一、控制器定义
控制器提供访问应用程序的行为,通常通过服务接口定义或注解定义两种方法实现。 控制器解析用户的请求并将其转换为一个模型。在Spring MVC中一个控制器可以包含多个Action(动作、方法)。
1.1、实现接口Controller定义控制器
Controller是一个接口,处在包org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc下,接口中只有一个未实现的方法,具体的接口如下所示:
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; //实现该接口的类获得控制器功能与类型, 解析用户的请求并将其转换为一个模型
public interface Controller { //处理请求且返回一个模型与视图对象
ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
}
在自定义控制器前先创建一个基于maven的web项目,添加包的依赖,pom.xml文件如下:
4.0.0
com.zr.activiti
HelloSpringMVC
war
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
HelloSpringMVC Maven Webapp
http://maven.apache.org
UTF-8
4.10
4.1.3.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-context
${spring.version}
org.springframework
spring-webmvc
${spring.version}
如果不配置scope,会把jar包发布,会跟容器里的jar包冲突、scope要设置为provided,由容器提供,不会发布(或者不配这两个依赖,在项目的Java BuildPath的Libraries里添加Server Runtime)目前scope可以使用5个值:
compile:缺省值,适用于所有阶段,会随着项目一起发布。
provided:类似compile,期望JDK、容器或使用者会提供这个依赖。如servlet.jar。
runtime:只在运行时使用,如JDBC驱动,适用运行和测试阶段。test,只在测试时使用,用于编译和运行测试代码。不会随项目发布。
system:类似provided,需要显式提供包含依赖的jar,Maven不会在Repository中查找它。
创建一个名为Foo的类,实现接口Controller,重写handleRequest方法,代码如下:
package com.zhangguo.springmvc02.controllers;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller; /* * 定义控制器 */
public class FooController implements Controller {
@Override public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { //返回一个模型视图对象,指定路径,指定模型的名称为message,值为一段字符串
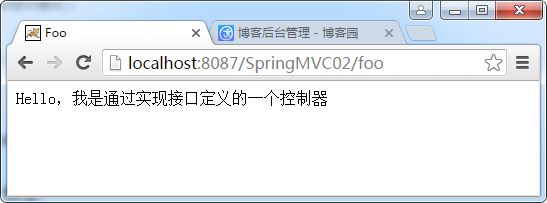
return new ModelAndView("foo/index", "message", "Hello,我是通过实现接口定义的一个控制器");
}
}
在WEB-INF/views/foo目录下创建一个名为index.jsp的视图,内容如下:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
Foo
${message}
修改springContext.xml配置文件,增加一个控制器bean的声明,具体内容如下:
基中name是访问路径,class是自定义的控制器的全名称。运行后的结果如下:
小结:实现接口Controller定义控制器是较老的办法,缺点是:一个控制器中只有一个Action,如果要多个Action则需要定义多个Controller;定义的方式比较麻烦;Spring 2.5以后采用注解的方式定义解决这引起问题。
1.2、使用注解@Controller定义控制器
org.springframework.stereotype.Controller注解类型用于声明Spring类的实例是一个控制器(在讲IOC时还提到了另外3个注解);Spring可以使用扫描机制来找到应用程序中所有基于注解的控制器类,为了保证Spring能找到你的控制器,需要在配置文件中声明组件扫描。
创建一个名了Bar的类,定义为一个控制器,类的具体实现如下:
package com.zhangguo.springmvc02.controllers;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* 定义控制器
*/
//BarController类的实例是一个控制器,会自动添加到Spring上下文中
@Controller
public class BarController {
//映射访问路径
@RequestMapping("/bar")
public String index(Model model){
//Spring MVC会自动实例化一个Model对象用于向视图中传值
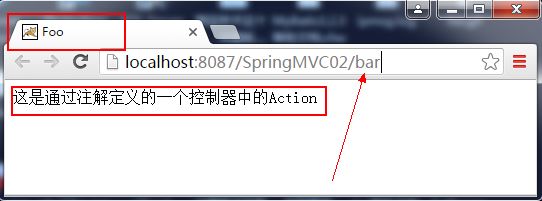
model.addAttribute("message", "这是通过注解定义的一个控制器中的Action");
//返回视图位置
return "foo/index";
}
}
还要需要修改Spring mvc配置文件springContext.xml,启用自动组件扫描功能,在beans中增加如下配置:
base-package属性用于指定扫描的基础包,可以缩小扫描的范围。运行结果如下:
小结:从代码与运行结果可以看出BarController与FooController同时都指定了一个视图foo/index.jsp,但是页面结果的结果是不一样的,从这里可以看出视图是被复用的,而控制器与视图之间是弱偶合关系。
二、@RequestMapping详解
@RequestMapping注释用于映射url到控制器类或一个特定的处理程序方法。可用于类或方法上。用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径。该注解共有8个属性,注解源码如下:
package org.springframework.web.bind.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
/**
* 用于映射url到控制器类或一个特定的处理程序方法.
*/
//该注解只能用于方法或类型上
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
/**
* 指定映射的名称
*/
String name() default "";
/**
* 指定请求的路径映射,指定的地址可以是uri模板,别名为path
*/
@AliasFor("path")
String[] value() default {};
/** 别名为value,使用path更加形象
* 只有用在一个Servlet环境:路径映射URI(例如“/myPath.do”)。
* Ant风格的路径模式,同时也支持(例如,“/myPath/*.do”)。在方法层面,在主要的映射在类型级别表示相对路径(例如,“edit.do”)
* 的支持。路径映射的URI可能包含占位符(例如“/$ {}连接”)
*/
@AliasFor("value")
String[] path() default {};
/**
* 指定请求谓词的类型如GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE. 收窄请求范围 The
* HTTP request methods to map to, narrowing the primary mapping: GET, POST,
* HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE.
