[TOC]
Android 控件架构与自定义控件详解
Android控价架构
控件树,上层控件负责下层子控件的测量与绘制,并传递交互事件。
为什么要自定义控件:
特定的显示风格
处理特有的用户交互
优化我们的布局
封装等...
如何自定义控件
自定义属性的声明
测量onMeasure
布局onLayout(ViewGroup)
绘制onDraw
onTouchEvent
onInterceptTouchEvent(ViewGroup)
View的测量——onMeasure
如果该Vewi还需要使用wrap_content属性,那么还需要重写onMeasure()方法。
EXACTLY、AT_MOST、UMSPECIFIED
MeasureSpec类
setMeasuerdDimension()
requestLayout()
|Mode|描述
|-------------|
| EXACTLY | 精确模式,控件布局中,指定为100dp或者match_parent
| AT_MOST | 最大值模式,不超过父控件的最大尺寸,需要重写onMeasure()方法,Math.min(result,specSize),指定为wrap_content
| UNSPECIFIED | View有多大就多大,自定义View绘制使用
源代码中,在重写onMeasure()方法后,就是把测量后的宽高作为参数设置给setMeasuredDimension().
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
源代码
/**
* Extracts the mode from the supplied measure specification.
*
* @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the mode from
* @return {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#UNSPECIFIED},
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#AT_MOST} or
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#EXACTLY}
*/
@MeasureSpecMode
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
//noinspection ResourceType
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
//从提供的测量规范中提取模式。
/**
* Extracts the size from the supplied measure specification.
*
* @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the size from
* @return the size in pixels defined in the supplied measure specification
*/
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
//绘制的大小
测量模板代码
public void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec,int heightMeasuureSpec){
setMeasureDimension(measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec),measureHeight(heightMeasureSpec));
}
private int measureWidth(int measureSpec) {
int result = 0;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
result = specSize;
}else {
result = 400;
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
result = Math.min(result,specSize);
}
}
return result;
}
布局onLayout(VIewGroup)
决定子View的位置
尽可能将onMeasure中一些操作移动到此方法中
requestLayout()
绘制onDraw
绘制内容区域
invaliudate(),postInvalidate()invalidate(),主线程
postInvalidate(),子线程
Canvas.drawXXX
translate、rotate、scale、skew
save() 、restore()
Canvas就像是一个画板,使用Paint就可以在上面作画。
Canvas canvas= new Canvas(bitmap);穿进去的bitmap与通过这个bitmap创建的Canvas画布是紧紧联系在一起的,这个过程我们称之为装载画布。这个bitmap用来存储所有绘制在Canvas上的像素信息
事件拦截机制分析
Android为触摸事件封装了一个类 ——MotionEvent,本质就是动作类型加坐标。当同一个事件,子View和父ViewGroup都有可能想要处理的时候就产生了“事件拦截”。整个流程就是事件的分发、拦截、处理。
对ViewGroup来说,会重写三个方法
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)//一般不重写这个方法
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)
而对于View来说,只重写两个方法
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)
intercept 拦截 v. 拦截者 n.
dispatch 派遣,调度,分发 v. 新闻报道n.
事件的传递顺序是最外层的父ViewGroup一层一层的派遣然后决定是否拦截任务;
事件的处理顺序是最里层的子View依次递交这个onTouchEvent()的处理结果直至任务完成。
初始情况下,返回值都是false。
parent.requestDisallow-InterceptTouchEvent(true);告诉父控件不要拦截我的手势
自定义View的方式:
对现有控件进行扩展
public class AmazingTV extends TextView {
private Paint mPaint1;
private Paint mPaint2;
public AmazingTV(Context context,AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
initView();
//绘制外层
canvas.drawRect(0,0,getMeasuredWidth(),getMeasuredHeight(),mPaint1);
//绘制内层
canvas.drawRect(5,5,getMeasuredWidth()-5,getMeasuredHeight()-5,mPaint2);
canvas.save();//save()方法的目的是什么?
