openGL学习笔记七: glad库及使用
glad库与glew作用相同,可以看作它的升级版,GLAD的配置与大多数的开源库有些许的不同,GLAD使用了一个在线服务。在这里我们能够告诉GLAD需要定义的OpenGL版本,并且根据这个版本加载所有相关的OpenGL函数。
官方网址为:https://glad.dav1d.de/
安装及使用
环境:win7 VS2013
1. 下载glad:
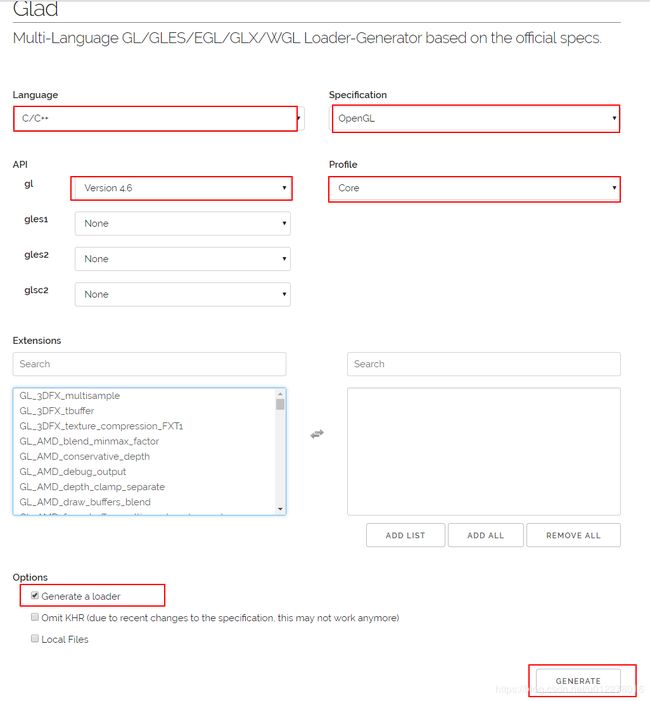
打开GLAD的在线服务,将语言(Language)设置为C/C++,在API选项中,选择3.3以上的OpenGL(gl)版本(我们的教程中将使用3.3版本,但更新的版本也能正常工作)。之后将模式(Profile)设置为Core,并且保证生成加载器(Generate a loader)的选项是选中的。现在可以先(暂时)忽略拓展(Extensions)中的内容。都选择完之后,点击生成(Generate)按钮来生成库文件。
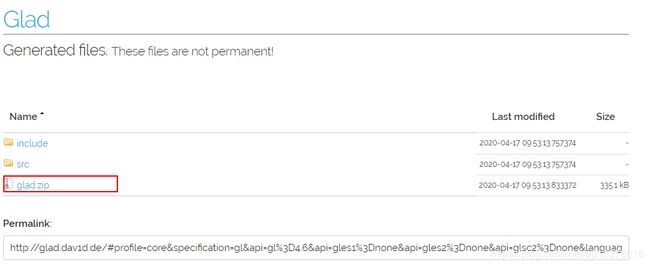
下载glad.zip文件解压,就可以得到我们需要的include\glad\glad.h、include\KHR\khrplatform.h和src\glad.c这3个文件
2. opengl项目配置:
a. 项目属性 ----> C/C++ —> 附加包含目录 —> your_path\glad\include
b. 项目中添加glad.c 文件
将两个头文件目录(glad和KHR)复制到你的Includes文件夹中(注意这个Includes是配置GLFW时配置的Libraries文件夹下的子目录,而非工程下的目录),并添加glad.c文件到你的工程中。
glad库非常小,只有三个文件,可以不用编译成库直接拿来使用,在opengl项目中引入glad.c 文件,设置好头文件路径即可
3. 使用代码:
注意:glad.h 必须放在glfw3.h 或者glut.h文件之前。
#include