Android View绘制原理源码解析
众所周知,Android有四大组件,分别是Activity、服务(Service)、广播接收者(BroadcastReceiver)和内容提供者(ContentProvider),虽然View并不属于其中,但是在Android的体系中View一直扮演了非常重要的作用,因为它是视觉上的呈现,同时也是为了满足用户与应用之间的正常交互,Android系统给我们提供了一套GUI库,里面有很多控件,比如布局控件LinearLayout和RelativeLayout,功能控件TextView和Button等,但是在开发中系统提供的控件往往并不能都满足需求,一来是避免应用界面过于同类化,二来是为了完成应用特定的一些功能操作,这就意味着这时我们需要自己自定义View了。为了更好的自定义View满足需求,我们需要对View的工作原理有一定的了解,下面我们就来分析下View的绘制源码。
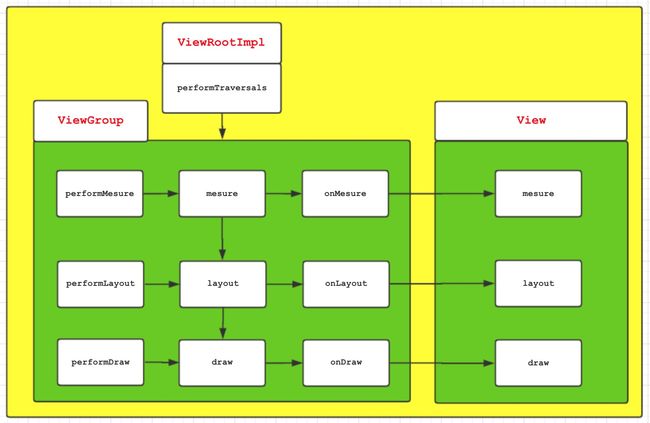
View的绘制流程是从ViewRootImpl的performTraversals方法开始的,performTraversals会依次调用performMesure、performLayout和performDraw方法,这三个方法分别完成顶级View的mesure、layout和draw这三大流程,performMesure会调用mesure方法,mesure方法又会调用onMesure方法,在onMesure方法又会循环调用子元素的mesure方法,这样就传到给子View同时完成一次measure过程,同理,performLayout和performDraw也是类似的。总体来说经过measure(测量View的宽和高)、layout(确定View在父容器的位置)和draw(View的绘制)才最终完成View的整个绘制流程,将View显示出来,整体流程可以用下图所示
1、measure过程
想要更好的理解测量过程,就需要先了解MeasureSpec,MeasureSpec在很大程度上决定了View的测量宽高,View的MeasureSpec创建受到父View的MeasureSpec和自身LayoutParams的影响。MeasureSpec代表着一个32位的int值,其中前两位代表specMode(测量模式),后30位代表specSize(在某个测量模式下的大小),MeasureSpec之所以打包成int值是为了避免过多的对象内存分配,它提供了打包和解包的方法,这种实现思想值得我们在开发中进行借鉴,MeasureSpec的源码如下所示,代码还是比较简单的:
public static class MeasureSpec {
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static int makeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {
if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {
return size + mode;
} else {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
}
public static int makeSafeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {
if (sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec && mode == UNSPECIFIED) {
return 0;
}
return makeMeasureSpec(size, mode);
}
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
//noinspection ResourceType
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
}
测量模式specMode有三类:
- UNSPECIFIED:未指定模式,父容器不对View作任何约束,想要多大就给多大。这种情况一般用在系统内部,表示一种测量的状态。一般情况下,我们不用关注该测量模式。
- EXACTLY:精准模式,父容器已经检测出View所需要的精准大小,这时候 View 的最终大小就是 SpecSize ,它对应于 LayoutParams 中的 match_parent 和具体的数值这两种情况。
- AT_MOST:最大模式,父容器指定了一个可用大小即specSize,具体大小要看不同View的具体实现,但确定的是View的大小不能超过这个值,它对应于LayoutParams 中的 wrap_content这种情况。
对于普通View,它的MeasureSpec创建受到父View的MeasureSpec和自身LayoutParams的影响,但是对于顶级View也就是DecorView来说,它的MeasureSpec创建是受到窗口的尺寸和自身LayoutParams影响的,MeasureSpec一旦确定下来,就可以确定View的测量宽高了。我们先来看看DecorView的MeasureSpec是如何创建的,在ViewRootImpl的performTraversals中会调用一个方法measureHierarchy,measureHierarchy方法中有下面这样一段代码,其中desiredWindowWidth和desiredWindowHeight是窗口的尺寸大小。
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowWidth, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
我们来看看getRootMeasureSpec方法的实现,这个方法并不长也很明确,当rootDimension也就是LayoutParams为MATCH_PARENT时,此时为精确模式,大小是窗口的大小;当rootDimension为WRAP_CONTENT时,此时为最大模式,大小不定,但是不能超过窗口的大小;当rootDimension为某个确定值时,此时为精确模式,大小就是这个确定值。
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}
接下来再来看看performMeasure方法的实现,代码比较简短,可以看到这边调用了View的measure方法,这个mView就是DecorView。
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
measure方法是一个final类型的方法,说明View的继承类ViewGroup等子类不能重写此方法,在View的Measure方法中会去调用onMeasure方法,对于View的测量我们主要看的就是onMeasure方法,它是完成View的测量过程的关键方法。
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
// first clears the measured dimension flag
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
resolveRtlPropertiesIfNeeded();
int cacheIndex = forceLayout ? -1 : mMeasureCache.indexOfKey(key);
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
...
