上一篇:Spring学习笔记(三、IoC)
** Bean常用的配置项**
- Id:在IoC容器中Bean的唯一标识
- Class:具体要实例化的类
- Scope:作用域
- Constructor arguments:构造器参数
- properties:属性
- Autowiring mode:自动装配模式
- lazy-initialization mode:懒加载模式
- initialization/destruction method:初始化/销毁的方法
Bean的作用域
- singleton:单例,指一个Bean容器中只存在一份(默认)
- prototype:每次请求(每次使用)创建新的实例,destory方法不生效(因为用完会被垃圾回收期回收)
- request:每次http请求创建一个实例且仅在当前request内有效
- session: 每次http请求创建一个实例且仅在当前session内有效
- global session:基于portlet的web中有效(portlet定义了global session),如果是在web中,同session
这里global session有可能还是不懂,特此解释:举个例子,一个大型的系统,有多个独立的模块组成,他们有一个统一的登录入口,登录进入后,用户可以在整个系统内操作,不需要在登录其他模块时,重新登录。这就是portlet的global session。
下面用例子证明:
-
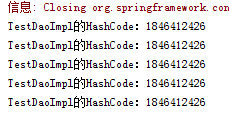
singleton
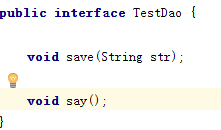
在TestDao增加接口:
TestDaoImpl实现:
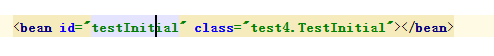
spring-ioc.xml:
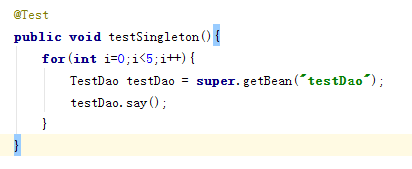
JUnit测试:
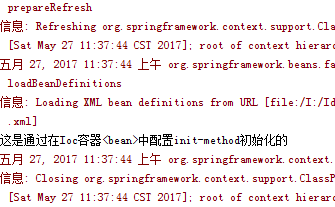
上图可见,声明了singleton作用域,即使获取多次实例,也依旧是原来的那一个。
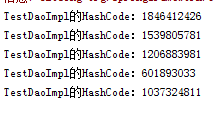
- prototype
修改spring-ioc.xml:
Junit测试结果变成:
上图可见,声明了prototype作用域,获取多次实例,每一次的hashcode都不同。
余下三个,由于涉及到web,在此就不做测验了。相信工作中,会有很多机会去尝试。
Bean的生命周期
- 生命周期
- 定义:在xml中定义
内容 - 初始化:IoC容器启动(context.start();)时生成bean的实例
- 使用:在测试或者开发时从Ioc容器中取出bean的实例调用它的方法
- 销毁:在IoC容器销毁(context.destroy();)的时候,销毁它创建的所有实例。
- 定义:在xml中定义
生命周期 —— 初始化
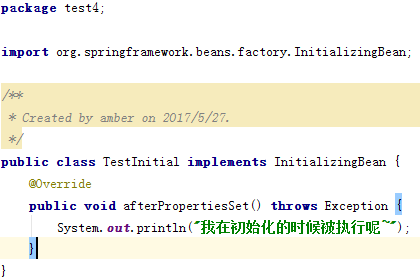
- 实现org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean接口,重写afterPropertiesSet方法
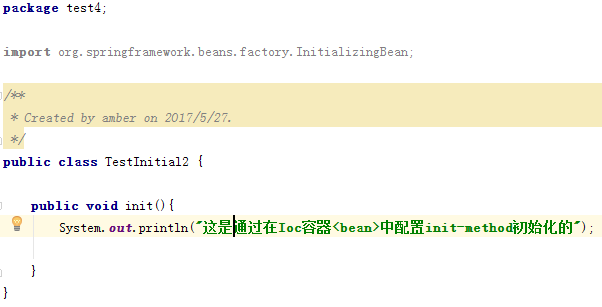
- 配置init-method
以上两种方法,可以在Ioc容器初始化实例时执行一些实例内部的初始化工作。
下面分别举例:
为了测试IoC容器启动,我加了一个空的测试方法。
执行后
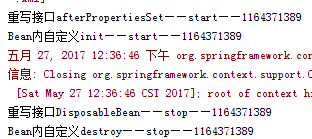
第一个【实现org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean接口,重写afterPropertiesSet方法】测试初始化成功。
第二个【配置init-method】测试初始化成功。
**生命周期 —— 销毁 **
- 实现org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean接口,重写destroy方法
- 配置destroy-method
这两个销毁方式和初始化测试方式是一样的,我就不做测试了。
还可以配置全局默认初始化、销毁方法,就是为当前IoC容器中所有的bean增加初始化和销毁时执行的方法
既然实现初始化和销毁有三种不同的方法,那么哪种优先级最高呢?下面来测试。
package test4;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
/**
* Created by amber on 2017/5/27.
