前端(三)js、jquery-学习笔记整理
JavaScript
JavaScript是运行在浏览器端的脚步语言,JavaScript主要解决的是前端与用户交互的问题,包括使用交互与数据交互。 JavaScript是浏览器解释执行的,前端脚本语言还有JScript(微软,IE独有),ActionScript( Adobe公司,需要插件)等。
前端三大块
- HTML:页面结构
- CSS:页面表现:元素大小、颜色、位置、隐藏或显示、部分动画效果
- JavaScript:页面行为:部分动画效果、页面与用户的交互、页面功能
JavaScript嵌入页面的方式
- 行间事件(主要用于事件)
<input type="button" name="" onclick="alert('ok!');">
- 页面script标签嵌入
<script type="text/javascript">
alert('ok!');
</script>
- 外部引入
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/index.js"></script>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>js嵌入页面title>
<script>
alert("hello world too!")
script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="./js/hello.js">script>
head>
<body>
<input type="button" name="" value="点击" onclick="alert('hello world')">
body>
html>
变量
JavaScript 是一种弱类型语言,javascript的变量类型由它的值来决定。 定义变量需要用关键字 ‘var’
弱类型语言和强类型语言
var iNum = 123;
var sTr = 'asd';
//同时定义多个变量可以用","隔开,公用一个‘var’关键字
var iNum = 45,sTr='qwe',sCount='68';
变量类型
5种基本数据类型:
- number 数字类型
- string 字符串类型
- boolean 布尔类型 true 或 false
- undefined undefined类型,变量声明未初始化,它的值就是undefined
- null null类型,表示空对象,如果定义的变量将来准备保存对象,可以将变量初始化为null,在页面上获取不到对象,返回的值就是null
1种复合类型:
- object
javascript语句与注释
一条javascript语句应该以“;”结尾
<script type="text/javascript">
var iNum = 123;
var sTr = 'abc123';
function fnAlert(){
alert(sTr);
};
fnAlert();
</script>
javascript注释
<script type="text/javascript">
// 单行注释
var iNum = 123;
/*
多行注释
1、...
2、...
*/
var sTr = 'abc123';
</script>
变量、函数、属性、函数参数命名规范
- 区分大小写
- 第一个字符必须是字母、下划线(_)或者美元符号($)
- 其他字符可以是字母、下划线、美元符或数字
匈牙利命名风格:
对象o Object 比如:oDiv
数组a Array 比如:aItems
字符串s String 比如:sUserName
整数i Integer 比如:iItemCount
布尔值b Boolean 比如:bIsComplete
浮点数f Float 比如:fPrice
函数fn Function 比如:fnHandler
正则表达式re RegExp 比如:reEmailCheck
获取元素方法一
可以使用内置对象document上的getElementById方法来获取页面上设置了id属性的元素,获取到的是一个html对象,然后将它赋值给一个变量
<script type="text/javascript">
var oDiv = document.getElementById('div1');
</script>
....
<div id="div1">这是一个div元素</div>
**注意:**上面的语句,如果把javascript写在元素的上面,就会出错,因为页面上从上往下加载执行的,javascript去页面上获取元素div1的时候,元素div1还没有加载,解决方法有两种:
第一种方法:将javascript放到页面最下边
....
<div id="div1">这是一个div元素div>
....
<script type="text/javascript">
var oDiv = document.getElementById('div1');
script>
body>
第二种方法:将javascript语句放到window.onload触发的函数里面,获取元素的语句会在页面加载完后才执行,就不会出错了。
<script type="text/javascript">
// window.onload 表示在整个页面加载完成以后再执行后续语句
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById('div1');
}
script>
....
<div id="div1">这是一个div元素div>
操作元素属性
获取的页面元素,就可以对页面元素的属性进行操作,属性的操作包括属性的读和写。
操作属性的方法
- “.” 操作
- “[ ]”操作
属性写法
- html的属性和js里面属性写法一样
- “class” 属性写成 “className”
- “style” 属性里面的属性,有横杠的改成驼峰式,比如:“font-size”,改成”style.fontSize”
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>属性操作01title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
var oA = document.getElementById("link");
var oDiv3 = document.getElementById("div3");
// 读取属性
var sID = oDiv.id;
alert(sID)
// 写属性
oDiv.style.color = "red";
oA.href = "http://www.baidu.com";
oA.title = "这是百度的链接";
// “class” 属性写成 “className”
oDiv3.className = "box";
}
script>
<style>
.box{
font-size:20px;
color:gold;
}
.box2{
font-size:30px;
color:green;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="div1">这是第一个div元素div>
这是一个链接a>
这是第二个divdiv>
这是第三个divdiv>
body>
html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>属性操作02title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("box");
var sMystyle = "color";
var sValue = "red";
// oDiv.style.color = "red";
// 属性用变量代替的话,需要用“[ ]”操作
oDiv.style[sMystyle] = sValue;
}
script>
head>
<body>
<div id="box">这是一个div元素div>
body>
html>
innerHTML
innerHTML可以读取或者写入标签包裹的内容
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>改变元素内部包裹的内容title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
// innerHTML可以读取或者写入标签包裹的内容 用于给页面塞数据
// 读取
var sText = oDiv.innerHTML;
alert(sText);
// 改写
oDiv.innerHTML = "这是修改的文字";
alert(oDiv.innerHTML);
oDiv.innerHTML = "百度网";
}
script>
head>
<body>
<div id="div1">这是一个div元素div>
body>
html>
函数
函数定义与执行
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>函数的定义和执行title>
<script>
// 由于函数执行在页面加载之后,因此不需要window.onload = function()
// 函数定义
function fnMyalert(){
alert("hello world");
}
// 函数执行 fnMyalert();
function fnChange(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
oDiv.style.color = "red";
oDiv.style.fontSize = "30px";
}
script>
head>
<body>
<div id="div1" onclick="fnMyalert()">这是一个div元素div>
<input type="button" value="改变div" onclick="fnChange()">
body>
html>
变量与函数预解析
JavaScript解析过程分为两个阶段,先是编译阶段,然后执行阶段,在编译阶段会将function定义的函数提前,并且将var定义的变量声明提前,将它赋值为undefined。
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>变量和函数预解析title>
<script>
// 变量预解析,会把变量的声明提前,但不会将变量的赋值预解析,因此弹出undefined
alert(iNum);
// 函数预解析会让函数的声明和定义提前,正常运行
myAlert();
// 使用一个未声明又未定义的变量,程序出错
// alert(iNum2);
var iNum = 12;
function myAlert(){
alert("hello world");
}
script>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
提取行间事件
在html行间调用的事件可以提取到javascript中调用,从而做到结构与行为分离。
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>提取行间事件title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn01");
// 函数在行间调用时候要写(),提取行间事件时候不能写()
// 即将事件属性和函数关联,不能写(),写了就会马上执行,产生逻辑错误
oBtn.onclick = fnChange;
function fnChange(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
oDiv.style.color = "red";
oDiv.style.fontSize = "30px";
}
}
script>
head>
<body>
<div id="div1">这是一个div元素div>
body>
html>
对比
<input type="button" value="改变div" onclick="fnChange()">
匿名函数
定义的函数可以不给名称,这个叫做匿名函数,可以将匿名函数直接赋值给元素绑定的事件来完成匿名函数的调用。
行间事件案例改写为匿名函数
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Documenttitle>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById('box');
var oBtn = document.getElementById('btn1');
oBtn.onclick = function(){
oDiv.style.color = 'red';
}
}
script>
head>
<body>
<div id="box">这是一个divdiv>
<input type="button" value='改变div' id='btn1'>
body>
html>
案例:网页换肤
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Documenttitle>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn1 = document.getElementById('btn1');
var oBtn2 = document.getElementById('btn2');
var oBtn3 = document.getElementById('btn3');
oBtn1.onclick = function(){
document.body.style.backgroundColor = 'red';
}
oBtn2.onclick = function(){
document.body.style.backgroundColor='green';
}
oBtn3.onclick = function(){
document.body.style.backgroundColor='gold';
}
}
script>
<style>
body{
background-color:cyan;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<input type="button" value='皮肤1' id='btn1'>
<input type="button" value='皮肤2' id='btn2'>
<input type="button" value='皮肤3' id='btn3'>
body>
html>
函数传参
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>函数传参title>
<script>
function fnMyalert(a){
alert(a);
}
fnMyalert("hello world");
window.onload = function(){
function fnChangestyle(mystyle,val){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
// 注意下方中括号用法
oDiv.style[mystyle] = val;
}
