SLAM从入门到放弃:SLAM十四讲第十三章习题(2-3)
以下均为简单笔记,如有错误,请多多指教。
- 把本讲的稠密深度估计改成半稠密,你可以先把梯度明显的地方筛选出来。
- 把本讲演示的单目稠密重建代码从正深度改成逆深度,并添加仿射变换。你的实验效果是否有改进?
解:此处把两个题目的解放在一起,以下就是所有的代码,将分别注释相关的代码。
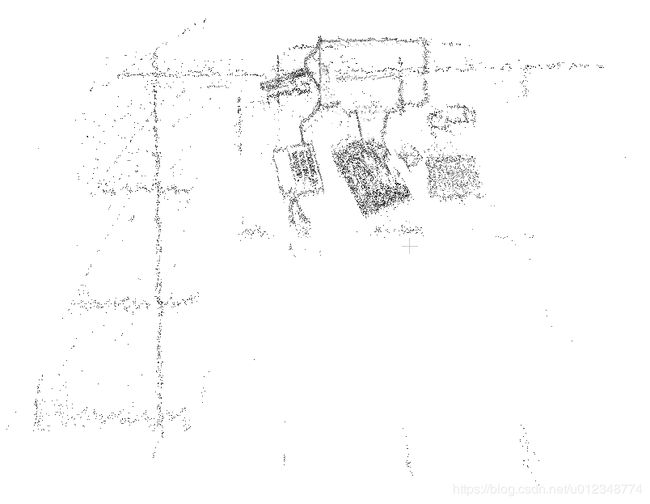
以下是经过代码更新后的点云图和原始的点云图,可以发现更新后质量明显更高。

#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#include
// for sophus
#include
using Sophus::SE3;
// for eigen
#include
#include
using namespace Eigen;
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
/**********************************************
* 本程序演示了单目相机在已知轨迹下的稠密深度估计
* 使用极线搜索 + NCC 匹配的方式,与书本的 13.2 节对应
* 请注意本程序并不完美,你完全可以改进它——我其实在故意暴露一些问题。
***********************************************/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// parameters
const int boarder = 20; // 边缘宽度
const int width = 640; // 宽度
const int height = 480; // 高度
const double fx = 481.2f; // 相机内参
const double fy = -480.0f;
const double cx = 319.5f;
const double cy = 239.5f;
const int ncc_window_size = 2; // NCC 取的窗口半宽度
const int ncc_area = (2*ncc_window_size+1)*(2*ncc_window_size+1); // NCC窗口面积
const double min_cov = 0.001; // 收敛判定:最小方差
const double max_cov = 0.5; // 发散判定:最大方差
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// 重要的函数
// 从 REMODE 数据集读取数据
bool readDatasetFiles(
const string& path,
vector& color_image_files,
vector& poses
);
// 根据新的图像更新深度估计
bool update(
const Mat& ref,
const Mat& curr,
const SE3& T_C_R,
Mat& depth,
Mat& depth_cov
);
// 极线搜索
bool epipolarSearch(
const Mat& ref,
const Mat& curr,
const SE3& T_C_R,
const Vector2d& pt_ref,
const double& depth_mu,
const double& depth_cov,
Vector2d& pt_curr
);
// 更新深度滤波器
bool updateDepthFilter(
const Vector2d& pt_ref,
const Vector2d& pt_curr,
const SE3& T_C_R,
Mat& depth,
Mat& depth_cov
);
// 计算 NCC 评分
double NCC( const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr, const Vector2d& pt_ref, double depth, Vector2d& pt_cur, const SE3& T_C_R );
// 双线性灰度插值
inline double getBilinearInterpolatedValue( const Mat& img, const Vector2d& pt ) {
uchar* d = & img.data[ int(pt(1,0))*img.step+int(pt(0,0)) ];
double xx = pt(0,0) - floor(pt(0,0));
double yy = pt(1,0) - floor(pt(1,0));
return (( 1-xx ) * ( 1-yy ) * double(d[0]) +
xx* ( 1-yy ) * double(d[1]) +
( 1-xx ) *yy* double(d[img.step]) +
xx*yy*double(d[img.step+1]))/255.0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// 一些小工具
// 显示估计的深度图
void plotDepth( const Mat& depth );
// 像素到相机坐标系
inline Vector3d px2cam ( const Vector2d px ) {
return Vector3d (
(px(0,0) - cx)/fx,
(px(1,0) - cy)/fy,
1
);
}
// 相机坐标系到像素
inline Vector2d cam2px ( const Vector3d p_cam ) {
return Vector2d (
p_cam(0,0)*fx/p_cam(2,0) + cx,
p_cam(1,0)*fy/p_cam(2,0) + cy
);
}
// 检测一个点是否在图像边框内
inline bool inside( const Vector2d& pt ) {
return pt(0,0) >= boarder && pt(1,0)>=boarder