*/
public class TestInitial3 implements InitializingBean,DisposableBean {
public void initInBean() {
System.out.println("Bean内自定义init——start——" + hashCode());
}
public void destroyInBean(){
System.out.println("Bean内自定义destroy——stop——" + hashCode());
}
public void defaultInit() {
System.out.println("IoC全局默认defaultInit——start——" + hashCode());
}
public void defaultDestroy(){
System.out.println("IoC全局默认defaultDestroy——stop——" + hashCode());
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("重写接口afterPropertiesSet——start——" + hashCode());
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("重写接口DisposableBean——stop" + hashCode());
}
}
测试后结果:
发现,三种初始化和销毁方法同时执行时,全局默认的是不执行的。其次,最先执行的是接口。然后是bean内自定义的。
也就是三个优先级为:接口>Bean中配置>全局默认
其中全局默认即使配置了,类里面不写也不会报错,其他两个,则会报错。
Aware
- Spring中提供了一些以Aware结尾的接口,实现了Aware接口的bean在被初始化之后,可以获取相应资源
- 通过实现Aware接口,可以对Spring相应资源进行操作(一定要慎重)
- 为对Spring进行简单的扩展,提供了方便的接口
Aware相关常用接口
- ApplicationContextAware:实现了此接口的bean,可以获取到当前ApplicationContext的信息。这个类就可以方便获得ApplicationContext中的所有bean。换句话说,就是这个类可以直接获取spring配置文件中,所有有引用到的bean对象。
- BeanNameAware:实现了此接口的bean,可以获取到自己在IoC中的beanId。
以上接口,都是在bean初始化时候调用。
下面测试接口功能是否如上所述:
package test5;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
/**
* Created by amber on 2017/5/27.
*/
public class TestAware implements ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware {
private String beanName;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("setApplicationContext执行时间戳:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("获取当前bean的hashCode:" + applicationContext.getBean(beanName).hashCode());
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
beanName = name;
System.out.println("setBeanName执行时间戳:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
IoC容器中
单元测试中
@Test
public void testAware(){
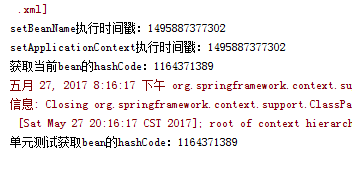
System.out.println("单元测试获取bean的hashCode:"+getBean("testAware").hashCode());
}
结果如下。
为什么我要加时间戳呢,主要是为了看哪个回调会先执行,经过多次测试发现BeanNameAware的setBeanName(String name)会先执行。
Bean的自动装配(AutoWiring)
为什么需要自动装配?
