Zygote进程启动过程源代码分析
Zygote进程介绍
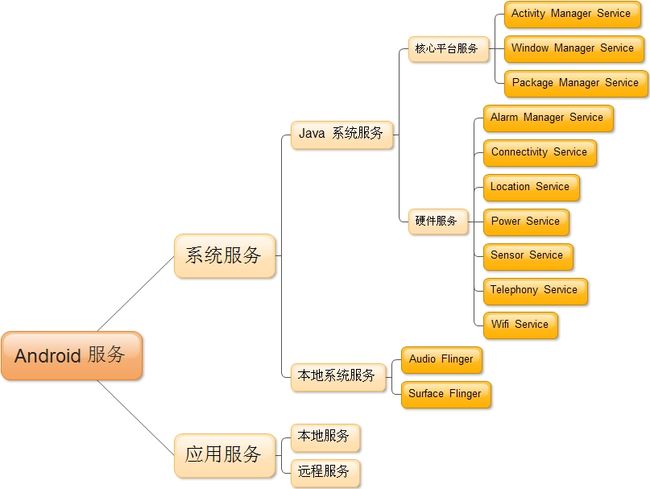
在Android系统中,存在不同的服务,这些服务可以分为:
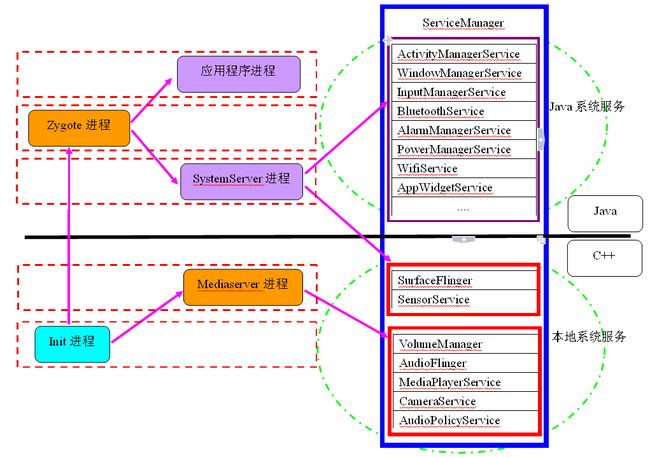
Android系统借用Binder通信机制实现了C/S架构设计,客户端应用程序如需要实现某些功能,只需请求指定的服务,由服务端来实现。Android服务包括以上的系统服务和应用服务,系统服务是指Android系统在启动过程就已经启动实现了的服务,对于系统服务又分为Java服务和本地服务,其实很好区分,Java服务是由Java代码编写而成,由SystemServer进程提供,而本地服务是由C/C++实现的服务,由Init进程在系统启动时启动的服务。应用服务是由开发者自行实现的某些特定服务。对于本地系统服务,我们知道它们是由Init进程来启动的,那对于Java系统服务,又是如何启动的呢?
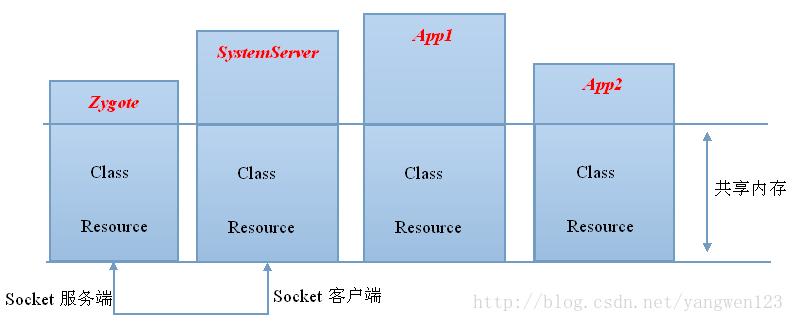
所有的应用程序进程以及系统服务进程SystemServer都是由Zygote进程孕育(fork)出来的,zygote和system_server分别是Java世界的半边天,任何一个进程的死亡都会导致Java崩溃。zygote本身是Native应用程序,与驱动内核无关。zygote进程对应的具体程序是“app_process”,这个可执行文件名称在Android.mk文件中指定,在Zygote进程启动时,将进程名称设置为"zygote"。
我们知道,Android系统是基于Linux内核的,而在Linux系统中,所有的进程都是init进程的子孙进程,也就是说,所有的进程都是直接或者间接地由init进程fork出来的。Zygote进程也不例外,它是在系统启动的过程,由init进程创建的。在系统启动脚本system/core/rootdir/init.rc文件中。
//关键字service告诉init进程创建一个名为"zygote"的进程,这个zygote进程要执行的程序是/system/bin/app_process,后面是要传给app_process的参数。
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server //socket关键字表示这个zygote进程需要一个名称为"zygote"的socket资源,这样,系统启动后,我们就可以在/dev/socket目录下看到有一个名为zygote的文件。这里定义的socket的类型为unix domain socket,它是用来作本地进程间通信用的
socket zygote stream 666
critical
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
onrestart restart mlistenerframeworks\base\cmds\app_process\App_main.cpp
frameworks\base\core\jni\AndroidRuntime.cpp
frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\ZygoteInit.java
1. 虚拟机启动 --- 通过native启动
startVm(&mJavaVM, &env) 启动虚拟机
onVmCreated(env) 虚拟机启动后的初始化
startReg(env) 注册JNI函数
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray) 调用ZygoteInit类的main函数开创java世界
2.SystemServer进程 --- 通过Java启动
registerZygoteSocket() 为zygote进程注册监听socket
preload() 加载常用的JAVA类和系统资源
startSystemServer() 启动SystemServer进程
runSelectLoopMode() 进入循环监听模式
closeServerSocket() 进程退出时,关闭socket监听
Zygote进程包含两个主要模块:
1. Socket服务端,该Socket服务端用于接收启动新的Dalvik进程命令。
2. Framework共享类及共享资源,当Zygote进程启动后,会装载一些共享类和资源,共享类是在preload-classes文件中定义的,共享资源是在preload-resources文件中定义。因为其他Dalvik进程是由Zygote进程孵化出来的,因此只要Zygote装载好了这些类和资源后,新的Dalvik进程就不需要在装载这些类和资源了,它们共享Zygote进程的资源和类。
app_process
App_main.cpp
Zygote进程是通过app_process启动的,app_process通过解析命令行参数,然后启动一个Android虚拟机,调用Java的入口函数从而启动一个进程,app_process也可以启动其他进程,比如monkey,am,pm等。
int main(int argc, const char* const argv[])
{
//zygote 是由init进程fork而来,init.rc文件中为zygote进程设置的启动参数如下
//argc = 4
//argv = [-Xzygote, /system/bin, --zygote, --start-system-server]
// These are global variables in ProcessState.cpp
mArgC = argc;
mArgV = argv;
mArgLen = 0;
for (int i=0; i从上面的代码可以知道,app_process就是通过启动一个Android虚拟机并加载相应的Java类来启动一个进程。
虚拟机启动过程
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const char* options)
{
blockSigpipe();
/*
* 'startSystemServer == true' means runtime is obsolete and not run from
* init.rc anymore, so we print out the boot start event here.
*/
if (strcmp(options, "start-system-server") == 0) {
/* track our progress through the boot sequence */
const int LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START = 3000;
LOG_EVENT_LONG(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START,ns2ms(systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC)));