*/
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
/**
* 映射请求的参数,收窄请求范围 The parameters of the mapped request, narrowing the
* primary mapping.
*/
String[]params() default {};
/**
* 映射请求头部,收窄请求范围 The headers of the mapped request, narrowing the primary
* mapping. RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers =
* "content-type=text/*")
*/
String[] headers() default {};
/**
* 指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),例如application/json, text/html,收窄请求范围 The
* consumable media types of the mapped request, narrowing the primary
* mapping.
*/
String[] consumes() default {};
/**
* 指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回 The producible media types
* of the mapped request, narrowing the primary mapping. produces =
* "text/plain" produces = {"text/plain", "application/*"} produces =
* "application/json; charset=UTF-8"
*/
String[] produces() default {};
}
从上面的源码可以发现除了name基本都是数组类型,在设置时我们可以指定单个值,如@RequestMapping(value="/foo");也可以同时指定多个值如:@RequestMapping(value={"/foo","/bar"})。
2.1、value 属性指定映射路径或URL模板
指定请求的实际地址,指定的地址可以是URL模板,正则表达式或路径占位,该属性与path互为别名关系,@RequestMapping("/foo")} 与 @RequestMapping(path="/foo")相同。该属性是使用最频繁,最重要的一个属性,如果只指定该属性时可以把value略去。Spring Framework 4.2引入了一流的支持声明和查找注释属性的别名。@AliasFor注解可用于声明一双别名属性,来给注解的属性起别名, 让使用注解时, 更加的容易理解(比如给value属性起别名, 更容易让人理解)。先看一个官网的示例:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/appointments")
public class AppointmentsController {
private final AppointmentBook appointmentBook;
@Autowired
public AppointmentsController(AppointmentBook appointmentBook) {
this.appointmentBook = appointmentBook;
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Map get() {
return appointmentBook.getAppointmentsForToday();
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{day}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Map getForDay(@PathVariable @DateTimeFormat(iso = ISO.DATE) Date day, Model model) {
return appointmentBook.getAppointmentsForDay(day);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/new", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public AppointmentForm getNewForm() {
return new AppointmentForm();
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String add(@Valid AppointmentForm appointment, BindingResult result) {
if (result.hasErrors()) {
return "appointments/new";
}
appointmentBook.addAppointment(appointment);
return "redirect:/appointments";
}
}
2.1.1、指定具体路径字符
2.1.1.1 只注解方法
@Controller
public class FooBarController {
@RequestMapping("/action1")
public String action1(){
return "foo/index";
}
}
访问路径:http://localhost:8087/SpringMVC02/action1
2.1.1.2 同时注解类与方法
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/foobar")
public class FooBarController {
@RequestMapping("/action1")
public String action1(){
return "foo/index";
}
}
访问路径:http://localhost:8087/SpringMVC02/foobar/action1
需要先指定类的路径再指定方法的路径
2.1.1.3 当value为空值
注解在方法上时,如果value为空则表示该方法为类下默认的Action。
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/foobar")
public class FooBarController {
@RequestMapping("/action1")
public String action1(Model model){
//在模型中添加属性message值为action1,渲染页面时使用
model.addAttribute("message", "action1");
return "foo/index";
}
@RequestMapping
public String action2(Model model){
//在模型中添加属性message值为action2,渲染页面时使用
model.addAttribute("message", "action2");
return "foo/index";
}
}
访问action2的路径是:http://localhost:8087/SpringMVC02/foobar,如果加上action2就错误了。
注解在类上时,当value为空值则为默认的控制器,可以用于设置项目的起始页。
@Controller
@RequestMapping
public class FooBarController {
@RequestMapping("/action1")
public String action1(Model model){
//在模型中添加属性message值为action1,渲染页面时使用
model.addAttribute("message", "action1");
return "foo/index";
}
@RequestMapping
public String action2(Model model){
//在模型中添加属性message值为action2,渲染页面时使用
model.addAttribute("message", "action2");
return "foo/index";
}
}
访问路径:http://localhost:8087/SpringMVC02/,同时省去了控制器名与Action名称,可用于欢迎页。
访问action1的路径是:http://localhost:8087/SpringMVC02/action1
2.1.2、路径变量占位,URI模板模式
在Spring MVC可以使用@PathVariable 注释方法参数的值绑定到一个URI模板变量。
@RequestMapping("/action3/{p1}/{p2}")
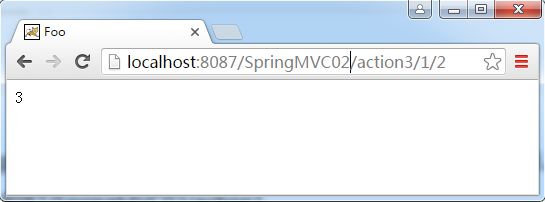
public String action3(@PathVariable int p1,@PathVariable int p2,Model model){
model.addAttribute("message", p1+p2);
return "foo/index";
}
运行结果:
使用路径变量的好处:使路径变得更加简洁;获得参数更加方便,框架会自动进行类型转换。通过路径变量的类型可以约束访问参数,如果类型不一样,则访问不到action,如这里访问是的路径是/action3/1/a,则路径与方法不匹配,而不会是参数转换失败。
2.1.3、正则表达式模式的URI模板
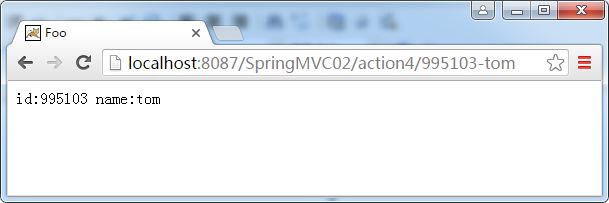
@RequestMapping(value="/action4/{id:\\d{6}}-{name:[a-z]{3}}")
public String action4(@PathVariable int id,@PathVariable String name,Model model){
model.addAttribute("message", "id:"+id+" name:"+name);
