算法:图(Graph)的遍历、最小生成树和拓扑排序
背景
不同的数据结构有不同的用途,像:数组、链表、队列、栈多数是用来做为基本的工具使用,二叉树多用来作为已排序元素列表的存储,B 树用在存储中,本文介绍的 Graph 多数是为了解决现实问题(说到底,所有的数据结构都是这个目的),如:网络布局、任务安排等。
图的基本概念
示例
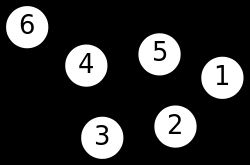
顶点(Vertex)
上图的 1、2、3、4、5、6 就是顶点。
邻接(Adjoin)
如果 A 和 B 通过定向边相连,且方向为 A -> B,则 B 为 A 的邻接,如果相连的边是没有方向的,则 A 和 B 互为邻接。
边(Edge)
顶点之间的连线就是边。
连通图(Connected Graph)
不考虑边的方向性,从任何一个节点都可以遍历到其它节点。本文的所有算法(除了拓扑排序)只适合连通图。
定向图(Directed Graph)
图中的所有边都带方向。
权重图(Weighted Graph)
图中的所有边都有权重。
图的程序表示
如果图 T 有 A、B、C 三个节点,有 A -> B,B -> C,C -> A 三个边(没有方向),如何在程序中表示 T 呢?
邻接矩阵
A B C
A 0 1 0
B 0 0 1
C 1 0 0
矩阵的行代表了定向边的起始顶点,矩阵的列代表了定向边的介绍顶点,矩阵中的值:1 代表了列是行的邻接,0 则反之。如果边没有方向,则矩阵是相对于正对角线是对称的。
邻接列表
A:[ B ]
B:[ C ]
C:[ A ]
这个就不多说了,多数书籍使用都是邻接矩阵。
代码
1 class Vertex<T> 2 { 3 public T Value { get; set; } 4 5 public bool WasVisited { get; set; } 6 } 7 8 class Graph<T> 9 { 10 #region 私有字段 11 12 private int _maxSize; 13 private Vertex<T>[] _vertexs; 14 private bool[][] _edges; 15 private int _vertexCount = 0; 16 17 #endregion 18 19 #region 构造方法 20 21 public Graph(int maxSize) 22 { 23 _maxSize = maxSize; 24 _vertexs = new Vertex<T>[_maxSize]; 25 _edges = new bool[_maxSize][]; 26 for (var i = 0; i < _maxSize; i++) 27 { 28 _edges[i] = new bool[_maxSize]; 29 } 30 } 31 32 #endregion 33 34 #region 添加顶点 35 36 public Graph<T> AddVertex(T value) 37 { 38 _vertexs[_vertexCount++] = new Vertex<T> { Value = value }; 39 40 return this; 41 } 42 43 #endregion 44 45 #region 添加边 46 47 public Graph<T> AddUnDirectedEdge(T startItem, T endItem) 48 { 49 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 50 var endIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(endItem); 51 52 _edges[startIndex][endIndex] = true; 53 _edges[endIndex][startIndex] = true; 54 55 return this; 56 } 57 58 public Graph<T> AddDirectedEdge(T startItem, T endItem) 59 { 60 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 61 var endIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(endItem); 62 63 _edges[startIndex][endIndex] = true; 64 65 return this; 66 } 67 68 #endregion 69 }
图的常见算法
遍历
本文的遍历算法只适合一般的无向图。
深度优先遍历
深度优先遍历的原则是:尽可能的离开始节点远,二叉树的三种遍历算法都属于这种算法。
示例

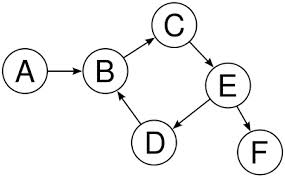
从 A 开始的遍历顺序为(邻接的遍历顺序为字母升序):ABCEDBF。
栈版本
1 #region 深度优先遍历:栈版本 2 3 public void DepthFirstSearch(T startItem, Action<T> action) 4 { 5 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 6 var stack = new Stack<int>(); 7 8 this.DepthFirstSearchVisit(stack, startIndex, action); 9 while (stack.Count > 0) 10 { 11 var adjoinVertexIndex = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndex(stack.Peek()); 12 if (adjoinVertexIndex >= 0) 13 { 14 this.DepthFirstSearchVisit(stack, adjoinVertexIndex, action); 15 } 16 else 17 { 18 stack.Pop(); 19 } 20 } 21 22 this.ResetVisited(); 23 } 24 25 private void DepthFirstSearchVisit(Stack<int> stack, int index, Action<T> action) 26 { 27 _vertexs[index].WasVisited = true; 28 action(_vertexs[index].Value); 29 stack.Push(index); 30 } 31 32 #endregion
递归版本