}
先来看看View的onMeasure方法的实现,里面只是调用了setMeasuredDimension,这个方法是用来设置保存测量宽高值的,getDefaultSize这个方法也比较简洁,可以看到,当specMode为UNSPECIFIED,返回的测量大小是第一个参数size,也就是getSuggestedMinimumWidth、getSuggestedMinimumHeight方法的返回值,当MeasureSpec的specMode为AT_MOST或者EXACTLY时,返回的就是测量大小specSize,可以发现specMode是AT_MOST时,返回的测量宽高和EXACTLY是一样的,这意味着我们在自定义View设置LayoutParams为wrap_content(对应AT_MOST)时需要自己去设定这种模式下的宽高,否则,它使用的是父容器剩余的可以使用的宽高。
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
getSuggestedMinimumWidth方法中会判断View是否设置有背景,如果没有,则返回mMinWidth,这个值是我们在布局中文件中设置的android:minWidth的值,如果设置有背景,则返回的是max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth()),我们看下Drawable中getMinimumWidth的实现,这个方法返回的是背景建议的最小宽度,也就是原始宽度,当然前提是这个Drawable有原始宽度,比如BitmapDrawable,否则就返回0,比如Drawable是ShapeDrawable。同理,getSuggestedMinimumHeight也是类似的。
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
public int getMinimumWidth() {
final int intrinsicWidth = getIntrinsicWidth();
return intrinsicWidth > 0 ? intrinsicWidth : 0;
}
再来看看ViewGroup的measure过程,ViewGroup不但需要完成自身的测量,还需要去遍历执行调用子View的measure方法,继续对子View进行测量,完成一次测量过程。ViewGroup并没有去实现onMeasure方法,因为对于很多ViewGroup的子类比如RelativeLayout、FrameLayout和LinearLayout它们的布局是不同的,有各自的特性,它们的onMeasure方法各有自身的实现,所以ViewGroup没有onMeasure方法的统一实现。
先通过FrameLayout的onMeasure方法实现来分析下它的测量过程,因为这个方法比较长,我们分段进行说明。从源码中首先判断FrameLayout的宽或者高为精确模式EXACTLY,那么measureMatchParentChildren为true,这个变量下面会用到,maxWidth和maxHeight是最终用来计算FrameLayout测量模式为最大模式AT_MOST或者未指定模式UNSPECIFIED时用来确定其测量宽高,接下里可以看得到,然后通过循环遍历子View,这里调用了measureChildWithMargins方法,这个方法是用来确定子View的MeasureSpec并调用子View的measure方法,把测量过程往下传递到子View的,同时,还可以看到最终循环下来maxWidtht的值是子View测量宽度加上左右两边Margin的最大值,maxHeight的值是子View测量高度加上上下两边Margin的最大值。
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
...