&& pt(0,0)+boarder color_image_files;
vector poses_TWC;
bool ret = readDatasetFiles( argv[1], color_image_files, poses_TWC );
if ( ret==false )
{
cout<<"Reading image files failed!"<(y)[x] > min_cov ) // 深度已收敛或发散
continue;
Vector3d f_ref = px2cam( Vector2d(x,y) );
f_ref.normalize();
Vector3d P_ref = f_ref*depth.ptr(y)[x]; // 参考帧的 P 向量
points<(y)[x])<<"\t"<(y)[x])<<"\t"<(y)[x])<<"\t"<& color_image_files,
std::vector& poses
)
{
ifstream fin( path+"/first_200_frames_traj_over_table_input_sequence.txt");
if ( !fin ) return false;
while ( !fin.eof() )
{
// 数据格式:图像文件名 tx, ty, tz, qx, qy, qz, qw ,注意是 TWC 而非 TCW
string image;
fin>>image;
double data[7];
for ( double& d:data ) fin>>d;
color_image_files.push_back( path+string("/images/")+image );
poses.push_back(
SE3( Quaterniond(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]),
Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2]))
);
if ( !fin.good() ) break;
}
return true;
}
// 对整个深度图进行更新
bool update(const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr, const SE3& T_C_R, Mat& depth, Mat& depth_cov )
{
#pragma omp parallel for
for ( int x=boarder; x(y)[x+1] - ref.ptr(y)[x-1],
ref.ptr(y+1)[x] - ref.ptr(y-1)[x]
);
// 把梯度小的区域过滤到
if ( delta.norm() < 50 )
continue;
// 遍历每个像素
if ( depth_cov.ptr(y)[x] < min_cov || depth_cov.ptr(y)[x] > max_cov ) // 深度已收敛或发散
continue;
// 在极线上搜索 (x,y) 的匹配
Vector2d pt_curr;
bool ret = epipolarSearch (
ref,
curr,
T_C_R,
Vector2d(x,y),
depth.ptr(y)[x],
sqrt(depth_cov.ptr(y)[x]),
pt_curr
);
if ( ret == false ) // 匹配失败
continue;
// 取消该注释以显示匹配
// showEpipolarMatch( ref, curr, Vector2d(x,y), pt_curr );
// 匹配成功,更新深度图
updateDepthFilter( Vector2d(x,y), pt_curr, T_C_R, depth, depth_cov );
}
}
// 极线搜索
// 方法见书 13.2 13.3 两节
bool epipolarSearch(
const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr,
const SE3& T_C_R, const Vector2d& pt_ref,
const double& depth_mu, const double& depth_cov,
Vector2d& pt_curr )
{
// 此处是为逆深度做准备
// 因此需要根据方差求解出逆深度的范围
double d_min = 1/depth_mu-3*depth_cov, d_max = 1/depth_mu+3*depth_cov;
// 防止小于0
if(d_min<0) d_min = 0.2;
// 求出深度范围
double dd_max = 1/d_min;
double dd_min = 1/d_max;
if ( dd_min<0.1 ) dd_min = 0.1;
// 在极线上搜索,以深度均值点为中心,左右各取半长度
double best_ncc = -1.0;
Vector2d best_px_curr;
for ( double l=dd_min; l<=dd_max; l+=0.1 ) // l+=sqrt(2)
{
// 计算待匹配点与参考帧的 NCC
Vector2d px_curr;
// 此处是增加了放射变换的NCC计算
double ncc = NCC( ref, curr, pt_ref, l, px_curr, T_C_R);
if ( ncc>best_ncc )
{
best_ncc = ncc;
best_px_curr = px_curr;
}
}
if ( best_ncc < 0.85f ) // 只相信 NCC 很高的匹配
return false;
pt_curr = best_px_curr;
return true;
}
double NCC (
const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr,
const Vector2d& pt_ref, double depth,
Vector2d& pt_cur,
const SE3& T_C_R
)
{
// 零均值-归一化互相关