return "foo/index";
}
正则要求id必须为6位的数字,而name必须为3位小写字母,访问结果如下:
2.1.4、矩阵变量@MatrixVariable
矩阵变量可以出现在任何路径段,每个矩阵变量用“;”分隔。例如:“/汽车;颜色=红;年=2012”。多个值可以是“,”分隔“颜色=红、绿、蓝”或变量名称可以重复“颜色=红;颜色=绿色;颜色=蓝”,如下所示:
// GET /pets/42;q=11;r=22
@RequestMapping(value = "/pets/{petId}")
public void findPet(@PathVariable String petId, @MatrixVariable int q) {
// petId == 42
// q == 11
}
// 矩阵变量
@RequestMapping(value = "/action5/{name}")
public String action5(Model model,
@PathVariable String name, //路径变量,用于获得路径中的变量name的值
@MatrixVariable String r,
@MatrixVariable(required = true) String g, //参数g是必须的
@MatrixVariable(defaultValue = "99", required = false) String b) { //参数b不是必须的,默认值是99
model.addAttribute("message", name + " is #" + r + g + b);
return "foo/index";
}
//Get http://localhost:8087/SpringMVC02/action5/the%20book%20color;r=33;g=66
//the book color is #336699
默认是不允许使用矩阵变量的,需要设置配置文中的RequestMappingHandlerMapping的属性removeSemicolonContent为false;在annotation-driven中增加属性enable-matrix-variables="true",修改后的springmvc-servlet.xml文件如下:
访问结果如下:
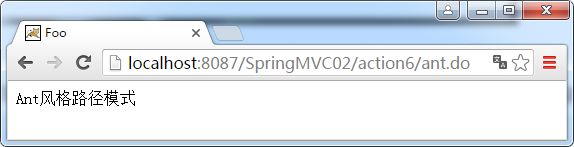
2.1.5、Ant风格路径模式
@RequestMapping注解也支持ant风格的路径模式,如/myPath/.do,/owners//pets/{petId},示例代码如下:
//Ant风格路径模式
@RequestMapping(value = "/action6/*.do")
public String action6(Model model){
model.addAttribute("message","Ant风格路径模式");
return "foo/index";
}
运行结果:
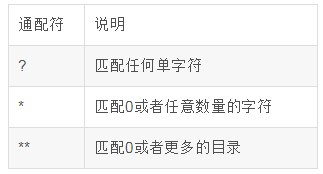
当然还有关于路径匹配的规则,特殊的优先级高过一般的,更多规则可以参考官方帮助。
ANT通配符有三种:
2.1.6、@RequestMapping 来处理多个 URI
你可以将多个请求映射到一个方法上去,只需要添加一个带有请求路径值列表的 @RequestMapping 注解就行了。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/home")
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping(value = {
"",
"/page",
"page*",
"view/*",
"**/msg"
})
String indexMultipleMapping() {
return "Hello from index multiple mapping.";
}
}
如你在这段代码中所看到的,@RequestMapping 支持统配符以及ANT风格的路径。前面这段代码中,如下的这些 URL 都会由 indexMultipleMapping() 来处理:
localhost:8080/home
localhost:8080/home/
localhost:8080/home/page
localhost:8080/home/pageabc
localhost:8080/home/view/
localhost:8080/home/view/view
2.2、method属性指定谓词类型
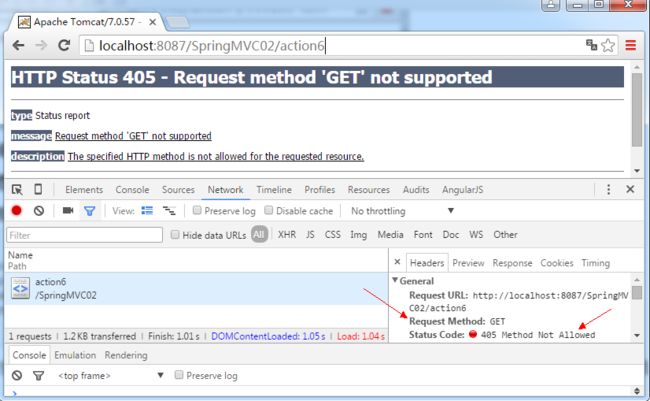
用于约束请求的谓词类型,可以收窄请求范围。指定请求谓词的类型如GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE,如下代码所示:
//谓词类型
@RequestMapping(value = "/action6",method={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.DELETE})
public String action6(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "请求谓词只能是POST与DELETE");
return "foo/index";
}
要访问action7请求谓词类型必须是POST或者为DELETE,当我们从浏览器的URL栏中直接请求时为一个GET请求,则结果是405,如下所示:
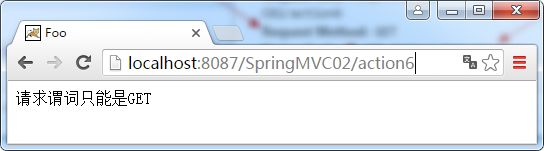
如果将POST修改为GET则正常了,如下所示:
//谓词类型
@RequestMapping(value = "/action6",method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String action6(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "请求谓词只能是GET");
return "foo/index";
}
Spring MVC 的 @RequestMapping 注解能够处理 HTTP 请求的方法, 比如 GET, PUT, POST, DELETE 以及 PATCH。
所有的请求默认都会是 HTTP GET 类型的。
为了能降一个请求映射到一个特定的 HTTP 方法,你需要在 @RequestMapping 中使用 method 来声明 HTTP 请求所使用的方法类型,如下所示:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/home")
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
String get() {
return "Hello from get";
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
String delete() {
return "Hello from delete";
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
String post() {
return "Hello from post";
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
String put() {
return "Hello from put";
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PATCH)
String patch() {
return "Hello from patch";
}
}
在上述这段代码中, @RequestMapping 注解中的 method 元素声明了 HTTP 请求的 HTTP 方法的类型。
所有的处理处理方法会处理从这同一个 URL( /home)进来的请求, 但要看指定的 HTTP 方法是什么来决定用哪个方法来处理。
例如,一个 POST 类型的请求 /home 会交给 post() 方法来处理,而一个 DELETE 类型的请求 /home 则会由 delete() 方法来处理。
你会看到 Spring MVC 将使用这样相同的逻辑来映射其它的方法。
2.3、consumes属性指定请求的Content-Type
@RequestMapping 注解的 produces 和 consumes 这两个元素来缩小请求映射类型的范围,达到处理生产和消费对象的目的。
指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),例如application/json, text/html,收窄请求范围,如果用户发送的请求内容类型不匹配则方法不会响应请求,具体使用如下代码所示:
package com.zhangguo.springmvc02.controllers;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/home")
public class HomeController {
// 请求内容类型必须为text/html,注意浏览器默认没有指定Content-type
@RequestMapping(value = "/action8",consumes="text/html")
public String action8(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type)是text/html");
return "foo/index";
}
}
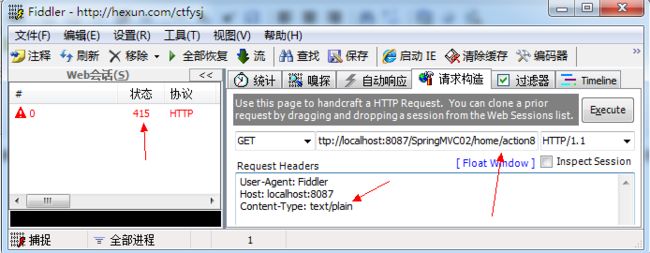
在action8的注解中约束发送到服务器的Content-Type必须是text/html类型,如果类型不一致则会报错(415),测试结果如下:
从两个图的对比可以看出当内容类型为text/plain时报客户端错误415,当内容类型为text/html时则响应正常,响应的结果如下:
*请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type)是text/html *