}
当对子View循环结束后,FrameLayout就会测量自己的大小,源码如下,首先是将maxWidth和maxHeight加上FrameLayout中的padding值,然后通过和背景和前景(如果有的话)的原始宽高进行对比获取最大值,setMeasuredDimension就是设置FrameLayout的测量宽高。
// Account for padding too
maxWidth += getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground();
maxHeight += getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// Check against our minimum height and width
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
// Check against our foreground's minimum height and width
final Drawable drawable = getForeground();
if (drawable != null) {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, drawable.getMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, drawable.getMinimumWidth());
}
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
FrameLayout的onMeasure方法还有一段代码,会对满足一些条件的子View重新测量,结合上面的代码,这些条件就是当FragLayout的宽或高的测量模式为EXACTLY,并且子View的布局中lp.width或者lp.height为MATCH_PARENT时,就会在最后对这些子View重新测量。
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int height = Math.max(0, getMeasuredHeight()
- getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground()
- lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
回过头来看看resolveSizeAndState方法是如何得到FrameLayout的测量宽高的,以得到测量宽度为例,如果它的测量模式是EXACTLY,也就是布局是match_parent或者具体的数值是,宽度为specSize,如果是AT_MOST,那么它的宽度是size,也就是maxWidth,但是不能超过父容器的剩余空间,如果是UNSPECIFIED,那么测量宽度就是maxWidth,具体可以看下源码:
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) {
final int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
final int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
final int result;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (specSize < size) {
result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;
} else {
result = size;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
default:
result = size;
}
return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}
上面提到measureChildWithMargins方法是用来测量子View的宽高的,将测量过程传递到子View,这个方法是在ViewGroup中的,ViewGroup还提供了一个measureChildren方法,不过这个方法是在AbsoluteLayout的onMeasure方法有调用,来看看measureChildWithMargins这个方法的实现,这个方法首先会调用getChildMeasureSpec来获取子元素的MeasureSpec,从传递的参数中很显然可以看出,View的MeasureSpec的创建与父View的MeasureSpec和View布局自身的LayoutParams有关,另外就是与子View的margin和父View的padding有关。
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
我们进到getChildMeasureSpec方法来看看View是如何得到它的MeasureSpec的,这个方法不难理解,首先获取父View的specMode和specSize,对子View来说可用的父View的空间大小size,然后根据各种情况进行判断,与获取测量宽度的MeasureSpec为例,比如当父View的specMode为EXACTLY时,如果子View的lp.width也就是childDimension为具体值是,那么resultMode就是这个具体值,resultMode为精准模式EXACTLY;如果子View的childDimension为MATCH_PARENT时,子View的resultSize是可用父View的空间大小size,resultMode也是精准模式EXACTLY;如果子View的childDimension为WRAP_CONTENT时,子View的resultSize是可用父View的空间大小size,resultMode是最大模式AT_MOST。其它情况大家可以自行结合自己在开发中在layout的布局效果自行分析即可,最后就是将resultSize和resultMode打包成MeasureSpec。
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//noinspection ResourceType
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
2、layout过程
layout是用来确定View的位置的,它会在layout方法中确定View的位置,对于ViewGroup来说,还会调用onLayout方法来继续遍历调用子View的layout方法确定子View的位置,把布局往下传递,layout过程是从performLayout方法开始的,host就是根View也就是DecorView。
private void performLayout(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, int desiredWindowWidth,
int desiredWindowHeight) {
mLayoutRequested = false;
mScrollMayChange = true;
mInLayout = true;
final View host = mView;
if (host == null) {
return;
}
...
try {
host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight());
...
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
mInLayout = false;
}
先来看看View的layout方法,首先会通过setFrame方法来给View的四个顶点mLeft、mTop、mRight和mBottom赋值,这四个顶点一旦确定,那么View在父容器的位置也就确定了,接着会调用onLayout方法,这个方法是用来确定子View位置的,对于View来说是空实现,因为View它没有子View。
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT) != 0) {
onMeasure(mOldWidthMeasureSpec, mOldHeightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
if (shouldDrawRoundScrollbar()) {
if(mRoundScrollbarRenderer == null) {
mRoundScrollbarRenderer = new RoundScrollbarRenderer(this);
}
} else {
mRoundScrollbarRenderer = null;
}
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) {
ArrayList listenersCopy =
(ArrayList)li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone();
int numListeners = listenersCopy.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB);
}
}
}
final boolean wasLayoutValid = isLayoutValid();
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_IS_LAID_OUT;
...