}
//设置ANDROID_ROOT环境变量
const char* rootDir = getenv("ANDROID_ROOT");
if (rootDir == NULL) {
rootDir = "/system";//如果获取结果为Null,则设置为"/system"
if (!hasDir("/system")) {
LOG_FATAL("No root directory specified, and /android does not exist.");
return;
}
setenv("ANDROID_ROOT", rootDir, 1);//重新设置环境变量ANDROID_ROOT
}
//启动虚拟机
JNIEnv* env;
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
//注册JNI函数
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
//这里调用java类的main入口函数
jclass stringClass;
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
jstring optionsStr;
//通过JNI查找java的java.lang.String类
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
assert(stringClass != NULL);
//创建字符串数组String strArray[] = new String[2];
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(2, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
//创建字符串classNameStr
//对于zygote进程: classNameStr = new String("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit")
//对于启动应用进程:classNameStr = new String("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit")
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
//设置字符串数组元素strArray[0]
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
//创建字符串optionsStr,对应进程启动参数
optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options);
//设置字符串数组元素strArray[1]
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 1, optionsStr);
//为符合JNI规范,将com.android.xxx中的.换成/,变为slashClassName = com/android/xxx
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);
//查找Java类com/android/xxx
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
} else {
//找到ZygoteInit类的静态main方法的jMethodID
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
//在调用Java类的main方法后,zygote就进入了java世界
} else {
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
}
}
free(slashClassName);
ALOGD("Shutting down VM\n");
if (mJavaVM->DetachCurrentThread() != JNI_OK)
ALOGW("Warning: unable to detach main thread\n");
if (mJavaVM->DestroyJavaVM() != 0)
ALOGW("Warning: VM did not shut down cleanly\n");
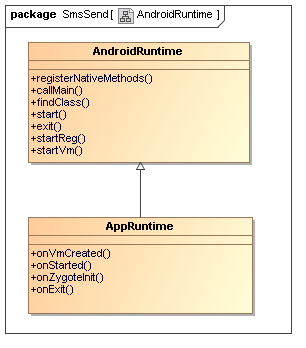
}① startVm(&mJavaVM, &env) 启动虚拟机
② onVmCreated(env) 虚拟机启动后的初始化
③ startReg(env) 注册JNI函数
④ env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray) 调用ZygoteInit类的main函数开创java世界
启动虚拟机
int AndroidRuntime::startVm(JavaVM** pJavaVM, JNIEnv** pEnv)
{
int result = -1;
JavaVMInitArgs initArgs;
JavaVMOption opt;
char propBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char stackTraceFileBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char dexoptFlagsBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char enableAssertBuf[sizeof("-ea:")-1 + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char jniOptsBuf[sizeof("-Xjniopts:")-1 + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char heapstartsizeOptsBuf[sizeof("-Xms")-1 + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char heapsizeOptsBuf[sizeof("-Xmx")-1 + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char heapgrowthlimitOptsBuf[sizeof("-XX:HeapGrowthLimit=")-1 + PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char extraOptsBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char* stackTraceFile = NULL;