注意:可以使用!号,如consumes="!text/html"
2.4、produces属性指定响应的Content-Type,约束Accept类型
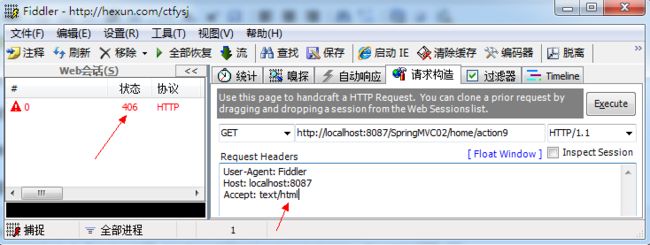
指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回,方法才处理客户端的请求否则会报406错误,常用设置如下:
produces = "text/plain" //客户端只接收纯文本
produces = {"text/plain", "application/"} //客户端接收纯文本与application/类型的内容
produces = "application/json; charset=UTF-8" //客户端接收json且编码为utf-8
//客户端接收json且编码为utf-8,多数浏览器Accept设置的为*/*,接收任意类型
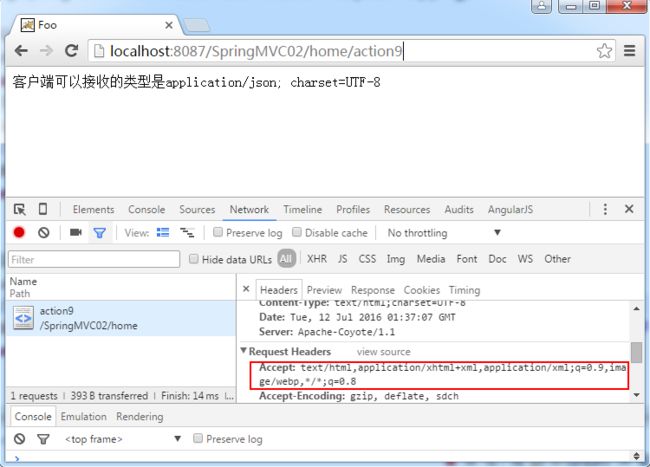
@RequestMapping(value = "/action9",produces="application/json; charset=UTF-8")
public String action9(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "客户端可以接收的类型是application/json; charset=UTF-8");
return "foo/index";
}
运行结果:
注意:可以使用!号,如produces="!text/html"
2.5、params属性指定请求中必须有特定参数与值
映射请求的参数,收窄请求范围。可以限制客户端发送到服务器的请求参数为某些特定值或不为某些值,如下代码所示:
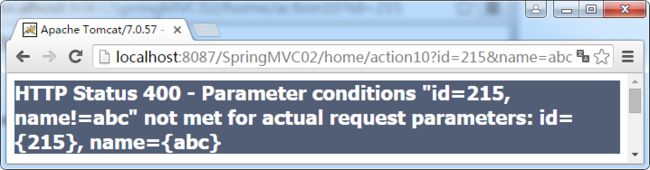
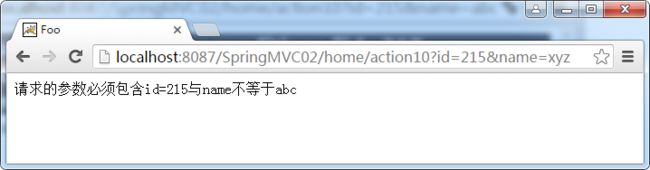
//请求的参数必须包含id=215与name不等于abc
@RequestMapping(value = "/action10",params={"id=215","name!=abc"})
public String action10(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "请求的参数必须包含id=215与name不等于abc");
return "foo/index";
}
运行结果如下:
name的值如没有指定也是通过的;可以使用不等于;
2.6、headers属性指定请求中必须有特定header值
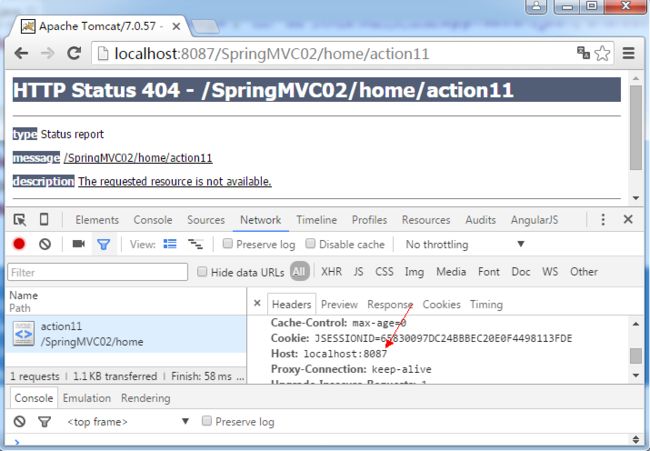
映射请求头部,收窄请求范围。约束客户端发送的请求头部信息中必须包含某个特定的值或不包含某个值,作用范围明显大于前面讲过的几种,示例代码如下:
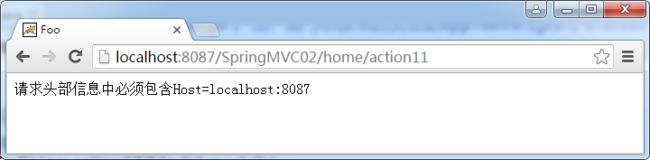
//请求头部信息中必须包含Host=localhost:8088
@RequestMapping(value = "/action11",headers="Host=localhost:8088")
public String action11(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "请求头部信息中必须包含Host=localhost:8088");
return "foo/index";
}
运行结果:
修改Host为8087时运行就正常了:
这里同样可以使用!号;可以使用通配符如:Content-Type="application/*"
2.7、name属性指定名称
为当前映射指定一个名称,不常用,一般不会指定。
2.8、path属性指定路径
先看源码中的path与value,定义如下:
@AliasFor("path")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] path() default {};
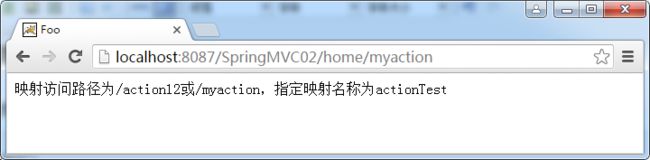
从Spring 4.2开始引入了@AliasFor注解,可以实现属性的别名,如value本身并没有特定的含义,而path会更加具体,能见名知义,通俗说可以认为两者在使用中是一样的如:@RequestMapping("/foo")} 与 @RequestMapping(path="/foo")相同。示例代码如下:
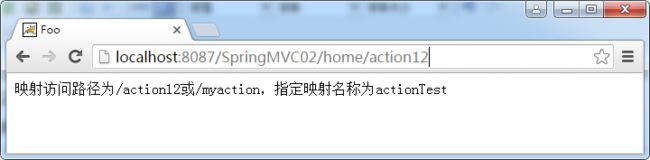
//映射访问路径为/action12或/myaction,指定映射名称为actionTest
@RequestMapping(path ={"/action12","/myaction"},name="actionTest")
public String action12(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "映射访问路径为/action12或/myaction,指定映射名称为actionTest");
return "foo/index";
}
运行结果:
2.9、@RequestMapping 快捷方式
Spring 4.3 引入了方法级注解的变体,也被叫做 @RequestMapping 的组合注解。组合注解可以更好的表达被注解方法的语义。它们所扮演的角色就是针对 @RequestMapping 的封装,而且成了定义端点的标准方法。
例如,@GetMapping 是一个组合注解,它所扮演的是 @RequestMapping(method =RequestMethod.GET) 的一个快捷方式。
方法级别的注解变体有如下几个:
@GetMapping
@PostMapping
@PutMapping
@DeleteMapping
@PatchMappin
如下面两个action就是基本等价的:
@RequestMapping(value = "/action3",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String action3(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","action3 get请求");
return "hi";
}
@GetMapping("/action4")
public String action4(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","action4 get请求");
return "hi";
}
action4的写法要简单一些,GetMapping与RequestMapping的具体用法一样,源码如下:
/* * Copyright 2002-2016 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.web.bind.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor; /** * Annotation for mapping web requests onto specific handler classes and/or * handler methods. Provides a consistent style between Servlet and Portlet * environments, with the semantics adapting to the concrete environment. * *. * *NOTE: The set of features supported for Servlets is a superset * of the set of features supported for Portlets. The places where this applies * are marked with the label "Servlet-only" in this source file. For Servlet * environments there are some further distinctions depending on whether an * application is configured with {@literal "@MVC 3.0"} or * {@literal "@MVC 3.1"} support classes. The places where this applies are * marked with {@literal "@MVC 3.1-only"} in this source file. For more * details see the note on the new support classes added in Spring MVC 3.1 * further below. * *
Handler methods which are annotated with this annotation are allowed to * have very flexible signatures. They may have parameters of the following * types, in arbitrary order (except for validation results, which need to * follow right after the corresponding command object, if desired): *
*
* *- Request and/or response objects (Servlet API or Portlet API). * You may choose any specific request/response type, e.g. * {@link javax.servlet.ServletRequest} / {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest} * or {@link javax.portlet.PortletRequest} / {@link javax.portlet.ActionRequest} / * {@link javax.portlet.RenderRequest}. Note that in the Portlet case, * an explicitly declared action/render argument is also used for mapping * specific request types onto a handler method (in case of no other * information given that differentiates between action and render requests). *
