JAVA核心知识点--IO流
目录
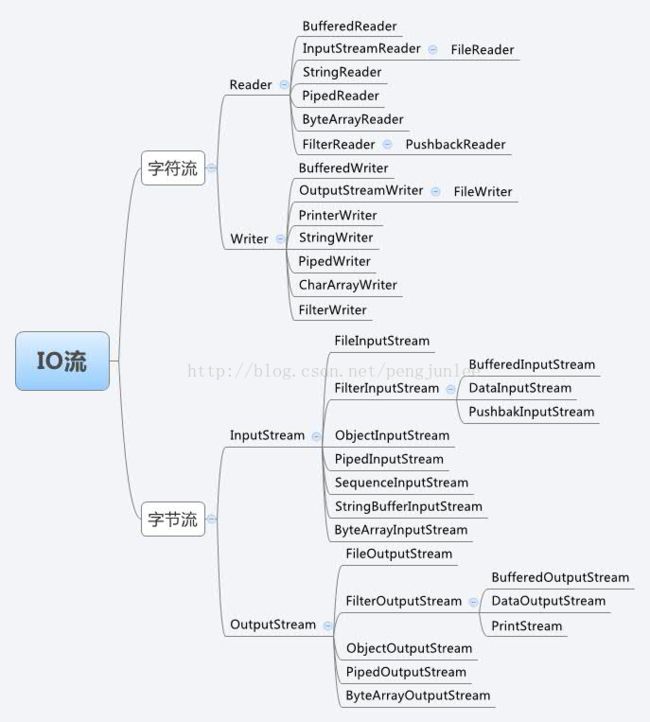
一、JavaIO流的分类
输入流和输出流
字节流和字符流
节点流和处理流
二、InputStream,OutputStream,Reader和Writer
三、节点流
四、处理流
缓冲流
转换流
数据流
Print流
Object流
五、流操作的典型示例
在Java中,对于数据的输入/输出(I/O)操作以“流”(stream)方式进行,数据的来源可以是文件、网络、内存缓存等。
一、JavaIO流的分类
J2SDK提供了各种各样的“流”,用以操作不同种类的数据,J2SDK所提供的所有流都位于java.io包内,从不同的角度对这些流进行归类:
- 按数据流向不同可以分为输入流和输出流。
- 按处理数据单位不同可以分为字节流和字符流。
- 按照流类的功能不同可以分为节点流和处理流。
输入流和输出流
流具有方向性,至于是输入流还是输出流则是一个相对的概念,一般是站在程序的角度去判断,从数据源读取数据到程序中的是输入流,相反从程序中向外写数据的是输出流。
字节流和字符流
字节流以字节(byte,1byte=8bit)为单位,一个字节一个字节的读写数据。从上图可以看出,所有的字节流均继承自抽象类InputStream/OutputStream。
字符流以字符(Java中,一个字符为2byte=16bit)为单位,一个字符一个字符的读写数据。所有的字符流均继承自抽象类Reader/Writer。
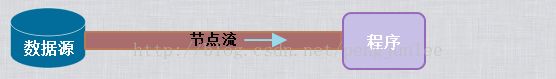
节点流和处理流
节点流为直接与数据源(节点)相连,可以从数据源读写数据的流。
处理流是“连接”在已存在的流(节点流或处理流)之上,可以为程序提供更加强大的读写操作功能的流。
二、InputStream,OutputStream,Reader和Writer
InputStream是所有字节输入流的超类,其包含的基本方法如下。
// 从输入流中读取一个字节。并以整数的形式返回(0-255)。
// 如果读取前已经到了输入流的末尾返回-1。
int read() throws IOException;
// 从输入流中读取一定数量的字节,并将其存储在缓冲区数组 b中。以整数形式返回实际读取的字节数。
// 如果读取前已经到了输入流的末尾返回-1。
int read(byte[] b) throws IOException;
// 读取输入流中len个字节到数组 b中,并将读取的第一个字节存储在元素 b[off] 中,下一个存储在 b[off+1] 中,依次类推。
// 读取的字节数最多等于 len,也可能小于该值。以整数形式返回实际读取的字节数。
// 如果读取前已经到了输入流的末尾返回-1。
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException;
// 跳过和丢弃此输入流中数据的 n个字节。返回跳过的实际字节数。
// 如果 n为负数,则不跳过任何字节。
long skip(long n) throws IOException;
// 返回此输入流下一个方法调用可以不受阻塞地从此输入流读取(或跳过)的估计字节数。
// 如果到达输入流末尾,则返回 0。
int available() throws IOException;
// 关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。
void close() throws IOException;
// 在此输入流中标记当前的位置。调用reset()方法会根据此标记的位置重新定位此流,以便后续重新读取相同的字节。
// readlimit参数告知此输入流在标记位置失效之前允许读取的字节数。
void mark(int readlimit);
// 将此流重新定位到最后一次对此输入流调用 mark()方法时的位置。
void reset() throws IOException;
// 测试此输入流是否支持 mark()和 reset() 方法。
// 是否支持 mark()和 reset()是特定输入流实例的不变属性。
boolean markSupported();OutputStream是所有字节输出流的超类,其包含的基本方法如下。
// 将指定的字节写入此输出流。
// 要写入的字节是参数 b的低8位,b的 24 个高位将被忽略。
void write(int b) throws IOException;
// 将一个字节数组中的数据写入输出流。
void write(byte[] b) throws IOException;
// 将指定 byte数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此输出流。
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException;
// 刷新此输出流并强制将输出流中缓存的数据写出。
void flush() throws IOException;
// 关闭此输出流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源。
void close() throws IOException;Reader是所有字符输入流的超类,其包含的基本方法如下。
// 试图将字符读入指定的字符缓冲区。
// 返回添加到缓冲区中的字符数量。
int read(CharBuffer target) throws IOException;
// 读取单个字符,并以整数的形式返还,范围在 0 到 65535 之间。
// 如果读取前已经到了输入流的末尾返回-1.