bool checkJni = false;
bool checkDexSum = false;
bool logStdio = false;
enum {
kEMDefault,
kEMIntPortable,
kEMIntFast,
#if defined(WITH_JIT)
kEMJitCompiler,
#endif
} executionMode = kEMDefault;
property_get("dalvik.vm.checkjni", propBuf, "");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "true") == 0) {
checkJni = true;
} else if (strcmp(propBuf, "false") != 0) {
/* property is neither true nor false; fall back on kernel parameter */
property_get("ro.kernel.android.checkjni", propBuf, "");
if (propBuf[0] == '1') {
checkJni = true;
}
}
property_get("dalvik.vm.execution-mode", propBuf, "");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "int:portable") == 0) {
executionMode = kEMIntPortable;
} else if (strcmp(propBuf, "int:fast") == 0) {
executionMode = kEMIntFast;
#if defined(WITH_JIT)
} else if (strcmp(propBuf, "int:jit") == 0) {
executionMode = kEMJitCompiler;
#endif
}
property_get("dalvik.vm.stack-trace-file", stackTraceFileBuf, "");
property_get("dalvik.vm.check-dex-sum", propBuf, "");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "true") == 0) {
checkDexSum = true;
}
property_get("log.redirect-stdio", propBuf, "");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "true") == 0) {
logStdio = true;
}
strcpy(enableAssertBuf, "-ea:");
property_get("dalvik.vm.enableassertions", enableAssertBuf+4, "");
strcpy(jniOptsBuf, "-Xjniopts:");
property_get("dalvik.vm.jniopts", jniOptsBuf+10, "");
/* route exit() to our handler */
opt.extraInfo = (void*) runtime_exit;
opt.optionString = "exit";
mOptions.add(opt);
/* route fprintf() to our handler */
opt.extraInfo = (void*) runtime_vfprintf;
opt.optionString = "vfprintf";
mOptions.add(opt);
/* register the framework-specific "is sensitive thread" hook */
opt.extraInfo = (void*) runtime_isSensitiveThread;
opt.optionString = "sensitiveThread";
mOptions.add(opt);
opt.extraInfo = NULL;
/* enable verbose; standard options are { jni, gc, class } */
//options[curOpt++].optionString = "-verbose:jni";
opt.optionString = "-verbose:gc";
mOptions.add(opt);
//options[curOpt++].optionString = "-verbose:class";
/*
* The default starting and maximum size of the heap. Larger
* values should be specified in a product property override.
*/
strcpy(heapstartsizeOptsBuf, "-Xms");
property_get("dalvik.vm.heapstartsize", heapstartsizeOptsBuf+4, "4m");
opt.optionString = heapstartsizeOptsBuf;
mOptions.add(opt);
strcpy(heapsizeOptsBuf, "-Xmx");
property_get("dalvik.vm.heapsize", heapsizeOptsBuf+4, "16m");
opt.optionString = heapsizeOptsBuf;
mOptions.add(opt);
// Increase the main thread's interpreter stack size for bug 6315322.
opt.optionString = "-XX:mainThreadStackSize=24K";
mOptions.add(opt);
strcpy(heapgrowthlimitOptsBuf, "-XX:HeapGrowthLimit=");
property_get("dalvik.vm.heapgrowthlimit", heapgrowthlimitOptsBuf+20, "");
if (heapgrowthlimitOptsBuf[20] != '\0') {
opt.optionString = heapgrowthlimitOptsBuf;
mOptions.add(opt);
}
/*
* Enable or disable dexopt features, such as bytecode verification and
* calculation of register maps for precise GC.