- Session object (Servlet API or Portlet API): either * {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpSession} or {@link javax.portlet.PortletSession}. * An argument of this type will enforce the presence of a corresponding session. * As a consequence, such an argument will never be {@code null}. * Note that session access may not be thread-safe, in particular in a * Servlet environment: Consider switching the * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter#setSynchronizeOnSession * "synchronizeOnSession"} flag to "true" if multiple requests are allowed to * access a session concurrently. *
- {@link org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest} or * {@link org.springframework.web.context.request.NativeWebRequest}. * Allows for generic request parameter access as well as request/session * attribute access, without ties to the native Servlet/Portlet API. *
- {@link java.util.Locale} for the current request locale * (determined by the most specific locale resolver available, * i.e. the configured {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver} * in a Servlet environment and the portal locale in a Portlet environment). *
- {@link java.io.InputStream} / {@link java.io.Reader} for access * to the request's content. This will be the raw InputStream/Reader as * exposed by the Servlet/Portlet API. *
- {@link java.io.OutputStream} / {@link java.io.Writer} for generating * the response's content. This will be the raw OutputStream/Writer as * exposed by the Servlet/Portlet API. *
- {@link org.springframework.http.HttpMethod} for the HTTP request method
*- {@link PathVariable @PathVariable} annotated parameters (Servlet-only) * for access to URI template values (i.e. /hotels/{hotel}). Variable values will be * converted to the declared method argument type. By default, the URI template * will match against the regular expression {@code [^\.]*} (i.e. any character * other than period), but this can be changed by specifying another regular * expression, like so: /hotels/{hotel:\d+}. * Additionally, {@code @PathVariable} can be used on a * {@link java.util.Map Map<String, String>} to gain access to all * URI template variables. *
- {@link MatrixVariable @MatrixVariable} annotated parameters (Servlet-only) * for access to name-value pairs located in URI path segments. Matrix variables * must be represented with a URI template variable. For example /hotels/{hotel} * where the incoming URL may be "/hotels/42;q=1". * Additionally, {@code @MatrixVariable} can be used on a * {@link java.util.Map Map<String, String>} to gain access to all * matrix variables in the URL or to those in a specific path variable. *
- {@link RequestParam @RequestParam} annotated parameters for access to * specific Servlet/Portlet request parameters. Parameter values will be * converted to the declared method argument type. Additionally, * {@code @RequestParam} can be used on a {@link java.util.Map Map<String, String>} or * {@link org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap MultiValueMap<String, String>} * method parameter to gain access to all request parameters. *
- {@link RequestHeader @RequestHeader} annotated parameters for access to * specific Servlet/Portlet request HTTP headers. Parameter values will be * converted to the declared method argument type. Additionally, * {@code @RequestHeader} can be used on a {@link java.util.Map Map<String, String>}, * {@link org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap MultiValueMap<String, String>}, or * {@link org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders HttpHeaders} method parameter to * gain access to all request headers. *
- {@link RequestBody @RequestBody} annotated parameters (Servlet-only) * for access to the Servlet request HTTP contents. The request stream will be * converted to the declared method argument type using * {@linkplain org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter message * converters}. Such parameters may optionally be annotated with {@code @Valid} * and also support access to validation results through an * {@link org.springframework.validation.Errors} argument. * Instead a {@link org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException} * exception is raised. *