}
protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
boolean changed = false;
if (mLeft != left || mRight != right || mTop != top || mBottom != bottom) {
changed = true;
// Remember our drawn bit
int drawn = mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWN;
int oldWidth = mRight - mLeft;
int oldHeight = mBottom - mTop;
int newWidth = right - left;
int newHeight = bottom - top;
boolean sizeChanged = (newWidth != oldWidth) || (newHeight != oldHeight);
// Invalidate our old position
invalidate(sizeChanged);
mLeft = left;
mTop = top;
mRight = right;
mBottom = bottom;
...
}
return changed;
}
跟onMeasure方法一样,每种ViewGroup的onLayout方法实现方式也是不同的,我们这次以LinerLayout的onLaout方法为例,LinerLayout有两种布局方式,我们来看下layoutVertical方法的实现。
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
layoutVertical(l, t, r, b);
} else {
layoutHorizontal(l, t, r, b);
}
}
layoutVertical这个方法会遍历所有的子View,然后调用setChildFrame,这个方法是用来确定子元素的位置的,这个方法的内部其实就是调用了子元素的layout方法,layout方法从上面就知道,它会确定view的4个顶点赋值,从而确定View在父View中的位置,然后再调用onLayout方法,这样就把布局过程往下传递,从而完成整个View树的遍历。同时可以看到childTop会逐渐增大,这意味着子View会不断放置到靠下的位置,这也符合LinerLayout布局设置Vertical方向时的布局特性。
void layoutVertical(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
...
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
childTop += measureNullChild(i);
} else if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
final LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp =
(LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
...
if (hasDividerBeforeChildAt(i)) {
childTop += mDividerHeight;
}
childTop += lp.topMargin;
setChildFrame(child, childLeft, childTop + getLocationOffset(child),
childWidth, childHeight);
childTop += childHeight + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child);
i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
}
}
}
private void setChildFrame(View child, int left, int top, int width, int height) {
child.layout(left, top, left + width, top + height);
}
3、draw过程
经过measure和layout过程之后就需要将View绘制到屏幕上显示出来,draw过程是从performDraw方法开始的,最终会执行到判断是否开启了硬件加速,如果没有开启则会执行drawSoftware方法,这个方法会直接去调用mView.draw(canvas),如果开启了则会去执行mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer.draw方法,这个方法的内部最终还是会执行到DecorView 的 draw 方法上,它的主要流程如下:
private void performDraw() {
...
try {
boolean canUseAsync = draw(fullRedrawNeeded);
if (usingAsyncReport && !canUseAsync) {
mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer.setFrameCompleteCallback(null);
usingAsyncReport = false;
}
} finally {
mIsDrawing = false;
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
...
}
private boolean draw(boolean fullRedrawNeeded) {
...
if (!dirty.isEmpty() || mIsAnimating || accessibilityFocusDirty) {
if (mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer != null && mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer.isEnabled()) {
...
mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer.draw(mView, mAttachInfo, this);
} else {
...
if (!drawSoftware(surface, mAttachInfo, xOffset, yOffset,
scalingRequired, dirty, surfaceInsets)) {
return false;
}
}
}
...
}
对于普通情况下View的绘制步骤主要遵循如下几步:绘制背景(drawBackground(canvas))、绘制自己(onDraw(canvas))、绘制children(dispatchDraw(canvas))、绘制装饰decorations(onDrawForeground(canvas)),如果需要对默认焦点突出显示还会调用drawDefaultFocusHighlight(canvas),其中,向下绘制children的分发是调用dispatchDraw方法,而测量和布局的向下分发是调用onMeasure和onLayout方法的,这是一个区别,源码中的也有详细绘制流程注释,draw的主要源码如下:
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags;
mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN;
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
*/
// Step 1, draw the background, if needed
int saveCount;
drawBackground(canvas);
// skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case)
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0;
boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0;
if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) {
// Step 3, draw the content
onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
drawAutofilledHighlight(canvas);
// Overlay is part of the content and draws beneath Foreground
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
// Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars)
onDrawForeground(canvas);
// Step 7, draw the default focus highlight
drawDefaultFocusHighlight(canvas);
if (debugDraw()) {
debugDrawFocus(canvas);
}
// we're done...
return;
}
...
}
View绘制原理源码就分析到这了,如果有不对的地方欢迎指出和交流。
参考:
书籍:《Android开发艺术探索》