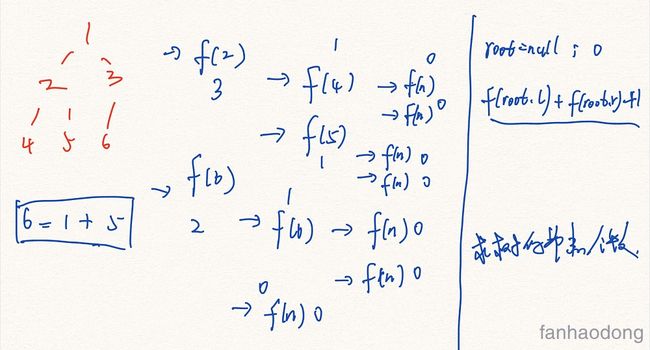二叉树 - DFS与BFS
深度优先遍历 (DFS
Depth First Search) 就是一个节点不到头(叶子节点为空) 不回头 广度有点遍历(BFS
Breadth First Search) 就是一层一层输出 , 输出到最下层的叶子节点, 为空的时候结束
其中深度遍历就是我们所说的 先序遍历 中序遍历 后序遍历 , 先中后指的是根节点输出的时机,先就是根左右
数据结构如下, 全文都是
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
输出要求
List search(TreeNode root) {
// do 需要返回一个数组
} 测试数据
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode left = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode right = new TreeNode(3);
root.left = left;
root.right = right;
left.left = new TreeNode(4);
left.right = new TreeNode(5);
right.left = new TreeNode(6);1. DFS
1. 递归实现
递归实现代码相当之简单 , 所以很容易写, 就算不会也能记忆下来
1. 先序遍历
private List preOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) return Collections.emptyList();
List list = new ArrayList<>();
recursion(list, root);
return list;
}
// 递归
private void recursion(List list, TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) return;
// 根
list.add(root.val);
// 左
recursion(list, root.left);
// 右
recursion(list, root.right);
} 2. 中序遍历
private List midOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) return Collections.emptyList();
List list = new ArrayList<>();
recursion(list, root);
return list;
}
private void recursion(List list, TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) return;
recursion(list, root.left);
// 调换到中间
list.add(root.val);
recursion(list, root.right);
} 3. 后序遍历
private List aftOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) return Collections.emptyList();
List list = new ArrayList<>();
recursion(list, root);
return list;
}
private void recursion(List list, TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) return;
recursion(list, root.left);
recursion(list, root.right);
// 调换到最后
list.add(root.val);
} 2. 递归执行流程
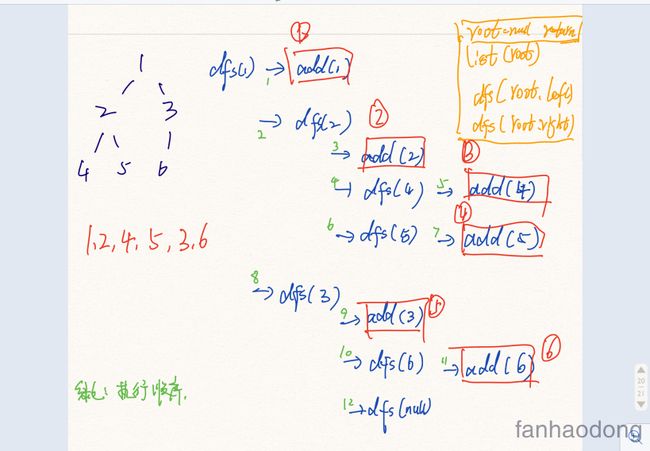
三种流程基本都差不多
好多人对于递归并不了解, 执行流程 , 我们知道方法的出栈需要一个return, 所以递归就是在找这个 , 就拿我们上面说的那个先序遍历为例子吧 .
3. 非递归实现(很重要)
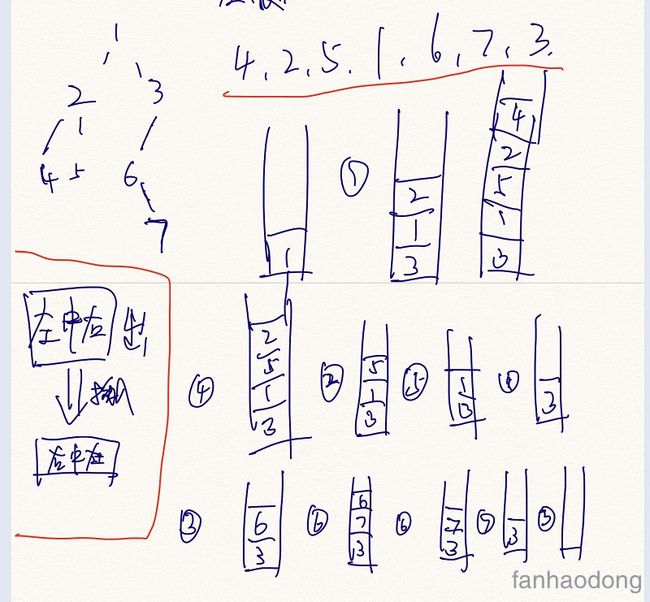
递归的坏处就是 , 出入栈消耗大量的内存, 每一次方法的调用都会保存大量的变量, 多以对于遍历来说并不好 ,
非递归遍历的实现 , 基于栈的实现, 对于遍历节点保存在栈中, 出入栈 , 主要利用栈的后进先出的特性 , 很好的保证了, 后进的优先遍历 .