其实目的很简单,是偷懒。自动装配可以不用让我们在IoC容器的Bean中声明这些东西啦:
关于Spring自动装配可以参考:spring的自动装配
本次讲设置在
- No:(默认)不自动装配。Bean的引用必须用ref元素定义。对于较大的部署不建议改变默认设置,因为明确指定协作者能更好控制和维护系统。 在某种程度上,它记录了系统的结构。
- byName:通过属性名称自动装配。Spring会寻找相同名称的bean并将其与属性自动装配。譬如,如果bean的定义设置了根据名称自动装配, 并且包含了一个master 属性(换句话说,它有setMaster(..)方法),Spring会寻找名为master的bean的定义,并用它来装配属性
- byType:如果容器中存在一个与指定属性类型相同的bean,那么将与该属性自动装配。如果存在多个该类型的bean,将会抛出异常,并指出不能使用byType自动装配这个bean。如果没有找到相同类型的,什么也不会发生。属性不会被设置。
- Constructor:和byType类似,不同之处在于它应用于构造器参数。如果在容器中没有找到与构造器参数类型一致的bean,就会抛出异常。
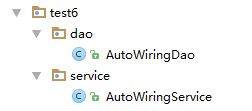
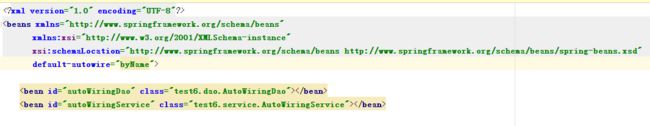
在测试之前呢,先把结构抛出来:
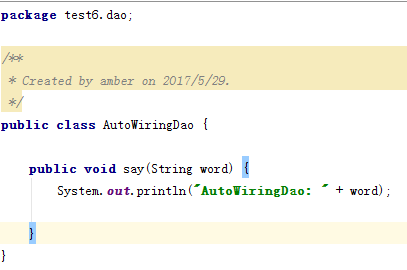
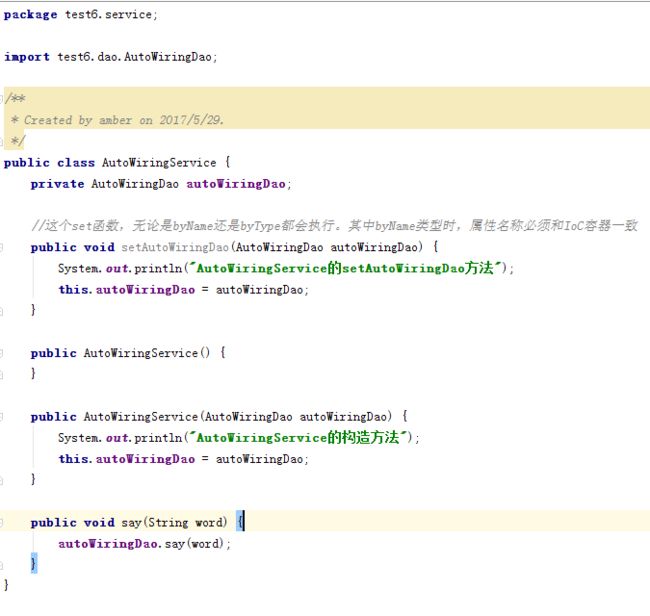
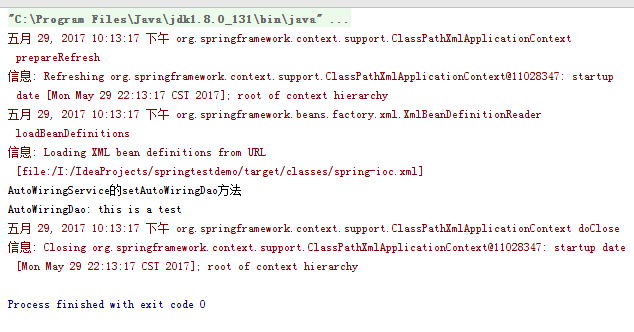
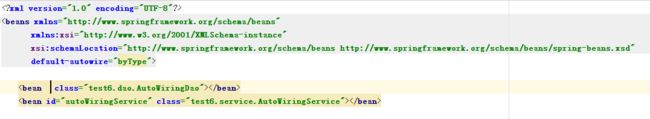
自动装配之byName:要保证beanId和调用它的类属性名称一致。
自动装配之byType:将IoC容器中AutoWiringDao的id去掉,只留下class。
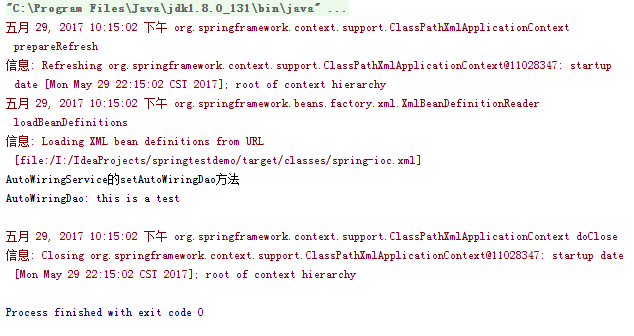
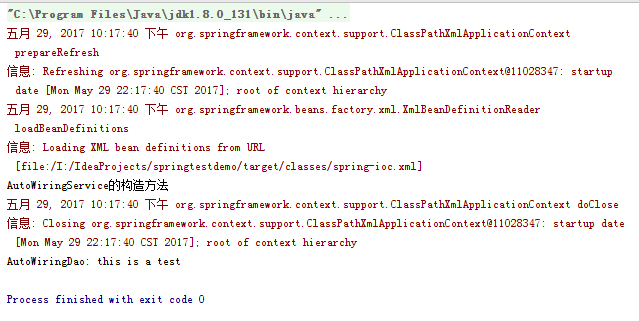
自动装配之constructor:
Resource
- 针对于资源文件的统一接口
- Resources