- {@link RequestPart @RequestPart} annotated parameters * (Servlet-only, {@literal @MVC 3.1-only}) * for access to the content * of a part of "multipart/form-data" request. The request part stream will be * converted to the declared method argument type using * {@linkplain org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter message * converters}. Such parameters may optionally be annotated with {@code @Valid} * and support access to validation results through a * {@link org.springframework.validation.Errors} argument. * Instead a {@link org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException} * exception is raised. *
- {@link SessionAttribute @SessionAttribute} annotated parameters for access * to existing, permanent session attributes (e.g. user authentication object) * as opposed to model attributes temporarily stored in the session as part of * a controller workflow via {@link SessionAttributes}. *
- {@link RequestAttribute @RequestAttribute} annotated parameters for access * to request attributes. *
- {@link org.springframework.http.HttpEntity HttpEntity<?>} parameters * (Servlet-only) for access to the Servlet request HTTP headers and contents. * The request stream will be converted to the entity body using * {@linkplain org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter message * converters}. *
- {@link java.util.Map} / {@link org.springframework.ui.Model} / * {@link org.springframework.ui.ModelMap} for enriching the implicit model * that will be exposed to the web view. *
- {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.RedirectAttributes} * (Servlet-only, {@literal @MVC 3.1-only}) to specify the exact set of attributes * to use in case of a redirect and also to add flash attributes (attributes * stored temporarily on the server-side to make them available to the request * after the redirect). {@code RedirectAttributes} is used instead of the * implicit model if the method returns a "redirect:" prefixed view name or * {@code RedirectView}. *
- Command/form objects to bind parameters to: as bean properties or fields, * with customizable type conversion, depending on {@link InitBinder} methods * and/or the HandlerAdapter configuration - see the "webBindingInitializer" * property on RequestMappingHandlerMethodAdapter. * Such command objects along with their validation results will be exposed * as model attributes, by default using the non-qualified command class name * in property notation (e.g. "orderAddress" for type "mypackage.OrderAddress"). * Specify a parameter-level {@link ModelAttribute @ModelAttribute} annotation for * declaring a specific model attribute name. *
- {@link org.springframework.validation.Errors} / * {@link org.springframework.validation.BindingResult} validation results * for a preceding command/form object (the immediate preceding argument). *
- {@link org.springframework.web.bind.support.SessionStatus} status handle * for marking form processing as complete (triggering the cleanup of session * attributes that have been indicated by the {@link SessionAttributes @SessionAttributes} * annotation at the handler type level). *
- {@link org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilder} * (Servlet-only, {@literal @MVC 3.1-only}) * for preparing a URL relative to the current request's host, port, scheme, * context path, and the literal part of the servlet mapping. *
Note: Java 8's {@code java.util.Optional} is supported * as a method parameter type with annotations that provide a {@code required} * attribute (e.g. {@code @RequestParam}, {@code @RequestHeader}, etc.). The use * of {@code java.util.Optional} in those cases is equivalent to having * {@code required=false}. * *
The following return types are supported for handler methods: *
*
* *- A {@code ModelAndView} object (Servlet MVC or Portlet MVC), * with the model implicitly enriched with command objects and the results * of {@link ModelAttribute @ModelAttribute} annotated reference data accessor methods. *
- A {@link org.springframework.ui.Model Model} object, with the view name implicitly * determined through a {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator} * and the model implicitly enriched with command objects and the results * of {@link ModelAttribute @ModelAttribute} annotated reference data accessor methods. *
- A {@link java.util.Map} object for exposing a model, * with the view name implicitly determined through a * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator} * and the model implicitly enriched with command objects and the results * of {@link ModelAttribute @ModelAttribute} annotated reference data accessor methods. *