fnChangestyle("fontSize","30px");
fnChangestyle("color","red");
}
script>
head>
<body>
<div id="div1">这是一个div元素div>
body>
html>
函数中’return’关键字的作用:
- 返回函数执行的结果
- 结束函数的运行
- 阻止默认行为
<script type="text/javascript">
function fnAdd(iNum01,iNum02){
var iRs = iNum01 + iNum02;
return iRs;
alert('here!'); // 不弹出
}
var iCount = fnAdd(3,4);
alert(iCount); //弹出7
script>
条件语句
通过条件来控制程序的走向,就需要用到条件语句。
运算符
- 算术运算符: +(加)、 -(减)、 *(乘)、 /(除)、 %(求余)
- 赋值运算符:=、 +=、 -=、 *=、 /=、 %=
- 条件运算符:==、===、>、>=、<、<=、!=、&&(而且)、||(或者)、!(否)
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>加法练习title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oInput01 = document.getElementById("input01");
var oInput02 = document.getElementById("input02");
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn");
oBtn.onclick =function(){
// 获取后得到的是str类型,相加只会将字符串拼接
// 需要通过parseInt进行整型转换
var iVal01 = parseInt(oInput01.value);
var iVal02 = parseInt(oInput02.value);
alert(iVal01 + iVal02);
}
}
script>
head>
<body>
<input type="text" id="input01" placeholder="第一个数字">+
<input type="text" id="input02" placeholder="第二个数字">
<input type="button" id="btn" value="加法">
body>
html>
if else
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Documenttitle>
<script>
var iNum01 = 12;
var iNum02 = 24;
if(iNum01>iNum02){
alert('大于');
}
else{
alert('小于');
}
script>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
案例:制作单个按钮点击切换元素的显示和隐藏效果
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>按钮切换元素显示title>
<style>
.box{
width:200px;
height:400px;
background-color:gold;
}
style>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn01");
var oDiv = document.getElementById("box01");
// 由于默认div中无style这一行间属性,因此alert一开始为null
/*oDiv.style.display读取的是标签里
写的属性值,若没有写这个值,一开始为null*/
alert(oDiv.style.display);
oBtn.onclick = function(){
if(oDiv.style.display == "none"){
oDiv.style.display ="block";
}
else{
oDiv.style.display = "none";
}
/* // 改进方法
if(oDiv.style.display == "block" ||oDiv.style.display == "" ){
oDiv.style.display = "none";
}
else{
oDiv.style.display = "block";
}*/
}
}
script>
head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="切换" id="btn01">
<div class="box" id="box01">div>
body>
html>
多重if else语句
if(iWeek == 1){
oBody.style.backgroundColor = "gold";
}
else if(iWeek == 2){
oBody.style.backgroundColor = "green";
}
else if(iWeek == 3){
oBody.style.backgroundColor = "pink";
}
else if(iWeek == 4){
oBody.style.backgroundColor = "yellowgreen";
}
else if(iWeek == 5){
oBody.style.backgroundColor = "lightblue";
}
else{
oBody.style.backgroundColor = "lightgreen";
}
switch语句
多重if else语句可以换成性能更高的switch语句
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>switch语句title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oInput = document.getElementById("text01");
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn01");
var iNum;
oBtn.onclick = function(){
iNum = parseInt(oInput.value);
switch (iNum){
case 1:
document.body.style.backgroundColor = "gold";
break;
case 2:
document.body.style.backgroundColor = "green";
break;
case 3:
document.body.style.backgroundColor = "pink";
break;
case 4:
document.body.style.backgroundColor = "yellowgreen";
break;
case 5:
document.body.style.backgroundColor = "lightblue";
break;
// default 相当于 else
default:
document.body.style.backgroundColor = "lightgreen";
}
}
}
script>
head>
<body>
<input type="text" placeholder="输入星期数字" id="text01">
<input type="button" value="确定" id="btn01">
body>
html>
数组及操作方法
数组就是一组数据的集合,javascript中,数组里面的数据可以是不同类型的。
定义数组的方法
//对象的实例创建
var aList = new Array(1,2,3);
//直接量创建
var aList2 = [1,2,3,'asd'];
操作数组中数据的方法
- 获取数组的长度:aList.length
- 用下标操作数组的某个数据:aList[0]
- join() 将数组成员通过一个分隔符合并成字符串
- push() 和 pop() 从数组最后增加成员或删除成员
- unshift()和 shift() 从数组前面增加成员或删除成员
- reverse() 将数组反转
- indexOf() 返回数组中元素第一次出现的索引值
- splice() 在数组中增加或删除成员
var aList = [1,2,3,4];
aList.splice(2,1,7,8,9); //从第2个元素开始,删除1个元素,然后在此位置增加'7,8,9'三个元素
alert(aList); //弹出 1,2,7,8,9,4
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>数组title>
<script>
//对象的实例创建
var aList = new Array(1,2,3);
//直接量创建
var aList02 = [1,2,3,"asd"];
var aList03 = [1,2,"b",1,4,5,"b"];
// 获取数组长度
alert(aList02.length);
// 用下标操作数组的某个数据
alert(aList02[0]);
// join() 将数组成员通过一个分隔符合并成字符串
alert(aList02.join("+"));// 弹出 1+2+3+asd
alert(aList02.join("")); //弹出123asd
// push() 从数组最后增加成员
aList02.push("dasdsad");
alert(aList02);
// pop() 从数组最后删除成员
aList02.pop();
alert(aList02);
// reverse() 将数组反转
aList02.reverse();
alert(aList02);
// unshift()和 shift() 从数组前面增加成员或删除成员
aList02.shift("b");
alert(aList02);
aList02.unshift();
alert(aList02);
// indexOf() 返回数组中元素第一次出现的索引值
alert(aList03.indexof(1));
alert(aList03.indexof("b"));
// splice() 在数组中增加或删除成员
/*var aList = [1,2,3,4];
aList.splice(2,1,7,8,9); //从第2个元素开始,删除1个元素,然后在此位置增加'7,8,9'三个元素
alert(aList); //弹出 1,2,7,8,9,4*/
aList03.splice(1,0,"e");
alert(aList03); // 弹出 1,"e",2,"b",1,4,5,"b"
script>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
多维数组
多维数组指的是数组的成员也是数组的数组。
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>多维数组title>
<script>
var aList = [[1,2,3,4],["a","b","c"],[6,7,8]];
/*aList[0] = [1,2,3,4];
aList[1] = ["a","b","c"];
aList[2] = [6,7,8];*/
alert(aList.length); //弹出3
alert(aList[0].length); //a[0]这个数组的长度,弹出4
alert(aList[0][1]); //弹出2 a[0]数组中的第二个元素
alert(aList[1][0]); //弹出 a[1]数组中的第一个元素
alert(aList[2][0]); //弹出6 a[2]数组中的第一个元素
script>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
循环语句
程序中进行有规律的重复性操作,需要用到循环语句。
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>for循环title>
<script>
for(var i=0;i<5;i++){
alert("ok");
}
var aList = ["a","b","c","d"];
// 性能优化考虑可以先获取长度,避免每次获取
// var aLen = aList.length;
for(var i=0;i<aList.length;i++){
alert(aList[i]);
}
script>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
案例:将数组中的数据放入到页面中的列表中
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>将数据循环放入页面中title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var aList = ["美人鱼","疯狂动物城","魔兽","美队3","湄公河行动"];
var iLen = aList.length;
var oUl = document.getElementById("list");
var sTr = "";
for(var i=0;i<iLen;i++){
sTr += "" +aList[i] +"";
}
alert(sTr);
oUl.innerHTML = sTr;
}
script>
<style>
.list{
list-style: none;
margin:50px auto 0;
padding:0px;
width:300px;
height:300px;
}
.list li{
height:60px;
border-bottom:1px dotted #000;
line-height: 60px;
font-size:16px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<ul class="list" id="list">
ul>
body>
html>
案例:数组去重
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>数组去重title>
<script>
var aList = [1,2,3,4,4,3,2,1,2,3,4,5,6,5,5,3,3,4,2,1];
var aList2 = [];
for(var i=0;i<aList.length;i++){
// indexOf() 返回数组中元素第一次出现的索引值
//如果该元素第一次出现的索引等于当前索引,表示该元素第一次出现
if(aList.indexOf(aList[i])==i){
// push() 从数组最后增加成员,pop()为从最后删除成员
// unshift()和 shift() 从数组前面增加成员或删除成员
aList2.push(aList[i]);
}
}
alert(aList2);
script>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
while循环
var i=0;
while(i<8){
......