- UrlResource:URL对应的资源,根据一个Url地址即可构建
- ClassPathResource:获取类路径下的资源文件
- FieSystemResource:获取文件系统里面的资源
- ServletContextResource:ServletContext封装的资源,用于访问ServletContext环境下的资源
- InputStreamResource:针对于输入流封装的资源
- ByteArrayResource:针对于字节数封装的资源
Resource Loader
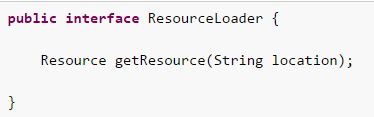
- ResourceLoader 接口是用来加载 Resource 对象的,换句话说,就是当一个对象需要获取 Resource 实例时,可以选择实现 ResourceLoader 接口。
- spring 里所有的应用上下文都是实现了 ResourceLoader 接口,因此,所有应用上下文都可以通过 getResource() 方法获取 Resource 实例。
Resource Loader接口详情:
可以看到,我们需要传入一个location进去,然后接口会返回一个对应Resource给我们。那么location这个值,我们都可以传哪样的呢?
| 前缀 | 样例 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| classpath: | classpath:com/myapp/config.xml | 从类路径加载 |
| file: | file:///data/config.xml | 将其作为 URL 对象,从文件系统加载 |
| http: | http://myserver/logo.png | 将其作为 URL 对象 加载 |
| (none) | /data/config.xml | 取决于底层的 ApplicationContext |
下面来测试:
使用classpath获取资源
1.首先在resource文件夹下增加一个config.txt文件。
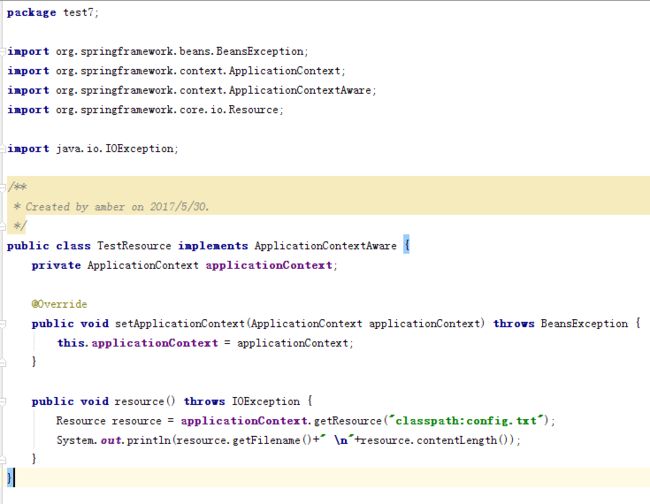
