3 0 0 -0.8 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1
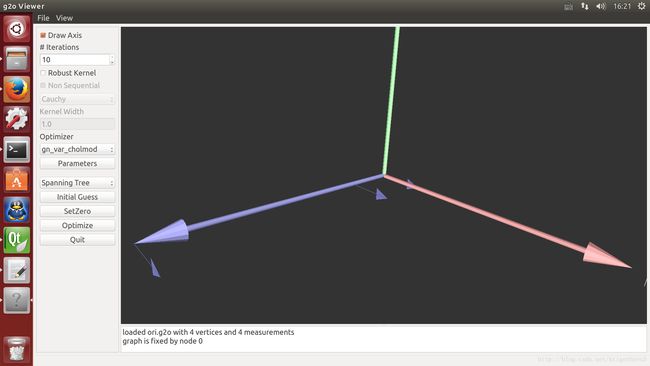
EDGE_SE3:QUAT 3 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 2.显示生成的拓扑地图
将以上生成的文件拷贝到
运行g2o安装文件夹下bin文件夹
cd到bin运行g2o_viewer
./g2o_viewer ori.g2o工程代码请到我的github上下载
https://github.com/QianFeifanhnu/topologicalMap/tree/master