int read() throws IOException;
// 将字符读入数组cbuf,并返回读取的字符数。
// 如果读取前已经到了输入流的末尾返回-1.
int read(char[] cbuf) throws IOException;
// 读取输入流中len个字符到数组 cbuf中,并将读取的第一个字符存储在元素cbuf[off]中,下一个存储在 cbuf[off+1]中,依次类推。
// 读取的字符数最多等于 len,也可能小于该值。以整数形式返回实际读取的字符数。
// 如果读取前已经到了输入流的末尾返回-1.
int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) throws IOException;
// 跳过和丢弃此输入流中数据的 n个字符。返回跳过的实际字符数。
// 如果 n 为负数,则不跳过任何字符。
long skip(long n) throws IOException;
// 判断是否准备读取此流。
boolean ready() throws IOException;
// 关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。
void close() throws IOException;
// 在此输入流中标记当前的位置。调用reset()方法会根据此标记的位置重新定位此流,以便后续重新读取相同的字符。
// readlimit参数告知此输入流在标记位置失效之前允许读取的字符数。
void mark(int readlimit);
// 将此流重新定位到最后一次对此输入流调用 mark()方法时的位置。
void reset() throws IOException;
// 测试此输入流是否支持 mark()和 reset() 方法。
// 是否支持 mark()和 reset()是特定输入流实例的不变属性。
boolean markSupported();Writer是所有字符输出流的超类,其包含的基本方法如下。
// 将指定的字符写入此输出流。
// 要写入的字符是参数 c的低16位。c的 16 个高位将被忽略。
void write(int c) throws IOException;
// 将一字符数组中的数据写入输出流。
void write(char[] cbuf) throws IOException;
// 将指定 cbuf数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字符写入此输出流。
void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) throws IOException;
// 将字符串str写入此输出流。
void write(String str) throws IOException;
// 将字符串str中从off开始的len个字符写入此输出流。
void write(String str, int off, int len) throws IOException;
// 将指定字符序列添加到此 writer。
Writer append(CharSequence csq) throws IOException;
// 将指定字符序列中索引从start到end之间的字符写入到此输出流。
Writer append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) throws IOException;
// 将指定字符添加到此 writer。
Writer append(char c) throws IOException;
// 刷新此输出流并强制将输出流中缓冲的数据写出。
void flush() throws IOException;
// 关闭此输出流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源。
void close() throws IOException;三、节点流
根据数据来源不同对节点流进行分类如下图。
| 数据源类型 | 字符流 | 字节流 |
| File(文件) | FileReader FileWriter |
FileInputStream FileOutputStream |
| Memory Array(内存数组) | CharArrayReader CharArrayWriter |
ByteArrayInputStream ByteArrayOutputStream |
| Memory String(字符串) | StringReader StringWriter |
/ |
| Pipe(管道) | PipedReader PipedWriter |
PipedInputStream PipedOutputStream |
四、处理流
缓冲流
J2SDK提供了四种缓冲流:BufferedReader、BufferedWriter、BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream。缓冲流对读写的数据提供了缓冲的功能,可以提高读写的效率,同时还增加了一些新的方法。
BufferedReader新增了readLine()方法用于读取一行字符串(以\r或\n分隔)。
BufferedWriter新增了newLine()方法用于写入一个分隔符。
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(
"D:\\io\\bufferedTest.txt"));
String s;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
s = String.valueOf(Math.random());
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
Reader reader = new FileReader("D:\\io\\bufferedTest.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(s);
}
br.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("找不到指定文件!");
System.exit(-1);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("系统错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
}转换流
J2SDK提供了InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter两个转换流,用于将字节流转换为字符流。
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
OutputStream outStream = new FileOutputStream(
"D:\\io\\transformIo.txt");
OutputStreamWriter outWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(outStream);
outWriter.write("2017年3月25日风雨大作。。。");
outWriter.close();
outWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(
"D:\\io\\transformIo.txt", true), "GBK");
outWriter.write("2017年3月26日电闪雷鸣。。。");
outWriter.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("找不到指定文件!");
System.exit(-1);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
System.out.println("编码异常!");
System.exit(-1);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("写入错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
System.out.println("写入成功!");
}数据流
J2SDK提供了DataInputStream和DataOutputStream两个数据流,用以提供存取与机器无关的Java原始数据类型数据(如:int,double等)的方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream byteOut = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dataOut = new DataOutputStream(byteOut);
dataOut.writeChar(65);
dataOut.writeUTF("B");
dataOut.writeBoolean(false);
dataOut.writeChars("CD");
dataOut.writeFloat(0.1111f);
dataOut.close();
DataInputStream dataIn = new DataInputStream(