2.新建一个TesrResource类,并通过实现ApplicationContextAware接口获取到ApplicationContext,然后传入classpath:位置的地址得到目标文件信息。
3.IoC容器注册bean
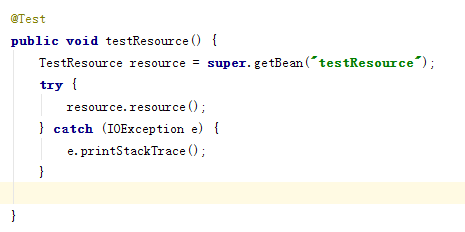
4.测试
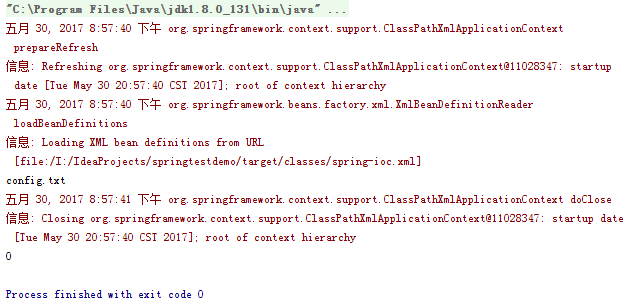
5.结果
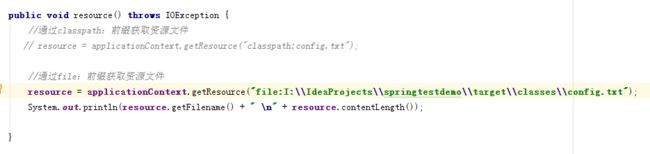
使用file:获取资源
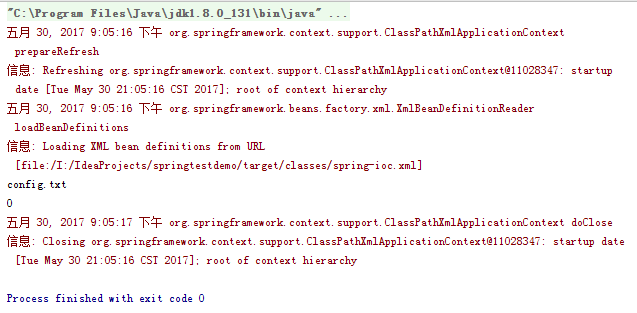
1.修改TestResource类的resource方法
2.测试结果:
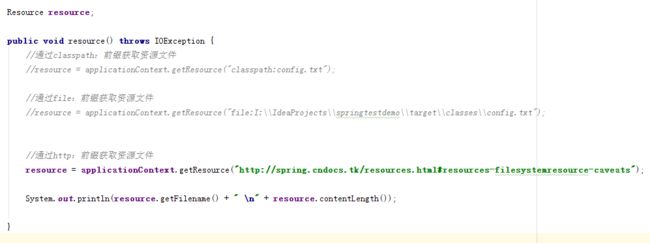
使用http:获取资源
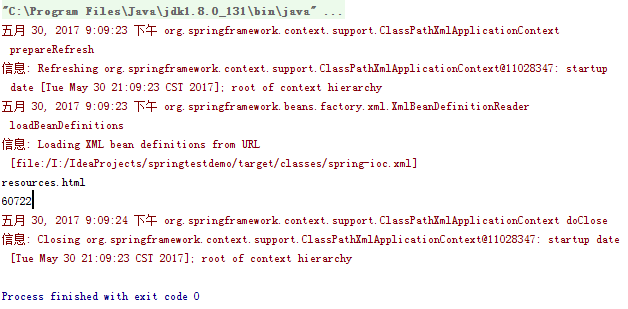
1.修改resource方法
2.测试结果
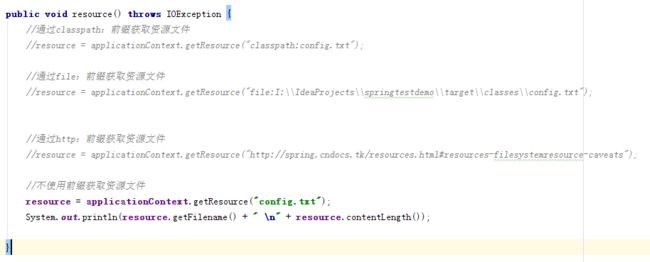
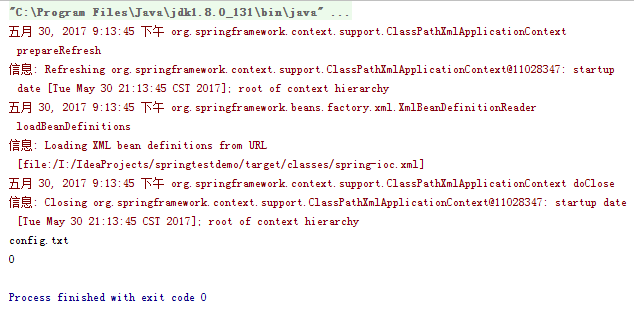
不使用前缀获取资源
1.修改resource方法
2.测试结果
为什么没有前缀也能获取到我们想要的文件呢?
- 当你在指定应用上下文调用 getResource() 方法时,而指定的位置路径又没有包含特定的前缀,spring 会根据当前应用上下文来决定返回哪一种类型 Resource。
- 这个例子,我们ApplicationContext是通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext获取到的,所以返回的是ClassPathResource对象。类似的,如果是通过实例 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 实例调用的,返回的是一个 FileSystemResource 对象;如果是通过 WebApplicationContext 实例的,返回的是一个 ServletContextResource 对象…… 如上所说,你就可以在指定的应用上下中使用 Resource 实例来加载当前应用上下文的资源。
下一篇:Spring学习笔记(五、Bean装配(下))