i++;
}
获取元素方法二
可以使用内置对象document上的getElementsByTagName方法来获取页面上的某一种标签,获取的是一个选择集,不是数组,但是可以用下标的方式操作选择集里面的标签元素。
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>通过标签获取元素title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
// 通过标签名获取li元素,生成一个选择集,赋值给aLi
var aLi = document.getElementsByTagName("li");
// 读取选择集内元素的个数
alert(aLi.length); //弹出13
// aLi.style.backgroundColor = 'gold'; // 出错!不能给选择集设置
//给单独一个aLi设置样式
aLi[0].style.backgroundColor="gold";
aLi[4].style.backgroundColor="green";
// 整体加背景色方法,通过for给每一个加
var aLen = aLi.length;
for(var i=0;i<aLen;i++){
aLi[i].style.backgroundColor = "pink";
}
//给每个ul 单独设置
var oLi01 = document.getElementById("list1");
var oLi02 = document.getElementById("list2");
var aLi01 = oLi01.getElementsByTagName('li');
alert(aLi01.length);
var aLi02 = oLi02.getElementsByTagName("li");
alert(aLi02.length);
var aLen01 = aLi01.length;
for(var i=0;i<aLen01;i++){
aLi01[i].style.color = "red";
}
var aLen02 = aLi02.length;
for(var i=0;i<aLen02;i++){
// 数组中 索引从0开始 因此要是偶数行需要 i%2!=0
if(i%2!=0){
aLi02[i].style.color = "#ddd";
}
}
}
script>
head>
<body>
<ul id="list1">
<li>1li>
<li>2li>
<li>3li>
<li>4li>
<li>5li>
<li>6li>
<li>7li>
<li>8li>
ul>
<ul id="list2">
<li>1li>
<li>2li>
<li>3li>
<li>4li>
<li>5li>
ul>
body>
html>
Javascript组成
- ECMAscript javascript的语法(变量、函数、循环语句等语法)
- DOM 文档对象模型 操作html和css的方法
- BOM 浏览器对象模型 操作浏览器的一些方法
字符串处理方法
- 字符串合并操作:“ + ”
- parseInt() 将数字字符串转化为整数
- parseFloat() 将数字字符串转化为小数
- split() 把一个字符串分隔成字符串组成的数组
- charAt() 获取字符串中的某一个字符
- indexOf() 查找字符串是否含有某字符
- substring() 截取字符串 用法: substring(start,end)(不包括end)
- toUpperCase() 字符串转大写
- toLowerCase() 字符串转小写
- reverse()字符串反转
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>字符串处理方法title>
<script>
var iNum01 = 12;
var sNum02 = "24";
var sTr = "abc";
// 字符串合并操作:“ + ”
// 数字和字符串相加,等同于字符串拼接
alert(iNum01+sNum02); //弹出1224
var sTr = "12.35";
// parseInt() 将数字字符串转化为整数
// parseFloat() 将数字字符串转化为小数
alert(parseInt(sTr)); //弹出12
alert(parseFloat(sTr)); //弹出12.35
// split() 把一个字符串分隔成字符串组成的数组
var sTr03 = "2017-04-22";
var aRr = sTr03.split("-");
alert(aRr); //弹出2017,04,22 表示["2017","04","22"]即2017 04 22,显示中的,不在格式内
var aRr2 = sTr03.split("");
alert(aRr2); // 弹出["2","0","1","7","-","0","4","-","2","2"]
// 获取字符串中的某一个字符
var sTr04 = "#div";
var sTr05 = sTr04.charAt(0); //sTr04.charAt(pos: int); 弹出#
alert(sTr05);
// indexOf() 查找字符串是否含有某字符
var sTr06 = "asda microsoft asda";
alert(sTr06.indexOf("microsoft"));//弹出5 ,表示存在且第一个字母索引为5 空格也计算索引
alert(sTr06.indexOf("yahei")); //弹出-1,表示不存在
// substring() 截取字符串 用法: substring(start,end)(不包括end)
var sTr07 = "abcdef123456edgf";
var sTr08 = sTr07.substring(6, 12); //sTr07.substring(start: int, end: int) 若sTr07.substring(6, 11)弹出12345;不能包含end,即sTr07.substring(6, 10),弹出123456
alert(sTr08);
var sTr09 = "#div";
alert(sTr09.substring(1)); //弹出 div ,1表示从1号索引开始切到最后
var sTr10 = "abcdEFG";
alert(sTr10.toUpperCase()); //弹出ABCDEFG;
alert(sTr10.toLowerCase()); //弹出abcdefg;
// 字符串反转
var sTr11 = 'asdfj12jlsdkf098';
// split() 将字符串分隔成字符串组成的数组,通过reverse倒置数组,再通过join()将数组成员通过一个分隔符合并成字符串
alert(sTr11.split("").reverse().join(""));
script>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
类型转换
直接转换 parseInt() 与 parseFloat()
alert('12'+7); //弹出127
alert( parseInt('12') + 7 ); //弹出19
alert( parseInt(5.6)); // 弹出5
alert('5.6'+2.3); // 弹出5.62.3
alert(parseFloat('5.6')+2.3); // 弹出7.8999999999999995
alert(0.1+0.2); //弹出 0.3000000000000004
alert((0.1*100+0.2*100)/100); //弹出0.3
alert((parseFloat('5.6')*100+2.3*100)/100); //弹出7.9
隐式转换 “==” 和 “-”
if('3'==3)
{
alert('相等');
}
// 弹出'相等'
alert('10'-3); // 弹出7
NaN 和 isNaN
alert( parseInt('123abc') ); // 弹出123
alert( parseInt('abc123') ); // 弹出NaN
定时器
定时器在javascript中的作用
- 制作动画
- 异步操作
- 函数缓冲与节流
定时器类型及语法
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>定时器title>
<script>
// 定时器可以隔一段时间调用函数,因此不必写在window.noload中
function fnMyalert(){
alert("hello world");
}
// 只执行一次的定时器
// setTimeout(函数名/匿名函数,毫秒值) 单位不写 1000ms=1s;
var timer01 = setTimeout(fnMyalert,2000);
//关闭只执行一次的定时器
clearTimeout(timer01);
//反复执行的定时器
var timer02 = setInterval(fnMyalert,1000);
//关闭定时器
clearInterval(timer02);
//匿名函数
var timer03 = setTimeout(function(){
alert("匿名函数");
},1000);
script>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
案例:定时器制作移动动画-定向移动
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>定时器动画title>
<style>
.box{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background-color:gold;
position:absolute;
left:0;
top:100px;
}
style>
<script>
/*window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
var iLeft = 0;
//30ms 经验值,动画效果连续
var timer = setInterval(moving,30);
function moving(){
iLeft +=2;
oDiv.style.left = iLeft + "px";
}
}*/
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
var iLeft = 0;
//30ms 经验值,动画效果连续
var timer = setInterval(function(){
iLeft +=2;
oDiv.style.left = iLeft + "px";
if(iLeft>700){
clearInterval(timer);
}
},30);
}
script>
head>
<body>
<div class="box" id="div1">div>
body>
html>
案例:定时器制作移动动画-往复运动
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>定时器动画title>
<style>
.box{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background-color:gold;
position:absolute;
left:0;
top:100px;
}
style>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
var iLeft = 0;
var iSpeed = 3;
//30ms 经验值,动画效果连续
var timer = setInterval(function(){
if(iLeft>100){
iSpeed = -3;
}
if(iLeft<0){
iSpeed = 3;
}
iLeft += iSpeed;
oDiv.style.left = iLeft + "px";
},30);
}
script>
head>
<body>
<div class="box" id="div1">div>
body>
html>
案例:定时器制作无缝滚动
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>无缝滚动title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
.btns_con{
width:1000px;
height:30px;
margin:50px auto 0;
position:relative;
}
.left,.right{
width:30px;
height:30px;
background-color:gold;
position:absolute;
left:-40px;
top:124px;
font-size:30px;
line-height:30px;
color:#000;
font-family: 'Arial';
text-align:center;
cursor:pointer;
border-radius:15px;
opacity:0.5;
}
.right{
left:1010px;
top:124px;
}
.list_con{
width:1000px;
height:200px;
border:1px solid #000;
margin:10px auto 0;
background-color:#f0f0f0;
position:relative;
overflow:hidden;
}
.list_con ul{
list-style:none;
width:2000px;
height:200px;
position:absolute;
left:0;
top:0;
}
.list_con li{
width:180px;
height:180px;
float:left;
margin:10px;
}
style>
<script type="text/javascript">
/*原理为在原来5个li后即右侧,拼接一张同样的图,实现无缝;
当两张图向左移动到最后一张也就是第十张末尾时候,瞬间将整个图拉回到起始位置.
当两张图向右移动时候,由于右边没有内容,因此在开始移动时候,将一张图拉至整个边框最左侧.
由于整张图拼接了一张图,即使将一张图拉至框的最左侧,框内还留有一张,因此框内并不会出现无内容效果*/
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("slide");
var oBtn01 = document.getElementById("btn01");
var oBtn02 = document.getElementById("btn02");
//通过标签获取元素,获取的是选择集,加上下标才能获取到元素
var oUl = document.getElementsByTagName("ul")[0];
//为了实现无缝滚动,将ul里面的内容复制一份,整个ul里面就包含了10个li
oUl.innerHTML = oUl.innerHTML + oUl.innerHTML;
var iLeft = 0;
// 默认开始向右移动
var iSpeed = 2;
// 定义一个变量用于存储当鼠标悬停时候的当前速度,便于赋值给鼠标移开后的当前速度
var iNowspeed = 0;
// 获取左右两个按钮效果,iLeft >0 往右边移动,<0 往左边移动
oBtn01.onclick = function(){
iSpeed = 2;
}
oBtn02.onclick = function(){
iSpeed = -2;
}
// 当鼠标悬停onmouseover在图片即oDiv上时候,图片停止运动
oDiv.onmouseover = function(){
iNowspeed = iSpeed;
iSpeed = 0;
}
//当鼠标移开onmouseout整个oDiv时候,图片继续保持现有速度和方式运动
oDiv.onmouseout = function(){
iSpeed = iNowspeed;
}
function moving(){
iLeft += iSpeed;
// 1000为整个盒子宽度,也就是5张图一次走完的宽度
// 当ul向左滚动到第5个li时,瞬间将整个ul拉回到初始位置
if(iLeft<-1000){
iLeft = 0;
}
// 当ul向右滚动时,瞬间将整个ul拉回到往左的第5个li的位置
if(iLeft >0){
iLeft = -1000;
}
oUl.style.left = iLeft + "px";
}
var timer = setInterval(moving, 30);
}
script>
head>
<body>
<div class="btns_con">
<div class="left" id="btn01"><div>
<div class="right" id="btn02">>div>
div>
<div class="list_con" id="slide">
<ul>
<li><a href=""><img src="images/goods001.jpg" alt="商品图片">a>li>
<li><a href=""><img src="images/goods002.jpg" alt="商品图片">a>li>
<li><a href=""><img src="images/goods003.jpg" alt="商品图片">a>li>
<li><a href=""><img src="images/goods004.jpg" alt="商品图片">a>li>
<li><a href=""><img src="images/goods005.jpg" alt="商品图片">a>li>
ul>
div>
body>
html>
案例:时钟
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>时钟title>
<style>
div{
text-align:center;
font-size:30px;
color:pink;
}
style>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
function fnTimego(){
var sNow = new Date();
// 获取年月日时分秒
var iYear = sNow.getFullYear();
// month默认为0-11,0为1月.因此需要+1
var iMonth = sNow.getMonth()+1;
var iDate = sNow.getDate();
// 星期是从0-6,周日为0
var iWeek = sNow.getDay();
var iHours = sNow.getHours();
var iMinutes = sNow.getMinutes();
var iSeconds = sNow.getSeconds();
// 将以上字符串拼接
var sTr = "当前时间是" +iYear + "年" +iMonth +"月" + iDate +"日" +fnToweek(iWeek)+
" "+fnTodouble(iHours) +":"+fnTodouble(iMinutes)+":"+fnTodouble(iSeconds);
oDiv.innerHTML = sTr;
}
// 修改星期的表现方式
function fnToweek(n){
if(n==0){
return "星期日";
}
else if(n==1){
return "星期一";
}
else if(n==2){
return "星期二";
}
else if(n==3){
return "星期三";
}
else if(n==4){
return "星期四";
}
else if(n==5){
return "星期五";
}
else {
return "星期六";
}
}
// 修改个位数时分秒的表现方式 1 改为01
function fnTodouble(n){
if(n<10){
return "0"+n;
}
else{
return n;
}
}
// 由于定时器开始第1S未开始执行会显示空白,因此先调用一次函数
fnTimego();
setInterval(fnTimego,1000);
}
script>
head>
<body>
<div id="div1">div>
body>
html>
案例:倒计时
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>倒计时title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
// 使用匿名函数还是会出现定时器第一秒空白的情况,因此不建议
setInterval(function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
//获取当前时间,实际开发中,需要通过ajax读取后台服务器时间
var sNow = new Date();
//未来时间假设为2020年5月1日0:0:0,由于月是0-11因此4月需要用3表示
var sFuture = new Date(2020,3,30,24,0,0);
// alert(sFuture -sNow); 弹出结果为毫秒值
var sLeft = parseInt((sFuture -sNow)/1000); //毫秒转为秒,并取整
// 计算剩余多少天多少时分秒,一天为86400,24*60*60
var iDays = parseInt(sLeft/86400);
var iHours = parseInt((sLeft%86400)/3600);
var iMinutes = parseInt(((sLeft%86400)%3600)/60);
var iSeconds = (sLeft%60);
/*执行结果相同
var iSecond01 = (((sLeft%86400)%3600)%60);
var iSeconds = (sLeft%60);
alert(iSecond01);
alert(iSeconds);*/
var sTr = "距离2020年5月1日还剩:"+fnTodou(iDays)+"天"+fnTodou(iHours)+"时"+fnTodou(iMinutes)+"分"+fnTodou(iSeconds)+"秒";
oDiv.innerHTML = sTr;
},1000);
function fnTodou(n){
if(n<10){
return "0"+n;
}
else{
return n;
}
}
}
script>
<style>
div{
text-align: center;
color:red;
font-size:30px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="div1" >div>
body>
html>
变量作用域
变量作用域指的是变量的作用范围,javascript中的变量分为全局变量和局部变量。
- 全局变量:在函数之外定义的变量,为整个页面公用,函数内部外部都可以访问。
- 局部变量:在函数内部定义的变量,只能在定义该变量的函数内部访问,外部无法访问
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Documenttitle>
<script type="text/javascript">
//函数外部定义的是全局变量,函数内部和外部都可以访问
var iNum01 = 12;
// 重复定义,后面的会覆盖前面的值
//var iNum01 = 14;
function myalert(){
//var iNum01 = 24;
// 函数内部定义的是局部变量,函数内部可以访问,外部不能访问
var iNum02 = 36;
alert(iNum01);
iNum01 += 10;
}
function myalert02(){
alert(iNum01);
}
myalert(); // 弹出 12
myalert02(); // 弹出 22
//alert(iNum02); 出错!