new ByteArrayInputStream(byteOut.toByteArray()));
System.out.println(dataIn.readChar());
System.out.println(dataIn.readUTF());
System.out.println(dataIn.readBoolean());
System.out.println(dataIn.readChar());
System.out.println(dataIn.readChar());
System.out.println(dataIn.readFloat());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("写入错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
}Print流
J2SDK提供了PrintWriter和PrintStream两个Print流,提供了重载的print()和println()方法用于多种数据类型的输出。
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileOutputStream in = new FileOutputStream(
"D:\\io\\PrintIoTest.txt");
PrintStream printer = new PrintStream(in);
System.setOut(printer);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
System.in));
String s;
while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) {
if (s.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) {
break;
}
System.out.println(s);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("系统错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
}Object流
J2SDK提供了ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream两个Object流,用于将实现了Serializable接口的对象实例直接以二进制的形式进行存取的方法。
import java.io.Serializable;
class User implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
String userName;
int userAge;
transient String phoneNum;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User();
user.phoneNum = "0756-8888888";
user.userAge = 17;
user.userName = "弄玉";
OutputStream os;
try {
os = new FileOutputStream("D:\\io\\ObjectIoTest.txt");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
oos.writeObject(user);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(
"D:\\io\\ObjectIoTest.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
user = (User) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(user.userName + " " + user.userAge + " "
+ user.phoneNum);
ois.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("找不到指定文件!");
System.exit(-1);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("类型错误!");
System.exit(-1);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("系统错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
}对于对象中使用transient关键字修饰的属性在序列化时将被忽略。对象还可以通过实现Externalizable接口,并实现writeExternal()和readExternal()方法来自己指定序列化和反序列化的实现过程。
五、流操作的典型示例
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class FileOperator {
private static final int bytes = 1024 * 1024;
/**
* 文件复制
* @param sourcePath 文件源路径,例如:“D:\\IO\text.txt”
* @param targetPath 目标文件路径
*/
public static void copyFile(String sourcePath, String targetPath) {
File sourceFile = new File(sourcePath);
long targetSize = 0;
try {
byte[] buffer = new byte[bytes];
InputStream inStream = new FileInputStream(sourceFile); // 读入源文件
OutputStream outStream = new FileOutputStream(targetPath);
int len;
while ((len = inStream.read(buffer)) > 0) {
outStream.write(buffer, 0, len);
targetSize += len;
}
outStream.close();
inStream.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("系统找不到指定文件:" + sourcePath);
System.exit(-1);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("文件复制发生错误,复制失败!");
System.exit(-1);
}
System.out.println("复制完成:");
System.out.println("源文件大小:" + sourceFile.length());
System.out.println("复制大小:" + targetSize);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sourcePath = "D:\\io\\";
String targetPath = "D:\\a";
File file=new File(sourcePath);
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println(file.getPath());
System.out.println(file.getName());
System.out.println(file.getParent());
copyFolder(sourcePath, targetPath);
}
/**
* 复制文件夹
* @param sourcePath 文件夹源路径,例如:“D:\\IO”
* @param targetPath 目标文件夹路径
*/
public static void copyFolder(String sourcePath, String targetPath) {
File sourceFile = new File(sourcePath);
File targetFolder=new File(targetPath);
if(!targetFolder.exists()){
targetFolder.mkdirs();
}
if(sourceFile.isDirectory()){
File[] files=sourceFile.listFiles();
for(File file:files){
if(file.isDirectory()){
copyFolder(file.getAbsolutePath(), targetPath+File.separator+file.getName());}
else{
copyFile(file.getAbsolutePath(),targetPath+File.separator+file.getName());
}
}
}
else{
copyFile(sourcePath,targetPath+File.separator+sourceFile.getName());
}
}
}