- A {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.View} object, with the * model implicitly determined through command objects and * {@link ModelAttribute @ModelAttribute} annotated reference data accessor methods. * The handler method may also programmatically enrich the model by * declaring a {@link org.springframework.ui.Model} argument (see above). *
- A {@link String} value which is interpreted as view name, * with the model implicitly determined through command objects and * {@link ModelAttribute @ModelAttribute} annotated reference data accessor methods. * The handler method may also programmatically enrich the model by * declaring a {@link org.springframework.ui.ModelMap} argument * (see above). *
- {@link ResponseBody @ResponseBody} annotated methods (Servlet-only) * for access to the Servlet response HTTP contents. The return value will * be converted to the response stream using * {@linkplain org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter message * converters}. *
- An {@link org.springframework.http.HttpEntity HttpEntity<?>} or * {@link org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity ResponseEntity<?>} object * (Servlet-only) to access to the Servlet response HTTP headers and contents. * The entity body will be converted to the response stream using * {@linkplain org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter message * converters}. *
- An {@link org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders HttpHeaders} object to * return a response with no body.
*- A {@link Callable} which is used by Spring MVC to obtain the return * value asynchronously in a separate thread transparently managed by Spring MVC * on behalf of the application. *
- A {@link org.springframework.web.context.request.async.DeferredResult} * which the application uses to produce a return value in a separate * thread of its own choosing, as an alternative to returning a Callable. *
- A {@link org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFuture} * which the application uses to produce a return value in a separate * thread of its own choosing, as an alternative to returning a Callable. *
- A {@link java.util.concurrent.CompletionStage} (implemented by * {@link java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture} for example) * which the application uses to produce a return value in a separate * thread of its own choosing, as an alternative to returning a Callable. *
- A {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseBodyEmitter} * can be used to write multiple objects to the response asynchronously; * also supported as the body within {@code ResponseEntity}.
*- An {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.SseEmitter} * can be used to write Server-Sent Events to the response asynchronously; * also supported as the body within {@code ResponseEntity}.
*- A {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.StreamingResponseBody} * can be used to write to the response asynchronously; * also supported as the body within {@code ResponseEntity}.
*- {@code void} if the method handles the response itself (by * writing the response content directly, declaring an argument of type * {@link javax.servlet.ServletResponse} / {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse} * / {@link javax.portlet.RenderResponse} for that purpose) * or if the view name is supposed to be implicitly determined through a * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator} * (not declaring a response argument in the handler method signature; * only applicable in a Servlet environment). *
- Any other return type will be considered as single model attribute * to be exposed to the view, using the attribute name specified through * {@link ModelAttribute @ModelAttribute} at the method level (or the default attribute * name based on the return type's class name otherwise). The model will be * implicitly enriched with command objects and the results of * {@link ModelAttribute @ModelAttribute} annotated reference data accessor methods. *
NOTE: {@code @RequestMapping} will only be processed if an * an appropriate {@code HandlerMapping}-{@code HandlerAdapter} pair * is configured. This is the case by default in both the * {@code DispatcherServlet} and the {@code DispatcherPortlet}. * However, if you are defining custom {@code HandlerMappings} or * {@code HandlerAdapters}, then you need to add * {@code DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping} and * {@code AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter} to your configuration.