script>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
封闭函数
封闭函数是javascript中匿名函数的另外一种写法,创建一个一开始就执行而不用命名的函数。
一般定义的函数和执行函数:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>封闭函数title>
<script>
/*function Myalert(){
alert("hello world");
}
Myalert();*/
// 封闭函数是javascript中匿名函数的另外一种写法,创建一个一开始就执行而不用命名的函数。
(function(){
alert("hello world!");
})();
/*封闭函数可以创造一个独立的空间,在封闭函数内定义的变量和函数不会影响外部同名的函数和变量,可以避免命名冲突,在页面上引入多个js文件时,用这种方式添加js文件比较安全,*/
function Myalert02(){
alert("hello world ");
}
var iNum01 = 12;
(function(){
var iNum01 =24;
function Myalert02(){
alert("hello hello!");
}
alert("封闭函数内"+iNum01);
Myalert02();
})();
alert("外部变量"+iNum01);
Myalert02();
// 还可以在函数定义前加上“~”和“!”等符号来定义封闭函数
!function(){
alert("hello");
}();
~function(){
alert("1234");
}();
// 在封闭函数前加 ; 可以避免js压缩时出错
;(function(){
var iNum01 =24;
function Myalert02(){
alert("hello hello!");
}
alert("封闭函数内"+iNum01);
Myalert02();
})();
script>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
常用内置对象
document
document.getElementById //通过id获取元素
document.getElementsByTagName //通过标签名获取元素
document.referrer //获取上一个跳转页面的地址(需要服务器环境)
location
window.location.href //获取或者重定url地址
window.location.search //获取地址参数部分
window.location.hash //获取页面锚点或者叫哈希值
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>location属性title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
// document.referrer //获取上一个跳转页面的地址(需要服务器环境)
//var sUrl = document.referrer;
var oBtn01 = document.getElementById("btn01");
oBtn01.onclick = function(){
// window.location.href //获取或者重定url地址
// window.location.href = oUrl;
window.location.href = "http://www.baidu.com";
}
}
script>
head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="跳转" id="btn01">
body>
html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>location属性title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oBody = document.getElementById("body01");
//通过?传递
var sData = window.location.search;
//通过#传递
var sHash = window.location.hash;
alert(sHash);
if(sData!=""){
/*split() 把一个字符串分隔成字符串组成的数组
var sTr = '2017-4-22';
var aRr = sTr.split("-");*/
//例如传入参数为?aa=1,经过split为[?aa,1],aRr[1]=1,获取到参数值
var aRr = sData.split("=");
var iNum = aRr[1];
if(iNum==1){
oBody.style.backgroundColor = "gold";
}
else if(iNum==2){
oBody.style.backgroundColor = "green";
}
else{
oBody.style.backgroundColor = "pink";
}
}
}
script>
head>
<body id="body01">
<h1>038页面h1>
body>
html>
Math
Math.random 获取0-1的随机数,不包括1
Math.floor 向下取整
Math.ceil 向上取整
案例:获取一定范围内随机数
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>获取固定区间的随机数title>
<script>
var iNum_min = 10;
var iNum_max = 20;
var aRr = [];
var aRr2 = [];
for(var i=0;i<30;i++){
var iNum = Math.floor((iNum_max-iNum_min)*Math.random() + iNum_min);
aRr.push(iNum);
}
console.log(aRr);
// 向下取整导致随机数里不含20,且random()不含1
//若要随机生成里含最大值
for(var i=0;i<30;i++){
var iNum2 = Math.floor((iNum_max-iNum_min +1)*Math.random() + iNum_min);
aRr2.push(iNum2);
}
console.log(aRr2);
script>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
案例:倒计时弹窗
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>倒计时弹框title>
<style type="text/css">
.menu{
height:80px;
background-color:gold;
position:fixed;
width:960px;
top:0px;
/*fixed定位后,left:50%水平居中*/
left:50%;
margin-left:-480px;
}
p{
text-align:center;
}
.popup{
width:500px;
height:300px;
border:1px solid #000;
background:#fff;
position:fixed;
left:50%;
margin-left:-251px;
top:50%;
margin-top:-151px;
z-index:999;
}
.popup h2{
background-color:gold;
margin:10px;
height:40px;
}
.mask{
position:fixed;
width:100%;
height:100%;
background-color:#000;
left:0px;
top:0px;
/*opacity 透明度*/
opacity:0.5;
z-index: 998;
}
.pop_con{
display:none;
}
style>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oPop = document.getElementById("pop_con");
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn");
var oPop_tip = document.getElementById("pop_tip");
var iTime = 5;
oBtn.onclick = function(){
oPop.style.display = "block";
var timer = setInterval(fnDaojishi,1000);
function fnDaojishi(){
iTime--;
oPop_tip.innerHTML = "还有"+iTime+"秒钟关闭弹框";
if(iTime==0){
oPop.style.display ="none";
clearInterval(timer);
iTime = 5;
oPop_tip.innerHTML = "还有5秒钟关闭弹框";
}
}
}
}
script>
head>
<body>
<div class="menu">菜单文字div>
<div class="pop_con" id="pop_con">
<div class="popup">
<h2>弹框h2>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<p id="pop_tip">还有5秒钟关闭弹框p>
div>
<div class="mask">div>
div>
<input type="button" value="弹出弹框" id="btn">
<p>网页文字p>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<p>网页文字p>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<p>网页文字p>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<p>网页文字p>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<p>网页文字p>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<p>网页文字p>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
body>
html>
jquery
jQuery是目前使用最广泛的javascript函数库。据统计,全世界排名前100万的网站,有46%使用jQuery,远远超过其他库。微软公司甚至把jQuery作为他们的官方库。
jQuery的版本分为1.x系列和2.x、3.x系列,1.x系列兼容低版本的浏览器,2.x、3.x系列放弃支持低版本浏览器
jquery是一个函数库,一个js文件,页面用script标签引入这个js文件就可以使用。
官方网站
版本下载
jquery加载
将获取元素的语句写到页面头部,会因为元素还没有加载而出错,jquery提供了ready方法解决这个问题,它的速度比原生的 window.onload 更快。
可以简写为:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jquery加载title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">
script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
alert("原生js"+oDiv);
}
/*等同于js中window.onload = function(){
}
$(document).ready(function(){
})*/
/*ready()完整写法
ready()比window.onload 快的原因是因为window.onload()标签加载并渲染完后才运行
ready()等标签加载完后就运行.