1 #region 深度优先遍历:递归版本 2 3 public void DepthFirstSearchRecursion(T startItem, Action<T> action) 4 { 5 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 6 7 this.DepthFirstSearchRecursionVisit(startIndex, action); 8 9 this.ResetVisited(); 10 } 11 12 private void DepthFirstSearchRecursionVisit(int index, Action<T> action) 13 { 14 _vertexs[index].WasVisited = true; 15 action(_vertexs[index].Value); 16 17 var adjoinVertexIndex = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndex(index); 18 while (adjoinVertexIndex >= 0) 19 { 20 this.DepthFirstSearchRecursionVisit(adjoinVertexIndex, action); 21 adjoinVertexIndex = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndex(index); 22 } 23 } 24 25 #endregion
广度优先遍历
广度优先遍历的原则是:尽可能的离开始节点近。这个算法没有办法通过递归实现,多数都是使用的队列(终于发现了队列的又一个用处)。
示例

从 A 开始的遍历顺序为(邻接的遍历顺序为字母升序):ABCEDFB。
代码
1 #region 广度优先遍历 2 3 public void BreadthFirstSearch(T startItem, Action<T> action) 4 { 5 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 6 var queue = new Queue<int>(); 7 8 this.BreadthFirstSearchVisit(queue, startIndex, action); 9 while (queue.Count > 0) 10 { 11 var adjoinVertexIndexs = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndexs(queue.Dequeue()); 12 foreach (var adjoinVertexIndex in adjoinVertexIndexs) 13 { 14 this.BreadthFirstSearchVisit(queue, adjoinVertexIndex, action); 15 } 16 } 17 18 this.ResetVisited(); 19 } 20 21 private void BreadthFirstSearchVisit(Queue<int> queue, int index, Action<T> action) 22 { 23 _vertexs[index].WasVisited = true; 24 action(_vertexs[index].Value); 25 queue.Enqueue(index); 26 } 27 28 #endregion
最小生成树
本文的最小生成树算法只适合一般的无向图。
将 N 个顶点连接起来的最小树叫:最小生成树。
给定一个颗有 N 个顶点的连通图,则最小生成树的边为:N - 1。
不同的遍历算法生成的最小生成树是不同的,下面使用广度优先遍历来生成最小树。
示例

从 A 开始的遍历顺序为(邻接的遍历顺序为字母升序):A->B、B->C、C->E、E->D、E->F、D->B。
代码
1 #region 最小生成树 2 3 public void DisplayMinimumSpanningTree(T startItem) 4 { 5 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 6 var queue = new Queue<int>(); 7 8 _vertexs[startIndex].WasVisited = true; 9 queue.Enqueue(startIndex); 10 while (queue.Count > 0) 11 { 12 var currentIndex = queue.Dequeue(); 13 var adjoinVertexIndexs = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndexs(currentIndex); 14 foreach (var adjoinVertexIndex in adjoinVertexIndexs) 15 { 16 Console.WriteLine(_vertexs[currentIndex].Value + "->" + _vertexs[adjoinVertexIndex].Value); 17 18 _vertexs[adjoinVertexIndex].WasVisited = true; 19 queue.Enqueue(adjoinVertexIndex); 20 } 21 } 22 23 this.ResetVisited(); 24 } 25 26 #endregion
拓扑排序
拓扑排序只适合定向图,且图中不存在循环结构。其算法非常简单,依次获取图中的没有邻接顶点的顶点,然后删除该顶点。
示例

上图出现了循环结构,假如没有顶点 C,拓扑排序的结果为(顶点的遍历顺序为字母升序):EFDAB。
算法
1 #region 拓扑排序 2 3 public List<T> TopologySort() 4 { 5 var cloneVertexs = (Vertex<T>[])_vertexs.Clone(); 6 var cloneEdges = (bool[][])_edges.Clone(); 7 var cloneVertexCount = _vertexCount; 8 9 var results = new List<T>(); 10 while (_vertexCount > 0) 11 { 12 var successor = this.NextSuccessor(); 13 if (successor == -1) 14 { 15 throw new InvalidOperationException("出现循环了!"); 16 } 17 18 results.Insert(0, _vertexs[successor].Value); 19 20 this.RemoveVertex(successor); 21 _vertexCount--; 22 } 23 24 _vertexs = cloneVertexs; 25 _edges = cloneEdges; 26 _vertexCount = cloneVertexCount; 27 28 return results; 29 } 30 31 private int NextSuccessor() 32 { 33 for (var row = 0; row < _vertexCount; row++) 34 { 35 if (_edges[row].Take(_vertexCount).All(x => !x)) 36 { 37 return row; 38 } 39 } 40 41 return -1; 42 } 43 44 private void RemoveVertex(int successor) 45 { 46 for (int i = successor; i < _vertexCount - 1; i++) 47 { 48 _vertexs[i] = _vertexs[i + 1]; 49 } 50 51 for (int row = successor; row < _vertexCount - 1; row++) 52 { 53 for (int column = 0; column < _vertexCount; column++) 54 { 55 _edges[row][column] = _edges[row + 1][column]; 56 } 57 } 58 59 for (int column = successor; column < _vertexCount - 1; column++) 60 { 61 for (int row = 0; row < _vertexCount; row++) 62 { 63 _edges[row][column] = _edges[row][column + 1]; 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 68 #endregion
完整代码

1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Collections.ObjectModel; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace DataStuctureStudy.Graphs 9 { 10 class GraphTest 11 { 12 public static void Test() 13 { 14 var graph = new Graph<String>(50); 15 graph 16 .AddVertex("A") 17 .AddVertex("B") 18 .AddVertex("C") 19 .AddVertex("D") 20 .AddVertex("E") 21 .AddVertex("F") 22 .AddVertex("G") 23 .AddVertex("H") 24 .AddVertex("I"); 25 graph 26 .AddDirectedEdge("A", "B").AddDirectedEdge("A", "C").AddDirectedEdge("A", "D").AddDirectedEdge("A", "E") 27 .AddDirectedEdge("B", "F") 28 .AddDirectedEdge("D", "G") 29 .AddDirectedEdge("F", "H") 30 .AddDirectedEdge("G", "I"); 31 32 Console.WriteLine("深度遍历,栈版本:"); 33 graph.DepthFirstSearch("A", Console.Write); 34 Console.WriteLine(); 35 Console.WriteLine(); 36 37 Console.WriteLine("深度遍历,递归版本:"); 38 graph.DepthFirstSearchRecursion("A", Console.Write); 39 Console.WriteLine(); 40 Console.WriteLine(); 41 42 Console.WriteLine("广度遍历:"); 43 graph.BreadthFirstSearch("A", Console.Write); 44 Console.WriteLine(); 45 Console.WriteLine(); 46 47 Console.WriteLine("最小生成树:"); 48 graph.DisplayMinimumSpanningTree("A"); 49 Console.WriteLine(); 50 Console.WriteLine(); 51 52 Console.WriteLine("拓扑排序:"); 53 var results = graph.TopologySort(); 54 Console.WriteLine(String.Join("->", results.ToArray())); 55 Console.WriteLine(); 56 } 57 58 class Vertex<T> 59 { 60 public T Value { get; set; } 61 62 public bool WasVisited { get; set; } 63 } 64 65 class Graph<T> 66 { 67 #region 私有字段 68 69 private int _maxSize; 70 private Vertex<T>[] _vertexs; 71 private bool[][] _edges; 72 private int _vertexCount = 0; 73 74 #endregion 75 76 #region 构造方法 77 78 public Graph(int maxSize) 79 { 80 _maxSize = maxSize; 81 _vertexs = new Vertex<T>[_maxSize]; 82 _edges = new bool[_maxSize][]; 83 for (var i = 0; i < _maxSize; i++) 84 { 85 _edges[i] = new bool[_maxSize]; 86 } 87 } 88 89 #endregion 90 91 #region 添加顶点 92 93 public Graph<T> AddVertex(T value) 94 { 95 _vertexs[_vertexCount++] = new Vertex<T> { Value = value }; 96 97 return this; 98 } 99 100 #endregion 101 102 #region 添加边 103 104 public Graph<T> AddUnDirectedEdge(T startItem, T endItem) 