NOTE: Spring 3.1 introduced a new set of support classes for * {@code @RequestMapping} methods in Servlet environments called * {@code RequestMappingHandlerMapping} and * {@code RequestMappingHandlerAdapter}. They are recommended for use and * even required to take advantage of new features in Spring MVC 3.1 (search * {@literal "@MVC 3.1-only"} in this source file) and going forward. * The new support classes are enabled by default from the MVC namespace and * with use of the MVC Java config ({@code @EnableWebMvc}) but must be * configured explicitly if using neither. * *
NOTE: When using controller interfaces (e.g. for AOP proxying), * make sure to consistently put all your mapping annotations - such as * {@code @RequestMapping} and {@code @SessionAttributes} - on * the controller interface rather than on the implementation class. * * @author Juergen Hoeller * @author Arjen Poutsma * @author Sam Brannen * @since 2.5 * @see GetMapping * @see PostMapping * @see PutMapping * @see DeleteMapping * @see PatchMapping * @see RequestParam * @see RequestAttribute * @see PathVariable * @see ModelAttribute * @see SessionAttribute * @see SessionAttributes * @see InitBinder * @see org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter * @see org.springframework.web.portlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping * @see org.springframework.web.portlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter */ @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Mapping public @interface RequestMapping { /** * Assign a name to this mapping. *
Supported at the type level as well as at the method level! * When used on both levels, a combined name is derived by concatenation * with "#" as separator. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.MvcUriComponentsBuilder * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy */ String name() default ""; /** * The primary mapping expressed by this annotation. *
In a Servlet environment this is an alias for {@link #path}. * For example {@code @RequestMapping("/foo")} is equivalent to * {@code @RequestMapping(path="/foo")}. *
In a Portlet environment this is the mapped portlet modes * (i.e. "EDIT", "VIEW", "HELP" or any custom modes). *
Supported at the type level as well as at the method level! * When used at the type level, all method-level mappings inherit * this primary mapping, narrowing it for a specific handler method. */ @AliasFor("path") String[] value() default {}; /** * In a Servlet environment only: the path mapping URIs (e.g. "/myPath.do"). * Ant-style path patterns are also supported (e.g. "/myPath/*.do"). * At the method level, relative paths (e.g. "edit.do") are supported within * the primary mapping expressed at the type level. Path mapping URIs may * contain placeholders (e.g. "/${connect}") *
Supported at the type level as well as at the method level! * When used at the type level, all method-level mappings inherit * this primary mapping, narrowing it for a specific handler method. * @see org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ValueConstants#DEFAULT_NONE * @since 4.2 */ @AliasFor("value") String[] path() default {}; /** * The HTTP request methods to map to, narrowing the primary mapping: * GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE. *
Supported at the type level as well as at the method level! * When used at the type level, all method-level mappings inherit * this HTTP method restriction (i.e. the type-level restriction * gets checked before the handler method is even resolved). *
Supported for Servlet environments as well as Portlet 2.0 environments. */ RequestMethod[] method() default {}; /** * The parameters of the mapped request, narrowing the primary mapping. *
Same format for any environment: a sequence of "myParam=myValue" style * expressions, with a request only mapped if each such parameter is found * to have the given value. Expressions can be negated by using the "!=" operator, * as in "myParam!=myValue". "myParam" style expressions are also supported, * with such parameters having to be present in the request (allowed to have * any value). Finally, "!myParam" style expressions indicate that the * specified parameter is not supposed to be present in the request. *
Supported at the type level as well as at the method level! * When used at the type level, all method-level mappings inherit * this parameter restriction (i.e. the type-level restriction * gets checked before the handler method is even resolved). *
In a Servlet environment, parameter mappings are considered as restrictions * that are enforced at the type level. The primary path mapping (i.e. the * specified URI value) still has to uniquely identify the target handler, with * parameter mappings simply expressing preconditions for invoking the handler. *
In a Portlet environment, parameters are taken into account as mapping * differentiators, i.e. the primary portlet mode mapping plus the parameter * conditions uniquely identify the target handler. Different handlers may be * mapped onto the same portlet mode, as long as their parameter mappings differ. */ String[] params() default {}; /** * The headers of the mapped request, narrowing the primary mapping. *
Same format for any environment: a sequence of "My-Header=myValue" style * expressions, with a request only mapped if each such header is found * to have the given value. Expressions can be negated by using the "!=" operator, * as in "My-Header!=myValue". "My-Header" style expressions are also supported, * with such headers having to be present in the request (allowed to have * any value). Finally, "!My-Header" style expressions indicate that the * specified header is not supposed to be present in the request. *
Also supports media type wildcards (*), for headers such as Accept * and Content-Type. For instance, *
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers = "content-type=text/*") ** will match requests with a Content-Type of "text/html", "text/plain", etc. *Supported at the type level as well as at the method level! * When used at the type level, all method-level mappings inherit * this header restriction (i.e. the type-level restriction * gets checked before the handler method is even resolved). *
Maps against HttpServletRequest headers in a Servlet environment, * and against PortletRequest properties in a Portlet 2.0 environment. * @see org.springframework.http.MediaType */ String[] headers() default {}; /** * The consumable media types of the mapped request, narrowing the primary mapping. *
The format is a single media type or a sequence of media types, * with a request only mapped if the {@code Content-Type} matches one of these media types. * Examples: *
* consumes = "text/plain" * consumes = {"text/plain", "application/*"} ** Expressions can be negated by using the "!" operator, as in "!text/plain", which matches * all requests with a {@code Content-Type} other than "text/plain". *Supported at the type level as well as at the method level! * When used at the type level, all method-level mappings override * this consumes restriction. * @see org.springframework.http.MediaType * @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest#getContentType() */ String[] consumes() default {}; /** * The producible media types of the mapped request, narrowing the primary mapping. *
The format is a single media type or a sequence of media types, * with a request only mapped if the {@code Accept} matches one of these media types. * Examples: *
* produces = "text/plain" * produces = {"text/plain", "application/*"} * produces = "application/json; charset=UTF-8" **It affects the actual content type written, for example to produce a JSON response * with UTF-8 encoding, {@code "application/json; charset=UTF-8"} should be used. *
Expressions can be negated by using the "!" operator, as in "!text/plain", which matches * all requests with a {@code Accept} other than "text/plain". *
Supported at the type level as well as at the method level! * When used at the type level, all method-level mappings override * this produces restriction. * @see org.springframework.http.MediaType */ String[] produces() default {}; }
转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/best/p/5659596.html