$(document).ready(function(){
var $div = $("#div1");
alert("jquery弹出"+$div);
})*/
$(function(){
var $div = $("#div1");
alert("jquery弹出"+$div);
})
script>
head>
<body>
<div id="div1">这是一个div元素div>
body>
html>
注意:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jquery引入容易出错的地方title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(function(){
})
script>
head>
<body>
<div id="div1">div元素div>
body>
html>
jquery选择器
jquery用法思想一
选择某个网页元素,然后对它进行某种操作
jquery选择器
jquery选择器可以快速地选择元素,选择规则和css样式相同,使用length属性判断是否选择成功。
$('#myId') //选择id为myId的网页元素
$('.myClass') // 选择class为myClass的元素
$('li') //选择所有的li元素
$('#ul1 li span') //选择id为ul1元素下的所有li下的span元素
$('input[name=first]') // 选择name属性等于first的input元素
jquery样式操作
jquery用法思想二
同一个函数完成取值和赋值
操作行间样式
// 获取div的样式
$("div").css("width");
$("div").css("color");
//设置div的样式
$("div").css("width","30px");
$("div").css("height","30px");
$("div").css({fontSize:"30px",color:"red"});
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jquery选择器title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(function(){
// 有id的标签选择用#,class选择用.类名
var $div = $("#div1");
$div.css({"color":"red"});
var $div2 = $(".box");
$div2.css({"color":"green"});
var $li = $(".list li");
// jquery有容错,background-color也兼容
$li.css({"backgroundColor":"pink","color":"red"});
})
script>
head>
<body>
<div id="div1">这是第一个div元素div>
<div class="box">这是第二个div元素div>
<div class="box">这是第三个div元素div>
<ul class="list">
<li>1li>
<li>2li>
<li>3li>
<li>4li>
<li>5li>
<li>6li>
<li>7li>
<li>8li>
ul>
body>
html>
对选择集进行过滤
$('div').has('p'); // 选择包含p元素的div元素
$('div').not('.myClass'); //选择class不等于myClass的div元素
$('div').filter('.myClass'); //选择class等于myClass的div元素
$('div').eq(5); //选择第6个div元素
选择集转移
$('div').prev(); //选择div元素前面紧挨的同辈元素
$('div').prevAll(); //选择div元素之前所有的同辈元素
$('div').next(); //选择div元素后面紧挨的同辈元素
$('div').nextAll(); //选择div元素后面所有的同辈元素
$('div').parent(); //选择div的父元素
$('div').children(); //选择div的所有子元素
$('div').siblings(); //选择div的同级元素
$('div').find('.myClass'); //选择div内的class等于myClass的元素
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jquery选择器过滤title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
// 针对使用一次的变量可以
// $("div").css({"backgroundColor":"gold"});
var $div = $("div");
$div.css({"backgroundColor":"gold"});
$div.has("p").css({"fontSize":"30px"});
$div.eq(4).css({"textIndent":"20px"});
$div.eq(3).prev().css({"color":"red"});
$div.find(".tip").css({"fontSize":"30px"});
})
script>
head>
<body>
<div>1div>
<div><p>2p>div>
<div>3div>
<div>4div>
<div>5div>
<div>6div>
<div>7div>
<div><span>8span><span class="tip">9span>div>
body>
html>
判断是否选择到了元素
jquery有容错机制,即使没有找到元素,也不会出错,可以用length属性来判断是否找到了元素,length等于0,就是没选择到元素,length大于0,就是选择到了元素。
var $div1 = $('#div1');
var $div2 = $('#div2');
alert($div1.length); // 弹出1
alert($div2.length); // 弹出0
......
这是一个div
操作样式类名
$("#div1").addClass("divClass2") //为id为div1的对象追加样式divClass2
$("#div1").removeClass("divClass") //移除id为div1的对象的class名为divClass的样式
$("#div1").removeClass("divClass divClass2") //移除多个样式
$("#div1").toggleClass("anotherClass") //重复切换anotherClass样式
$("#div1").hasClass("divClass")//判断是否有divClass样式,若有返回true
绑定click事件
给元素绑定click事件,可以用如下方法:
$('#btn1').click(function(){
// 内部的this指的是原生对象
// 使用jquery对象用 $(this)
})
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绑定click事件title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(function(){
var $Btn = $("#btn");
// //方法1
// $Btn.click(function(){
// // hasClsss()判断是否含有某个样式名,若有返回true
// if($(".box").hasClass("col01")!=true){
// $(".box").addClass("col01");
// }
// else{
// $(".box").removeClass("col01")
// }
// })
//方法2
$Btn.click(function(){
$(".box").toggleClass("col01");
})
})
script>
<style>
.box{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background-color:gold;
}
.col01{
background-color: green;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<input type="button" id="btn" value="切换样式">
<div class="box">div元素div>
body>
html>
获取元素的索引值
有时候需要获得匹配元素相对于其同胞元素的索引位置,此时可以用index()方法获取
$(function(){
var $Li = $(".list li");
// alert($Li.eq(3).index()); //3
// $('div').filter('.myClass'); //选择class等于myClass的div元素
// 有时候需要获得匹配元素相对于其同胞元素的索引位置,此时可以用index()方法获取
alert($Li.filter(".myli").index()); //4
})
......
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
案例:选项卡
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>选项卡title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(function(){
var $Btn = $(".btns input");
var $Div = $(".cons div");
$Btn.click(function(){
/*js:this 表示当前点击/选中的对象
jquery:$(this)*/
// $('div').siblings(); //选择除了自身外所有的div的同级元素
// 当前选中对象添加current,且除this外的元素删除current
$(this).addClass("current").siblings().removeClass("current");
//将当前点击按钮的索引和cons中的div关联起来
//alter($(this).index()); // 0 1 2
$Div.eq($(this).index()).addClass("active").siblings().removeClass("active");
})
})
script>
<style>
.btns input{
width:100px;
height:40px;
background-color: #ddd;
border:0;
}
.btns .current{
background-color:gold;
}
.cons div{
width:500px;
height:300px;
background-color: gold;
display:none;
text-align: center;
line-height: 300px;
font-size:30px;
}
.cons .active{
display:block;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="btns">
<input type="button" value="01" class="current">
<input type="button" value="02">
<input type="button" value="03">
div>
<div class="cons">
<div class="active">选项卡1的内容div>
<div>选项卡2的内容div>
<div>选项卡3的内容div>
div>
body>
html>
jquery特殊效果
fadeIn() 淡入
$btn.click(function(){
$('#div1').fadeIn(1000,'swing',function(){
alert('done!');
});
});
fadeOut() 淡出
fadeToggle() 切换淡入淡出
hide() 隐藏元素
show() 显示元素
toggle() 切换元素的可见状态
slideDown() 向下展开
slideUp() 向上卷起
slideToggle() 依次展开或卷起某个元素
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jquery特殊效果title>
<script src="./js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(function(){
var $Btn = $("#btn");
$Btn.click(function(){
//fadeIn/Out(1000,"swing",function(){})
// 3个参数分别代表时间,运动曲线,回调函数
//运动方式有swing缓冲运动和linear匀速运动
$(".box").fadeIn(1000,"swing",function(){
alert("动画结束");
})
})
})
$(function(){
$("#btn01").click(function(){
$(".box").fadeToggle();
})
})
$(function(){
$("#btn02").click(function(){
// hide() 隐藏元素/toggle()切换/show() 显示元素
$(".box").toggle();
})
})
$(function(){
$("#btn03").click(function(){
/*slideDown() 向下展开
slideUp() 向上卷起
slideToggle() 依次展开或卷起某个元素*/
$(".box").slideDown(1000,function(){
alert("由于盒子默认隐藏,因此不能卷起,但可以展开");
});
})
})
script>
<style>
.box{
width:300px;
height:300px;
background-color:gold;
display:none;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="动画" id="btn">
<input type="button" value="切换淡入淡出" id="btn01">
<input type="button" value="切换显示隐藏" id="btn02">
<input type="button" value="展开" id="btn03">
<div class="box">div>
body>
html>
jquery链式调用
jquery对象的方法会在执行完后返回这个jquery对象,所有jquery对象的方法可以连起来写:
$('#div1') // id为div1的元素
.children('ul') //该元素下面的ul子元素
.slideDown('fast') //高度从零变到实际高度来显示ul元素
.parent() //跳到ul的父元素,也就是id为div1的元素
.siblings() //跳到div1元素平级的所有兄弟元素
.children('ul') //这些兄弟元素中的ul子元素
.slideUp('fast'); //高度实际高度变换到零来隐藏ul元素
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>层级菜单title>
<style type="text/css">
body{
font-family:'Microsoft Yahei';
}
body,ul{
margin:0px;
padding:0px;
}
ul{
list-style:none;
}
.menu{
width:200px;
margin:20px auto 0;
}
.menu .level1,.menu li ul a{
display:block;
width:200px;
height:30px;
line-height:30px;
text-decoration:none;
background-color:#3366cc;
color:#fff;
font-size:16px;
text-indent:10px;
}
.menu .level1{
border-bottom:1px solid #afc6f6;
}
.menu li ul a{
font-size:14px;
text-indent:20px;
background-color:#7aa1ef;
}
.menu li ul li{
border-bottom:1px solid #afc6f6;
}
.menu li ul{
display:none;
}