// 先算均值
double mean_ref = 0, mean_curr = 0;
vector values_ref, values_curr; // 参考帧和当前帧的均值
// 以下代码中又进行放射变换计算的代码
// 其核心思路是假设参考影像上一点附近都为一个平面且深度都一样
for ( int x=-ncc_window_size; x<=ncc_window_size; x++ )
for ( int y=-ncc_window_size; y<=ncc_window_size; y++ )
{
// 从像平面坐标系到像空间坐标系
Vector2d pointRef(int(x+pt_ref(0,0)),int(y+pt_ref(1,0)));
Vector3d f_ref = px2cam( pointRef );
f_ref.normalize();
double value_ref = double(ref.ptr( int(pointRef(1,0)) )[ int(pointRef(0,0)) ])/255.0;
mean_ref += value_ref;
// 根据放射变换算出到参考影像上的坐标
Vector3d P_ref = f_ref*depth; // 参考帧的 P 向量
Vector2d px_curr = cam2px( T_C_R*P_ref ); // 按深度均值投影的像素
if( x==0 && y==0 )
{
pt_cur = px_curr;
}
if ( !inside(px_curr) )
return -1.0;
double value_curr = getBilinearInterpolatedValue( curr, px_curr );
mean_curr += value_curr;
values_ref.push_back(value_ref);
values_curr.push_back(value_curr);
}
mean_ref /= ncc_area;
mean_curr /= ncc_area;
// 计算 Zero mean NCC
double numerator = 0, demoniator1 = 0, demoniator2 = 0;
for ( int i=0; i [ f_ref^T f_ref, -f_ref^T f_cur ] [d_ref] = [f_ref^T t]
// [ f_cur^T f_ref, -f_cur^T f_cur ] [d_cur] = [f_cur^T t]
// 二阶方程用克莱默法则求解并解之
Vector3d t = T_R_C.translation();
Vector3d f2 = T_R_C.rotation_matrix() * f_curr;
Vector2d b = Vector2d ( t.dot ( f_ref ), t.dot ( f2 ) );
double A[4];
A[0] = f_ref.dot ( f_ref );
A[2] = f_ref.dot ( f2 );
A[1] = -A[2];
A[3] = - f2.dot ( f2 );
double d = A[0]*A[3]-A[1]*A[2];
Vector2d lambdavec =
Vector2d ( A[3] * b ( 0,0 ) - A[1] * b ( 1,0 ),
-A[2] * b ( 0,0 ) + A[0] * b ( 1,0 )) /d;
Vector3d xm = lambdavec ( 0,0 ) * f_ref;
Vector3d xn = t + lambdavec ( 1,0 ) * f2;
Vector3d d_esti = ( xm+xn ) / 2.0; // 三角化算得的深度向量
double depth_estimation = d_esti.norm(); // 深度值
// 计算不确定性(以一个像素为误差)
Vector3d p = f_ref*depth_estimation;
Vector3d a = p - t;
double t_norm = t.norm();
double a_norm = a.norm();
double alpha = acos( f_ref.dot(t)/t_norm );
double beta = acos( -a.dot(t)/(a_norm*t_norm));
double beta_prime = beta + atan(1/fx);
double gamma = M_PI - alpha - beta_prime;
double p_prime = t_norm * sin(beta_prime) / sin(gamma);
// 逆深度的方差更新方式
double d_cov = 1/p_prime - 1/depth_estimation;
double d_cov2 = d_cov*d_cov;
// 高斯融合
double mu = depth.ptr( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ];
double sigma2 = depth_cov.ptr( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ];
double mu_fuse = (d_cov2/mu+sigma2/depth_estimation) / ( sigma2+d_cov2);
double sigma_fuse2 = ( sigma2 * d_cov2 ) / ( sigma2 + d_cov2 );
depth.ptr( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ] = 1/mu_fuse;
depth_cov.ptr( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ] = sigma_fuse2;
return true;
}
// 后面这些太简单我就不注释了(其实是因为懒)
void plotDepth(const Mat& depth)
{
imshow( "depth", depth*0.4 );
waitKey(1);
}