canvas.translate(10,0);//绘制文字前平移10像素
//在回调父类方法前,实现自己的逻辑,对TextView来说即是在绘制文本内容前
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.restore();
}
private void initView() {
mPaint1 = new Paint();
mPaint1.setColor(getResources().getColor(android.R.color.holo_blue_bright));
mPaint1.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
mPaint2 = new Paint();
mPaint2.setColor(Color.YELLOW);
mPaint2.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
}
}
动态的闪光灯效果:
其中最关键的就是getPaint()方法中获取当前Textview的paint对象,并且设置LinearGradient属性,最后用矩阵不断平移渐变效果,就实现了这个效果。
public class CustomTextView extends TextView {
int mViewWidth = 0;
private Paint mPaint;
private LinearGradient mLinearGradient;
private Matrix matrix;
private int mTranslate;
public CustomTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
if (mViewWidth == 0) {
mViewWidth = getMeasuredWidth();
if (mViewWidth > 0) {
//获取画笔对象
mPaint = getPaint();
//Shader渲染器来设置一个不断变化的LinearGradient
mLinearGradient = new LinearGradient(0, 0, mViewWidth, 0, new int[]{Color.BLUE, 0xffffffff, Color.BLUE},
null, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP);
mPaint.setShader(mLinearGradient);
//矩阵
matrix = new Matrix();
}
}
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
if (matrix != null) {
mTranslate += mViewWidth + 5;
if (mTranslate > 2 * mViewWidth / 5) {
mTranslate = -mViewWidth;
}
matrix.setTranslate(mTranslate, 0);
mLinearGradient.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
//每隔100毫秒闪动一下
postInvalidateDelayed(100);
}
}
}
通过组合来显示新的控件
设计需要的属性(res/value/attrs.xml)
实现一个我们的View(继承View并实现带属性参数的构造方法)
引用我们的View(xml导包并添加xmlns)
设计UI模板的时候,还可以给TopBar增加相应的接口,让调用者能够更加灵活地控制TopBar,修改UI时能够快速修改。
public class TopBar extends RelativeLayout {private String title;private int titleTextSize;private int titleTextColor;private int leftTextColor;private Drawable leftBackground;private String leftText;private int rightTextColor;private Drawable rightBackground;private String rightText;private Button leftButton;private Button rightButton;private TextView tvTitle;private LayoutParams leftParams,rightParams,titleParams;private topbarClickListener listener;public interface topbarClickListener{public void leftClick();public void rightClick();}
//定义接口
public void setOntopbarClikListener(topbarClickListener listener){this.listener = listener;}public TopBar(Context context){super(context);}public TopBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {super(context, attrs);TypedArray ta = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.Toolbar);
//TypedArray 存放键值对,通过下划线链接一个新的名字leftTextColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.TopBar_leftTextColor,0);leftBackground = ta.getDrawable(R.styleable.TopBar_leftBackground);leftText = ta.getString(R.styleable.TopBar_leftText);rightTextColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.TopBar_rightTextColor,0);rightBackground = ta.getDrawable(R.styleable.TopBar_rightBackground);rightText = ta.getString(R.styleable.TopBar_rightText);title = ta.getString(R.styleable.TopBar_title);titleTextColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.TopBar_titleTextColor,0);titleTextSize = ta.getInt(R.styleable.TopBar_titleTextSize,0);ta.recycle();//防止资源浪费或者缓存引起的错误 //组合模式,把几个存在的建立为一个新的控件 leftButton = new Button(context);rightButton = new Button(context);tvTitle = new TextView(context);leftButton.setBackground(leftBackground);leftButton.setTextColor(leftTextColor);leftButton.setText(leftText);rightButton.setTextColor(rightTextColor);rightButton.setBackground(rightBackground);rightButton.setText(rightText);tvTitle.setText(title);tvTitle.setTextColor(titleTextColor);tvTitle.setTextSize(titleTextSize);tvTitle.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);setBackgroundColor(0xfff59563);leftParams = new LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);leftParams.addRule(RelativeLayout.ALIGN_PARENT_LEFT,TRUE);addView(leftButton,leftParams);rightParams = new LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);rightParams.addRule(RelativeLayout.ALIGN_PARENT_RIGHT,TRUE);addView(rightButton,rightParams);titleParams = new LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);//宽和高 titleParams.addRule(RelativeLayout.CENTER_IN_PARENT,TRUE);//添加规则,是根据相对布局的方式 addView(tvTitle,titleParams);//加载布局的方式