.menu li ul.current{
display:block;
}
.menu li ul li a:hover{
background-color:#f6b544;
}
style>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
$('.level1').click(function(){
/*当前点击的元素$(this)即a
紧挨的同辈元素next()即ul
slideToggle()向下展开,
再跳到parent()此元素的父级(li),
再跳到此父级的其他的同辈元素siblings()即(li),
选择其他同辈元素children('ul')即(li)的子元素ul,然后将它向上收起slideUp()。
通过stop() 可以修正反复点击导致的持续动画的问题*/
$(this).next().stop().slideToggle().parent().siblings().children('ul').slideUp();
})
})
script>
head>
<body>
<ul class="menu">
<li>
<a href="#" class="level1">水果a>
<ul class="current">
<li><a href="#">苹果a>li>
<li><a href="#">梨子a>li>
<li><a href="#">葡萄a>li>
<li><a href="#">火龙果a>li>
ul>
li>
<li>
<a href="#" class="level1">海鲜a>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">蛏子a>li>
<li><a href="#">扇贝a>li>
<li><a href="#">龙虾a>li>
<li><a href="#">象拔蚌a>li>
ul>
li>
<li>
<a href="#" class="level1">肉类a>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">内蒙古羊肉a>li>
<li><a href="#">进口牛肉a>li>
<li><a href="#">野猪肉a>li>
ul>
li>
<li>
<a href="#" class="level1">蔬菜a>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">娃娃菜a>li>
<li><a href="#">西红柿a>li>
<li><a href="#">西芹a>li>
<li><a href="#">胡萝卜a>li>
ul>
li>
<li>
<a href="#" class="level1">速冻a>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">冰淇淋a>li>
<li><a href="#">湾仔码头a>li>
<li><a href="#">海参a>li>
<li><a href="#">牛肉丸a>li>
ul>
li>
ul>
body>
html>
jquery动画
通过animate方法可以设置元素某属性值上的动画,可以设置一个或多个属性值,动画执行完成后会执行一个函数。
$('#div1').animate({
width:300,
height:300
},1000,'swing',function(){
alert('done!');
});
参数可以写成数字表达式:
$('#div1').animate({
width:'+=100',
height:300
},1000,'swing',function(){
alert('done!');
});
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>animate动画title>
<script src="./js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
// animate类似与css的transition
$(function(){
$("#btn01").click(function(){
$(".box").animate({"width":"200px"});
})
})
$(function(){
$("#btn02").click(function(){
$(".box").animate({"width":"400px","height":"400px"});
})
})
$(function(){
$("#btn03").click(function(){
$(".box").animate({"width":"500px"},1000,function(){
$(".box").animate({"height":"500px"},function(){
// opacity透明度
$(".box").animate({"opacity":"0"});
})
})
})
})
$(function(){
$("#btn04").click(function(){
$(".box2").stop().animate({"width":"+=100"});
})
})
script>
<style>
.box,.box2{
width:100px;
height:100px;
background-color: gold;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="宽度改变" id="btn01">
<input type="button" value="宽高同时改变" id="btn02">
<input type="button" value="先宽后高改变" id="btn03">
<input type="button" value="参数表示数学式" id="btn04">
<div class="box">div>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<div class="box2">div>
body>
html>
案例:滑动选项卡
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>选项卡title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(function(){
var $Btn = $(".btns input");
var $slides = $(".cons .slides");
$Btn.click(function(){
/*js:this 表示当前点击/选中的对象
jquery:$(this)*/
// $('div').siblings(); //选择除了自身外所有的div的同级元素
// 当前选中对象添加current,且除this外的元素删除current
$(this).addClass("current").siblings().removeClass("current");
//将当前点击按钮的索引和cons中的div关联起来
//alter($(this).index()); // 0 1 2
$slides.stop().animate({"left":-500*$(this).index()});
})
})
script>
<style>
.btns input{
width:100px;
height:40px;
background-color: #ddd;
/*去除按钮自身的背景框*/
border:0;
/*去除按钮上选中时候响应的边框*/
outline: none;
}
.btns .current{
background-color:gold;
}
.cons{
width:500px;
height:300px;
overflow:hidden;
position:relative;
}
.cons .slides{
width:1500px;
height:300px;
position:absolute;
}
.cons .slides div{
width:500px;
height:300px;
background-color: gold;
/*display:none;*/
text-align: center;
line-height: 300px;
font-size:30px;
float:left;
}
.cons .active{
display:block;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="btns">
<input type="button" value="01" class="current">
<input type="button" value="02">
<input type="button" value="03">
div>
<div class="cons">
<div class="slides">
<div class="active">选项卡1的内容div>
<div>选项卡2的内容div>
<div>选项卡3的内容div>
div>
div>
body>
html>
尺寸相关、滚动事件
获取和设置元素的尺寸
width()、height() 获取元素width和height
innerWidth()、innerHeight() 包括padding的width和height
outerWidth()、outerHeight() 包括padding和border的width和height
outerWidth(true)、outerHeight(true) 包括padding和border以及margin的width和height
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>获取元素尺寸title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(function(){
var $Div = $(".box");
//盒子内容宽高
console.log($Div.width()); //300
console.log($Div.height()); //200
//盒子内容+两边padding
console.log($Div.innerWidth()); //300+20*2
console.log($Div.innerHeight()); //200+20*2
//盒子内容+两边padding+border即盒子真实尺寸
console.log($Div.outerWidth()); //300+20*2+20*2
console.log($Div.outerHeight()); //200+20*2+20*2
//盒子内容+padding+border+margin
console.log($Div.outerWidth(true)); // 300+20*2+20*2+30*2
console.log($Div.outerHeight(true)); //200+20*2+20*2+30*2
})
script>
<style>
.box{
width:300px;
height:200px;
padding:20px;
border:20px solid #000;
margin:30px;
background-color:gold;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="box">div>
body>
html>
获取元素相对页面的绝对位置
offset()
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>获取元素绝对位置title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(function(){
var $Div = $(".box");
$Div.click(function(){
var oPos = $Div.offset();
alert(oPos.left);
document.title = oPos.left+"|"+oPos.top;
})
// var $oPos = $Div.offset();
// console.log($oPos); //Object {top: 50, left: 102}
})
script>
<style>
.box{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background-color:gold;
margin:50px auto 0;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="box">div>
body>
html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>加入购物车title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(function(){
var $btn = $(".add");
var $chart = $(".chart");
var $count = $(".chart em");
var $point = $(".point");
//获取两个div的盒子的实际宽高,便于将圆点置于中间位置
var $w01 = $btn.outerWidth();
var $h01 = $btn.outerHeight();
var $w02 = $chart.outerWidth();
var $h02 = $chart.outerHeight();
$btn.click(function(){
//获取两个盒子的绝对位置
var oPos01 = $btn.offset();
var oPos02 = $chart.offset();
//默认圆点为隐藏,需要在点击加入购物车后,将圆点显示在div中间位置
$point.css({"left":oPos01.left+parseInt($w01/2)-8,"top":oPos01.top+parseInt($h01/2)-8});
$point.show();
//通过animate实现点击后,将圆点从加入购物车移动到购物车,并隐藏
$point.animate({"left":oPos02.left+parseInt($w02/2)-8,"top":oPos02.top+parseInt($h02/2)-8},1000,function(){
//移动圆点到指定位置后,隐藏圆点,并修改em中的值也就是购物数量
$point.hide();
//通过.html()获取em中的值,返回类型为string,相当于css中的innerHTML
var iNum = $count.html();
//修改em的值
$count.html(parseInt(iNum)+1);
});
})
})
script>
<style>
.chart{
width:150px;
height:50px;
text-align:center;
line-height: 50px;
float:right;
border:2px solid #000;
margin-right:50px;
margin-top:100px;
}
.chart em{
font-style: normal;
color:red;
font-weight:bold;
}
.add{
width:100px;
height:50px;
background-color:green;
border:0;
color:#fff;
float:left;
margin-top:300px;
margin-left:300px;
outline:none;
}
.point{
width:16px;
height:16px;
background-color: red;
/*便于定位,将小圆点设置为固定定位*/
position:fixed;
left:0;
top:0;
border-radius: 8px;
display:none;
/* z-index 属性设置元素的堆叠顺序。拥有更高堆叠顺序的元素总是会处于堆叠顺序较低的元素的前面。*/
z-index:999;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="chart">购物车<em>0em>div>
<input type="button" value="加入购物车" class="add">
<div class="point">div>
body>
html>
获取浏览器可视区宽度高度
$(window).width();
$(window).height();
获取页面文档的宽度高度
$(document).width();
$(document).height();
获取页面滚动距离
$(document).scrollTop();
$(document).scrollLeft();
页面滚动事件
$(window).scroll(function(){
......