1. 先序遍历
非递归实现先序遍历
private List preOrderUnRecursion(TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) return Collections.emptyList();
List list = new ArrayList<>();
// 栈
LinkedList stack = new LinkedList();
// 压栈
stack.push(root);
while (stack.size() > 0) {
// 出栈
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
TreeNode right = node.right;
if (null != right) {
stack.push(right);
}
TreeNode left = node.left;
if (null != left) {
stack.push(left);
}
list.add(node.val);
}
return list;
} 2. 中序遍历
这个实现就比较麻烦了 , 因为先序遍历, 根节点有先天的优势可以先出去 ,所以很
private List midOrderUnRecursion(TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) return Collections.emptyList();
List list = new ArrayList<>();
// 栈
LinkedList stack = new LinkedList();
// 压栈
stack.push(root);
while (stack.size() > 0) {
// 出栈
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
TreeNode right = node.right;
TreeNode left = node.left;
if (null != right) {
node.right = null;
stack.push(right);
}
// 重复入栈 , 是因为根节点不是最先出来的
if (null != right || null != left) {
stack.push(node);
}
if (null != left) {
node.left = null;
stack.push(left);
}
if (null == left && null == right) {
list.add(node.val);
}
}
return list;
} 3. 后序遍历
private List aftFirstSearchUnRecursion(TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) return Collections.emptyList();
List list = new ArrayList<>();
// 栈
LinkedList stack = new LinkedList();
// 压栈
stack.push(root);
while (stack.size() > 0) {
// 出栈
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
TreeNode right = node.right;
TreeNode left = node.left;
if (null != right || null != left) {
stack.push(node);
}
if (null != right) {
node.right = null;
stack.push(right);
}
if (null != left) {
node.left = null;
stack.push(left);
}
if (null == left && null == right) {
list.add(node.val);
}
}
return list;
} 4.非递归实现流程图
1. 先序遍历
2. 中序遍历和后序遍历一样
流程从左往右, 从上往下看 .
2. BFS
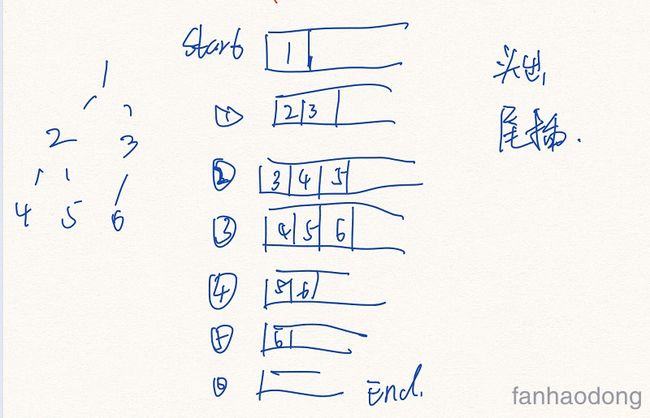
广度优先遍历就是一层 一层遍历 , 同一层, 从左到右输出,
基于队列实现的 , FIFO特性 , offer 和 poll , 操作
代码实现
private List breadthFirstSearch(TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) return Collections.emptyList();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (queue.peek() != null) {
TreeNode poll = queue.poll();
TreeNode left = poll.left;
if (null != left) {
queue.offer(left);
}
TreeNode right = poll.right;
if (null != right) {
queue.offer(right);
}
list.add(poll.val);
} 基本流程图
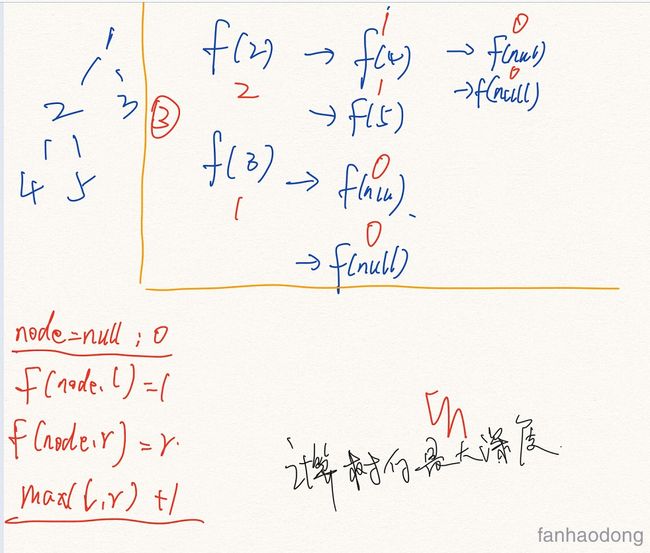
3. 求树的深度
利用树的先序遍历递归进行求树的深度
private int countDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) return 0;
int left = countDepth(root.left);
int right = countDepth(root.right);
return left >= right ? left + 1 : right + 1;
}4. 求数的节点个数
也是递归遍历
private int countNode(TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) return 0;
return countNode(root.left) + countNode(root.right)+1;
}