105 { 106 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 107 var endIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(endItem); 108 109 _edges[startIndex][endIndex] = true; 110 _edges[endIndex][startIndex] = true; 111 112 return this; 113 } 114 115 public Graph<T> AddDirectedEdge(T startItem, T endItem) 116 { 117 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 118 var endIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(endItem); 119 120 _edges[startIndex][endIndex] = true; 121 122 return this; 123 } 124 125 #endregion 126 127 #region 深度优先遍历:栈版本 128 129 public void DepthFirstSearch(T startItem, Action<T> action) 130 { 131 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 132 var stack = new Stack<int>(); 133 134 this.DepthFirstSearchVisit(stack, startIndex, action); 135 while (stack.Count > 0) 136 { 137 var adjoinVertexIndex = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndex(stack.Peek()); 138 if (adjoinVertexIndex >= 0) 139 { 140 this.DepthFirstSearchVisit(stack, adjoinVertexIndex, action); 141 } 142 else 143 { 144 stack.Pop(); 145 } 146 } 147 148 this.ResetVisited(); 149 } 150 151 private void DepthFirstSearchVisit(Stack<int> stack, int index, Action<T> action) 152 { 153 _vertexs[index].WasVisited = true; 154 action(_vertexs[index].Value); 155 stack.Push(index); 156 } 157 158 #endregion 159 160 #region 深度优先遍历:递归版本 161 162 public void DepthFirstSearchRecursion(T startItem, Action<T> action) 163 { 164 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 165 166 this.DepthFirstSearchRecursionVisit(startIndex, action); 167 168 this.ResetVisited(); 169 } 170 171 private void DepthFirstSearchRecursionVisit(int index, Action<T> action) 172 { 173 _vertexs[index].WasVisited = true; 174 action(_vertexs[index].Value); 175 176 var adjoinVertexIndex = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndex(index); 177 while (adjoinVertexIndex >= 0) 178 { 179 this.DepthFirstSearchRecursionVisit(adjoinVertexIndex, action); 180 adjoinVertexIndex = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndex(index); 181 } 182 } 183 184 #endregion 185 186 #region 广度优先遍历 187 188 public void BreadthFirstSearch(T startItem, Action<T> action) 189 { 190 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 191 var queue = new Queue<int>(); 192 193 this.BreadthFirstSearchVisit(queue, startIndex, action); 194 while (queue.Count > 0) 195 { 196 var adjoinVertexIndexs = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndexs(queue.Dequeue()); 197 foreach (var adjoinVertexIndex in adjoinVertexIndexs) 198 { 199 this.BreadthFirstSearchVisit(queue, adjoinVertexIndex, action); 200 } 201 } 202 203 this.ResetVisited(); 204 } 205 206 private void BreadthFirstSearchVisit(Queue<int> queue, int index, Action<T> action) 207 { 208 _vertexs[index].WasVisited = true; 209 action(_vertexs[index].Value); 210 queue.Enqueue(index); 211 } 212 213 #endregion 214 215 #region 最小生成树 216 217 public void DisplayMinimumSpanningTree(T startItem) 218 { 219 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 