})
案例:置顶菜单
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>置顶菜单title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(function(){
var $menu = $(".menu");
var $menu_back = $(".menu_back");
var $totop = $(".totop");
$(window).scroll(function(){
var iNum = $(document).scrollTop();
document.title = iNum;
if(iNum>200){
//定位元素水平居中方式:1.left = 50%,2.margin-left = -(width/2)
$menu.css({"position":"fixed","left":"50%","top":"0px","marginLeft":"-480px"});
$menu_back.show();
$totop.fadeIn();
}
else{
//static 默认值,没有定位,元素出现在正常的文档流中,相当于取消定位属性或者不设置定位属性。
$menu.css({"position":"static","marginLeft":"auto"});
$menu_back.hide();
$totop.fadeOut();
}
/*if(iNum>400){
$totop.fadeIn();
}
else{
$totop.fadeOut();
}
*/
})
$totop.click(function(){
//针对不同浏览器,兼容写法$("html,body")
$("html,body").animate({"scrollTop":0});
})
})
script>
<style>
body{
margin:0;
}
.banner{
width:960px;
height:200px;
background-color:cyan;
margin:0 auto;
}
.menu{
width:960px;
height:80px;
background-color:gold;
margin:0 auto;
text-align:center;
line-height:80px;
opacity:0.3;
/* {
opacity:0.1;
兼容IE
filter:alpha(opacity=10);
} */
}
.menu_back{
width:960px;
height:80px;
margin:0 auto;
display:none;
}
p{
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
.totop{
width:60px;
height:60px;
background-color:blue;
color:#fff;
font-size:40px;
text-align:center;
line-height:60px;
position:fixed;
right:20px;
bottom:50px;
border-radius:50%;
cursor:pointer;
display:none;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="banner">div>
<div class="menu">菜单div>
<div class="menu_back">div>
<div class="totop">↑div>
<p>文档内容p>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<p>文档内容p>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<p>文档内容p>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<p>文档内容p>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<p>文档内容p>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
body>
html>
jquery属性操作
html() 取出或设置html内容
// 取出html内容
var $htm = $('#div1').html();
// 设置html内容
$('#div1').html('添加文字');
prop() 取出或设置某个属性的值
// 取出图片的地址
var $src = $('#img1').prop('src');
// 设置图片的地址和alt属性
$('#img1').prop({src: "test.jpg", alt: "Test Image" });
jquery循环
对jquery选择的对象集合分别进行操作,需要用到jquery循环操作,此时可以用对象上的each方法
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>jquery循环title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(function(){
var $li = $(".list li");
/*$li.css({"backgroundColor":"gold"});
$li.eq(0).css({"backgroundColor":"gold"});*/
$li.each(function(){
// alert($(this).html()); //弹8次 执行8次
if($(this).index() % 2==0){
$(this).css({"backgroundColor":"gold"});
}
})
})
script>
head>
<body>
<ul class="list">
<li>1li>
<li>2li>
<li>3li>
<li>4li>
<li>5li>
<li>6li>
<li>7li>
<li>8li>
ul>
body>
html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<style>
*{
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
body{
font-size:12px;
}
#accordion{
width:727px;
height:350px;
margin:100px auto 0;
position:relative;
overflow:hidden;
border:1px solid #CCC;
}
#accordion ul{
list-style:none;
}
#accordion ul li{
width:643px;
height:350px;
position:absolute;
background:#FFF;
}
#accordion ul li span{
display:block;
width:20px;
height:350px;
float:left;
text-align:center;
color:#FFF;
padding-top:5px;
cursor:pointer;
}
#accordion ul li img{
display:block;
float:right;
}
.bar01{
left:0px;
}
.bar02{
left:643px;
}
.bar03{
left:664px;
}
.bar04{
left:685px;
}
.bar05{
left:706px;
}
.bar01 span{
background:#09E0B5;
}
.bar02 span{
background:#3D7FBB;
}
.bar03 span{
background:#5CA716;
}
.bar04 span{
background:#F28B24;
}
.bar05 span{
background:#7C0070;
}
style>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
var $li = $('#accordion li');
$li.click(function(){
//alert($(this).html());
//21是小标签宽度,21*$(this).index()就是每个的left定位位置
$(this).animate({'left':21*$(this).index()});
//点击的li,前面的li向左运动到各自的位置
$(this).prevAll().each(function(){
//这里的$(this)指的是循环选择的每个li
$(this).animate({'left':21*$(this).index()});
})
// 第5个li在右边的left值 727-21*1 等同于 727-21*(5-$(this).index())
// 第4个li在右边的left值 727-21*2 等同于 727-21*(5-$(this).index())
// 第3个li在右边的left值 727-21*3 等同于 727-21*(5-$(this).index())
$(this).nextAll().each(function(){
$(this).animate({'left':727-21*(5-$(this).index())});
})
})
})
script>
<title>手风琴效果title>
head>
<body>
<div id="accordion">
<ul>
<li class="bar01"><span>非洲景色01span><img src="images/001.jpg" />li>
<li class="bar02"><span>非洲景色02span><img src="images/002.jpg" />li>
<li class="bar03"><span>非洲景色03span><img src="images/003.jpg" />li>
<li class="bar04"><span>非洲景色04span><img src="images/004.jpg" />li>
<li class="bar05"><span>非洲景色05span><img src="images/005.jpg" />li>
ul>
div>
body>
html>
jquery事件
blur() 元素失去焦点 //用于表单验证
focus() 元素获得焦点 //用于表单验证
click() 鼠标单击
mouseover() 鼠标进入(进入子元素也触发)
mouseout() 鼠标离开(离开子元素也触发)
mouseenter() 鼠标进入(进入子元素不触发)
mouseleave() 鼠标离开(离开子元素不触发)
hover() 同时为mouseenter和mouseleave事件指定处理函数 //类似于toggle
ready() DOM加载完成
resize() 浏览器窗口的大小发生改变
scroll() 滚动条的位置发生变化
submit() 用户递交表单
绑定事件的其他方式
$(function(){
// $("#btn").click(function(){})
//点击或者移入的时候,都执行绑定的匿名函数
$("#btn").bind("click mouseover",function(){
alert("触发事件绑定的函数");
//解绑事件
$(this).unbind("mouseover");
})
})
事件冒泡
在一个对象上触发某类事件(比如单击onclick事件),如果此对象定义了此事件的处理程序,那么此事件就会调用这个处理程序,如果没有定义此事件处理程序或者事件返回true,那么这个事件会向这个对象的父级对象传播,从里到外,直至它被处理(父级对象所有同类事件都将被激活),或者它到达了对象层次的最顶层,即document对象(有些浏览器是window)
事件冒泡的作用
事件冒泡允许多个操作被集中处理(把事件处理器添加到一个父级元素上,避免把事件处理器添加到多个子级元素上),它还可以让你在对象层的不同级别捕获事件。
阻止事件冒泡
事件冒泡机制有时候是不需要的,需要阻止掉,通过 event.stopPropagation() 来阻止
阻止默认行为
阻止表单提交
$('#form1').submit(function(event){
event.preventDefault();
})
$('#form1').submit(function(event){
event.preventDefault();
})
合并阻止操作
实际开发中,一般把阻止冒泡和阻止默认行为合并起来写,合并写法可以用
// event.stopPropagation();
// event.preventDefault();
// 合并写法:
return false;
案例:页面弹框(点击弹框外弹框关闭)
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>页面弹框(点击弹框外弹框关闭)title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(function(){
$("#btn").click(function(){
$(".pop_con").show();
return false;
})
$(document).click(function(){
$(".pop_con").fadeOut();
})
$(".pop").click(function(){
return false;
})
$(".pop .close").click(function(){
$(".pop_con").fadeOut();
})
})
script>
<style>
.pop_con{
display: none;
}
.pop{
position:fixed;
width:500px;
height:300px;
background-color:#fff;
border:3px solid #000;
left:50%;
top:50%;
margin-top:-150px;
margin-left:-250px;
z-index:9999;
}
.mask{
position: fixed;
width:100%;
height:100%;
background-color:#000;
opacity:0.3;
filter: alpha(opacity=30);
left:0;
top:0;
z-index: 9990;
}
.pop .close{
float:right;
font-size:30px;
text-decoration: none;
color:#ddd;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="弹出" id="btn">
<div class="pop_con">
<div class="pop">
弹框里面的文字
<input type="text" placeholder="输入内容">
<a href="#" class="close">Xa>
div>
<div class="mask">div>
div>
body>
html>
事件委托
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>事件委托title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script>
$(function(){
/*
$(".list li").click(function(){
$(this).css({"backgroundColor":"red"});
})
//新建一个li元素 增加到ul子集的最后面
var $li = $("9 ");
$(".list").append($li);
//让新加入的li有相同事件,需要单独绑定
$li.click(function(){
$(this).css({"backgroundColor":"red"});
})
*/
//事件委托
/*事件委托就是利用冒泡的原理,把事件加到父级上,通过判断事件来源的子集,执行相应的操作,事件委托首先可以极大减少事件绑定次数,提高性能;其次可以让新加入的子元素也可以拥有相同的操作。*/
$(".list").delegate('li', 'click', function(event) {
// $(this)指每次委托的子元素
$(this).css({"backgroundColor":"red"});
});
//事件委托的方式不需要单独给新加入的li单独绑定相同事件
var $li = $("9 ")
$(".list").append($li);
})
script>
<style>
.list{
background-color:gold;
list-style: none;
padding:10px;
}
.list li{
height:30px;
background-color: green;
margin:10px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<ul class="list">
<li>1li>
<li>2li>
<li>3li>
<li>4li>
<li>5li>
<li>6li>
<li>7li>
<li>8li>
ul>
body>
html>
jquery元素节点操作
创建节点
var $div = $('');
var $div2 = $('这是一个div元素');
插入节点
- append()和appendTo():在现存元素的内部,从后面插入元素
- prepend()和prependTo():在现存元素的内部,从前面插入元素
- after()和insertAfter():在现存元素的外部,从后面插入元素
- before()和insertBefore():在现存元素的外部,从前面插入元素
删除节点
$('#div1').remove();
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>todolisttitle>
<style type="text/css">
.list_con{
width:600px;
margin:50px auto 0;
}
.inputtxt{
width:550px;
height:30px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
padding:0px;
text-indent:10px;
}
.inputbtn{
width:40px;
height:32px;
padding:0px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
margin-top:20px;
}
.list li{
height:40px;
line-height:40px;
border-bottom:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list li span{
float:left;
}
.list li a{
float:right;
text-decoration:none;
margin:0 10px;
}
style>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
var $inputtxt = $("#txt1");
var $btn = $("#btn1");
var $ul = $("#list");
$btn.click(function(){
//获取input输入框的内容
var $val = $inputtxt.val();
if($val == ""){
alert("请输入内容");
return;
}
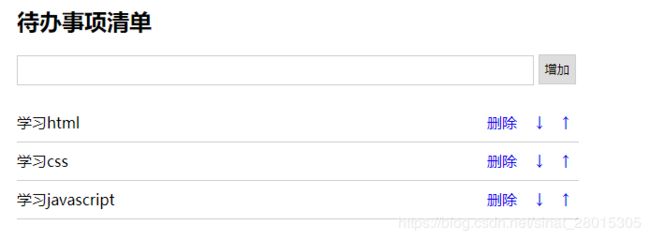
var $li = $(''+$val+' ↑ ↓ 删除 ');
$ul.append($li);
// 添加完成后,清空输入框内容
$inputtxt.val("");
/* 由于不是事件委托,因此需要对新增加标签的同样事件重复定义行为
$('div').find('.myClass'); //选择div内的class等于myClass的元素
var $a = $li.find('.del');
$a.click(function(){
$(this).parent().remove();
})*/
})
$ul.delegate("a", "click", function() {
//prop() 取出或设置某个属性的值
var $handler = $(this).prop("class");
if($handler =="del"){
// parent()在这里指a的父类,也就是li
$(this).parent().remove();
}
if($handler == "up"){
if($(this).parent().prev().length== 0){
alert('到顶了!');
return;
}
else{
$(this).parent().insertBefore($(this).parent().prev());
}
}
if($handler == "down"){
if($(this).parent().next().length== 0){
alert('到底了!');
return;
}
else{
$(this).parent().insertAfter($(this).parent().next());
}
}
})
})
script>
head>
<body>
<div class="list_con">
<h2>To do listh2>
<input type="text" name="" id="txt1" class="inputtxt">
<input type="button" name="" value="增加" id="btn1" class="inputbtn">
<ul id="list" class="list">
<li>
<span>学习htmlspan>
<a href="javascript:;" class="up"> ↑ a>
<a href="javascript:;" class="down"> ↓ a>
<a href="javascript:;" class="del">删除a>
li>
<li>
<span>学习cssspan>
<a href="javascript:;" class="up"> ↑ a>
<a href="javascript:;" class="down"> ↓ a>
<a href="javascript:;" class="del">删除a>
li>
<li>
<span>学习javascriptspan>
<a href="javascript:;" class="up"> ↑ a>
<a href="javascript:;" class="down"> ↓ a>
<a href="javascript:;" class="del">删除a>
li>
ul>
div>
body>
html>
滚轮事件与函数节流
jquery.mousewheel插件
jquery中没有鼠标滚轮事件,原生js中的鼠标滚轮事件不兼容,可以使用jquery的滚轮事件插件jquery.mousewheel.js
$(function(){
$(window).mousewheel(function(event,dat){
...