//暴露接口给调用者 leftButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {@Override public void onClick(View v) {listener.leftClick();}});rightButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {@Override public void onClick(View v) {listener.rightClick();}});}}
Activity中调用的时候实现接口回调
TopBar topbar = (TopBar) findViewById(R.id.topBar);topbar.setOntopbarClikListener(new TopBar.topbarClickListener() {@Override public void leftClick() {Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"left",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();}@Override public void rightClick() {Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"left",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();}});
引用UI模板
重写View来实现全新的控件
这里画一个半弧圆,分解图形,当脑海中有了一副设计图之后,剩下的事情就只是对坐标的计算了。
public class CircleView extends View {//圆的长度 private int mCircleXY;//屏幕高宽 private int w, h;//圆的半径 private float mRadius;//圆的画笔 private Paint mCirclePaint;//弧线的画笔 private Paint mArcPaint;//文本画笔 private Paint mTextPaint;//需要显示的文字 private String mShowText = "半弧圆";//文字大小 private int mTextSize = 50;//圆心扫描的弧度 private int mSweepAngle = 270;public CircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {super(context, attrs);//获取屏幕高宽 WindowManager wm = (WindowManager) getContext().getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);w = wm.getDefaultDisplay().getWidth();h = wm.getDefaultDisplay().getHeight();init();}private void init() {mCircleXY = w / 2;mRadius = (float) (w * 0.5 / 2);mCirclePaint = new Paint();mCirclePaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);mArcPaint = new Paint();//设置线宽 mArcPaint.setStrokeWidth(100);//设置空心 mArcPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);//设置颜色 mArcPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);mTextPaint = new Paint();mTextPaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);mTextPaint.setTextSize(mTextSize);}@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {super.onDraw(canvas);//绘制矩形(左,上,右,下) RectF mArcRectF = new RectF((float) (w * 0.1), (float) (w * 0.1), (float) (w * 0.9), (float) (w * 0.9));//绘制圆,(圆心x,圆心y,半径,画笔) canvas.drawCircle(mCircleXY, mCircleXY, mRadius, mCirclePaint);//绘制弧线(圆弧的外轮廓矩形区域,起始角度,圆弧扫过的角度,圆心包括与否,画笔)
//正右边为0°正上角为270°,第四个参数是是否和圆心有连线 canvas.drawArc(mArcRectF, 270, mSweepAngle, false, mArcPaint);//绘制文本(文字,开始,结束,x,y,画笔) canvas.drawText(mShowText, 0, mShowText.length(), mCircleXY - (mTextSize / 4), mCircleXY + (mTextSize / 4), mTextPaint);}//设置一些其他的状态,设置他的弧度,我们写一个对外的方法 public void setSweepValues(float sweepValues){if(sweepValues !=- 0){mSweepAngle = (int) sweepValues;}else{//如果没有,我们默认设置 mSweepAngle = 30;}//记得刷新 invalidate();}}
sweep 打扫,掠过 v.
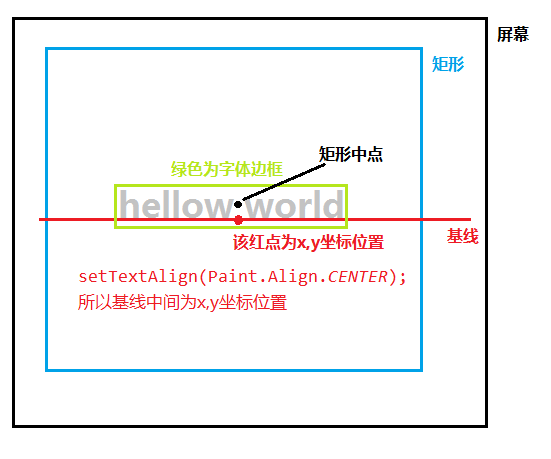
canvas.drawText文字居中
Android是基于基线(Baseline),top+bottom是字体高度
绘制的时候取决于基线,默认为left,但是可以通过
paint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.CENTER);设置
首先找到矩形的中心,已知矩形中心根据top和bottom可以算出Baseline的y位置,这样文字的位置就确定了。
int baseLineY = (int) (rect.centerY() - top/2 - bottom/2);//基线中间点的y轴计算公式
canvas.drawText("你好世界",rect.centerX(),baseLineY,textPaint);
这里有点要注意textPaint.getFontMetrics()这个方法一定要在设置字体大小或者样式等等一系列会影响字体的方法后在调用,不然获取到的top和bottom值不准.
Paint.FontMetrics fontMetrics = textPaint.getFontMetrics();float top = fontMetrics.top;//为基线到字体上边框的距离,即上图中的topfloat bottom = fontMetrics.bottom;//为基线到字体下边框的距离,即上图中的bottom
待: onTouchEvent