220 var queue = new Queue<int>(); 221 222 _vertexs[startIndex].WasVisited = true; 223 queue.Enqueue(startIndex); 224 while (queue.Count > 0) 225 { 226 var currentIndex = queue.Dequeue(); 227 var adjoinVertexIndexs = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndexs(currentIndex); 228 foreach (var adjoinVertexIndex in adjoinVertexIndexs) 229 { 230 Console.WriteLine(_vertexs[currentIndex].Value + "->" + _vertexs[adjoinVertexIndex].Value); 231 232 _vertexs[adjoinVertexIndex].WasVisited = true; 233 queue.Enqueue(adjoinVertexIndex); 234 } 235 } 236 237 this.ResetVisited(); 238 } 239 240 #endregion 241 242 #region 拓扑排序 243 244 public List<T> TopologySort() 245 { 246 var cloneVertexs = (Vertex<T>[])_vertexs.Clone(); 247 var cloneEdges = (bool[][])_edges.Clone(); 248 var cloneVertexCount = _vertexCount; 249 250 var results = new List<T>(); 251 while (_vertexCount > 0) 252 { 253 var successor = this.NextSuccessor(); 254 if (successor == -1) 255 { 256 throw new InvalidOperationException("出现循环了!"); 257 } 258 259 results.Insert(0, _vertexs[successor].Value); 260 261 this.RemoveVertex(successor); 262 _vertexCount--; 263 } 264 265 _vertexs = cloneVertexs; 266 _edges = cloneEdges; 267 _vertexCount = cloneVertexCount; 268 269 return results; 270 } 271 272 private int NextSuccessor() 273 { 274 for (var row = 0; row < _vertexCount; row++) 275 { 276 if (_edges[row].Take(_vertexCount).All(x => !x)) 277 { 278 return row; 279 } 280 } 281 282 return -1; 283 } 284 285 private void RemoveVertex(int successor) 286 { 287 for (int i = successor; i < _vertexCount - 1; i++) 288 { 289 _vertexs[i] = _vertexs[i + 1]; 290 } 291 292 for (int row = successor; row < _vertexCount - 1; row++) 293 { 294 for (int column = 0; column < _vertexCount; column++) 295 { 296 _edges[row][column] = _edges[row + 1][column]; 297 } 298 } 299 300 for (int column = successor; column < _vertexCount - 1; column++) 301 { 302 for (int row = 0; row < _vertexCount; row++) 303 { 304 _edges[row][column] = _edges[row][column + 1]; 305 } 306 } 307 } 308 309 #endregion 310 311 #region 帮助方法 312 313 private int GetVertexIndex(T item) 314 { 315 for (var i = 0; i < _vertexCount; i++) 316 { 317 if (_vertexs[i].Value.Equals(item)) 318 { 319 return i; 320 } 321 } 322 return -1; 323 } 324 325 private int GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndex(int index) 326 { 327 for (var i = 0; i < _vertexCount; i++) 328 { 329 if (_edges[index][i] && _vertexs[i].WasVisited == false) 330 { 331 return i; 332 } 333 } 334 335 return -1; 336 } 337 338 private List<int> GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndexs(int index) 339 { 340 var results = new List<int>(); 341 342 for (var i = 0; i < _vertexCount; i++) 343 { 344 if (_edges[index][i] && _vertexs[i].WasVisited == false) 345 { 346 results.Add(i); 347 } 348 } 349 350 return results; 351 } 352 353 private void ResetVisited() 354 { 355 for (var i = 0; i < _vertexCount; i++) 356 { 357 _vertexs[i].WasVisited = false; 358 } 359 } 360 361 #endregion 362 } 363 } 364 }
备注
本文没有解释权重图,下篇再介绍。