})
})
函数节流
javascript中有些事件的触发频率非常高,比如onresize事件(jq中是resize),onmousemove事件(jq中是mousemove)以及上面说的鼠标滚轮事件,在短事件内多处触发执行绑定的函数,可以巧妙地使用定时器来减少触发的次数,实现函数节流。
案例:整屏滚动
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>整页滚动title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/test.css">
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.12.4.min.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery.mousewheel.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
//使页面高度和屏幕可视区同宽
var $h = $(window).height();
var $pages = $(".pages");
$pages.css({"height":$h});
var $screen = $(".pages_con");
//定义一个参数用于接收dat的值,判断滚动方向和次数
var $nowscreen = 0;
//定义一个变量用于统计页面页数
var $len = $pages.length; //5
// 由于刚进页面后,未发生mousewheel事件,需要手动添加第一屏动画
$pages.eq(0).addClass('moving');
//获取屏幕右侧圆点
var $points = $(".points li");
//定义一个空对象,用于定时器节流处理高频触发事件
var $timer = null;
$(window).mousewheel(function(event,dat){
//每次触发前,先清空之前的定时器,保留最后一次的timer
clearTimeout($timer);
// 在短事件内多处触发执行绑定的函数,可以巧妙地使用定时器来减少触发的次数,实现函数节流。
timer = setTimeout(function(){
// alert(dat); // 向上1,向下-1
if(dat ==-1){
$nowscreen ++;
}
else{
$nowscreen --;
}
//页面最多5屏,需要对$nowscreen作以限制
if($nowscreen<0){
$nowscreen = 0;
}
if($nowscreen>$len -1){
$nowscreen = $len -1;
}
$screen.animate({"top":-$h*$nowscreen},300);
//通过将moving加入到滚动到的每一屏中实现动画效果,同时,取消其他屏的moving动画,否则回翻无动画效果
//$('div').siblings(); //选择div的同级元素
$pages.eq($nowscreen).addClass('moving').siblings().removeClass('moving');
//当翻页后,每页右侧小圆点的动画效果
$points.eq($nowscreen).addClass('active').siblings().removeClass('active');
},200)
})
//点击右侧圆圈实现切换页面
$points.click(function(){
$nowscreen = $(this).index();
$points.eq($nowscreen).addClass('active').siblings().removeClass('active');
//翻页效果和当前页动画
$screen.animate({"top":-$h*$nowscreen},300);
$pages.eq($nowscreen).addClass('moving').siblings().removeClass('moving');
})
})
script>
head>
<body>
<div class="pages_con">
<div class="pages page1">
<div class="main_con">
<div class="left_img"><img src="images/001.png">div>
<div class="right_info">
Web前端开发是从网页制作演变而来的,名称上有很明显的时代特征。在互联网的演化进程中,网页制作是Web1.0时代的产物,那时网站的主要内容都是静态的,用户使用网站的行为也以浏览为主。
div>
div>
div>
<div class="pages page2">
<div class="main_con">
<div class="right_img"><img src="images/002.png">div>
<div class="left_info">
2005年以后,互联网进入Web2.0时代,各种类似桌面软件的Web应用大量涌现,网站的前端由此发生了翻天覆地的变化。网页不再只是承载单一的文字和图片,各种富媒体让网页的内容更加生动,网页上软件化的交互形式为用户提供了更好的使用体验,这些都是基于前端技术实现的。
div>
div>
div>
<div class="pages page3">
<div class="main_con">
<div class="left_img"><img src="images/004.png">div>
<div class="right_info">
以前会Photoshop和Dreamweaver就可以制作网页,现在只掌握这些已经远远不够了。无论是开发难度上,还是开发方式上,现在的网页制作都更接近传统的网站后台开发,所以现在不再叫网页制作,而是叫Web前端开发。
div>
div>
div>
<div class="pages page4">
<div class="main_con">
<div class="left_img"><img src="images/003.png">div>
<div class="right_info">
Web前端开发在产品开发环节中的作用变得越来越重要,而且需要专业的前端工程师才能做好,这方面的专业人才近几年来备受青睐。Web前端开发是一项很特殊的工作,涵盖的知识面非常广,既有具体的技术,又有抽象的理念。简单地说,它的主要职能就是把网站的界面更好地呈现给用户。
div>
div>
div>
<div class="pages page5">
<div class="main_con">
<div class="center_img"><img src="images/005.png">div>
div>
div>
div>
<ul class="points">
<li class="active">li>
<li>li>
<li>li>
<li>li>
<li>li>
ul>
body>
html>
json
json是 JavaScript Object Notation 的首字母缩写,单词的意思是javascript对象表示法,这里说的json指的是类似于javascript对象的一种数据格式,目前这种数据格式比较流行,逐渐替换掉了传统的xml数据格式。
javascript自定义对象:
var oMan = {
name:'tom',
age:16,
talk:function(s){
alert('我会说'+s);
}
}
json格式的数据:
{
"name":"tom",
"age":18
}
与json对象不同的是,json数据格式的属性名称和字符串值需要用双引号引起来,用单引号或者不用引号会导致读取数据错误。
json的另外一个数据格式是数组,和javascript中的数组字面量相同。
ajax与jsonp
ajax技术的目的是让javascript发送http请求,与后台通信,获取数据和信息。ajax技术的原理是实例化xmlhttp对象,使用此对象与后台通信。ajax通信的过程不会影响后续javascript的执行,从而实现异步。
同步和异步
现实生活中,同步指的是同时做几件事情,异步指的是做完一件事后再做另外一件事,程序中的同步和异步是把现实生活中的概念对调,也就是程序中的异步指的是现实生活中的同步,程序中的同步指的是现实生活中的异步。
局部刷新和无刷新
ajax可以实现局部刷新,也叫做无刷新,无刷新指的是整个页面不刷新,只是局部刷新,ajax可以自己发送http请求,不用通过浏览器的地址栏,所以页面整体不会刷新,ajax获取到后台数据,更新页面显示数据的部分,就做到了页面局部刷新。
同源策略
ajax请求的页面或资源只能是同一个域下面的资源,不能是其他域的资源,这是在设计ajax时基于安全的考虑。特征报错提示:
XMLHttpRequest cannot load https://www.baidu.com/. No
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource.
Origin 'null' is therefore not allowed access.
$.ajax使用方法
常用参数:
- url 请求地址
- type 请求方式,默认是’GET’,常用的还有’POST’
- dataType 设置返回的数据格式,常用的是’json’格式,也可以设置为’html’
- data 设置发送给服务器的数据
- success 设置请求成功后的回调函数
- error 设置请求失败后的回调函数
- async 设置是否异步,默认值是’true’,表示异步
以前写法
$.ajax({
url: 'js/data.json',
type: 'GET',
dataType: 'json',
data:{'aa':1}
success:function(data){
alert(data.name);
},
error:function(){
alert('服务器超时,请重试!');
}
});
现在写法
$.ajax({
url: 'js/data.json',
type: 'GET',
dataType: 'json',
data:{'aa':1}
})
.done(function(data) {
alert(data.name);
})
.fail(function() {
alert('服务器超时,请重试!');
});
// data.json里面的数据: {"name":"tom","age":18}
本地存储
本地存储分为cookie,以及新增的localStorage和sessionStorage
- cookie 存储在本地,容量最大4k,在同源的http请求时携带传递,损耗带宽,可设置访问路径,只有此路径及此路径的子路径才能访问此cookie,在设置的过期时间之前有效。
jquery 设置cookie
//$.cookie(键名,'键值',{过期时间:天数,存储路径:根目录下'/'})
$.cookie('mycookie','123',{expires:7,path:'/'});
jquery 获取cookie
$.cookie('mycookie');
- localStorage 存储在本地,容量为5M或者更大,不会在请求时候携带传递,在所有同源窗口中共享,数据一直有效,除非人为删除,可作为长期数据。
//设置:
localStorage.setItem("dat", "456");
localStorage.dat = '456';
//获取:
localStorage.getItem("dat");
localStorage.dat
//删除
localStorage.removeItem("dat");
- sessionStorage 存储在本地,容量为5M或者更大,不会在请求时候携带传递,在同源的当前窗口关闭前有效。
localStorage 和 sessionStorage 合称为Web Storage , Web Storage支持事件通知机制,可以将数据更新的通知监听者,Web Storage的api接口使用更方便。