*/
property_get("dalvik.vm.dexopt-flags", dexoptFlagsBuf, "");
if (dexoptFlagsBuf[0] != '\0') {
const char* opc;
const char* val;
opc = strstr(dexoptFlagsBuf, "v="); /* verification */
if (opc != NULL) {
switch (*(opc+2)) {
case 'n': val = "-Xverify:none"; break;
case 'r': val = "-Xverify:remote"; break;
case 'a': val = "-Xverify:all"; break;
default: val = NULL; break;
}
if (val != NULL) {
opt.optionString = val;
mOptions.add(opt);
}
}
opc = strstr(dexoptFlagsBuf, "o="); /* optimization */
if (opc != NULL) {
switch (*(opc+2)) {
case 'n': val = "-Xdexopt:none"; break;
case 'v': val = "-Xdexopt:verified"; break;
case 'a': val = "-Xdexopt:all"; break;
case 'f': val = "-Xdexopt:full"; break;
default: val = NULL; break;
}
if (val != NULL) {
opt.optionString = val;
mOptions.add(opt);
}
}
...
}
}初始化虚拟机
virtual void onVmCreated(JNIEnv* env)
{
//在启动zygote时,没有设置mClassName,
if (mClassName == NULL) {
return; // Zygote. Nothing to do here.
}
//在启动其他进程时,设置了Java启动类
//将com.android.xxx中的.换成/,变为slashClassName = com/android/xxx
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(mClassName);
//查找Java类com/android/xxx,mClass为进程启动类
mClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (mClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("ERROR: could not find class '%s'\n", mClassName);
}
free(slashClassName);
//创建java类的全局引用,保存到mclass中
mClass = reinterpret_cast(env->NewGlobalRef(mClass));
} 注册JNI函数
创建好了虚拟机,因此需要给该虚拟机注册一些JNI函数。
int AndroidRuntime::startReg(JNIEnv* env)
{
/*
* This hook causes all future threads created in this process to be
* attached to the JavaVM. (This needs to go away in favor of JNI
* Attach calls.) 设置线程创建函数为javaCreateThreadEtc
*/
androidSetCreateThreadFunc((android_create_thread_fn) javaCreateThreadEtc);
LOGV("--- registering native functions ---\n");
/*
* Every "register" function calls one or more things that return
* a local reference (e.g. FindClass). Because we haven't really
* started the VM yet, they're all getting stored in the base frame
* and never released. Use Push/Pop to manage the storage.
*/
env->PushLocalFrame(200);
//注册JNI函数,所有的JNI函数存放在gRegJNI全局数组中
if (register_jni_procs(gRegJNI, NELEM(gRegJNI), env) < 0) {
env->PopLocalFrame(NULL);
return -1;
}
env->PopLocalFrame(NULL);
//createJavaThread("fubar", quickTest, (void*) "hello");
return 0;
}//JNI函数注册方法
static int register_jni_procs(const RegJNIRec array[], size_t count, JNIEnv* env)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (array[i].mProc(env) < 0) {
#ifndef NDEBUG
LOGD("----------!!! %s failed to load\n", array[i].mName);
#endif
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}//gRegJNI全局数组中
static const RegJNIRec gRegJNI[] = {
REG_JNI(register_android_debug_JNITest),
REG_JNI(register_com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit),
REG_JNI(register_android_os_SystemClock),
REG_JNI(register_android_util_EventLog),
REG_JNI(register_android_util_Log),
REG_JNI(register_android_util_FloatMath),
REG_JNI(register_android_text_format_Time),
REG_JNI(register_android_pim_EventRecurrence),
REG_JNI(register_android_content_AssetManager),
REG_JNI(register_android_content_StringBlock),
REG_JNI(register_android_content_XmlBlock),
REG_JNI(register_android_emoji_EmojiFactory),
REG_JNI(register_android_security_Md5MessageDigest),
REG_JNI(register_android_text_AndroidCharacter),
REG_JNI(register_android_text_AndroidBidi),
REG_JNI(register_android_text_KeyCharacterMap),
REG_JNI(register_android_os_Process),
REG_JNI(register_android_os_Binder),
REG_JNI(register_android_view_Display),
REG_JNI(register_android_nio_utils),
REG_JNI(register_android_graphics_PixelFormat),
REG_JNI(register_android_graphics_Graphics),
REG_JNI(register_android_view_Surface),
REG_JNI(register_android_view_ViewRoot),
REG_JNI(register_com_google_android_gles_jni_EGLImpl),
REG_JNI(register_com_google_android_gles_jni_GLImpl),
REG_JNI(register_android_opengl_jni_GLES10),
REG_JNI(register_android_opengl_jni_GLES10Ext),
REG_JNI(register_android_opengl_jni_GLES11),
REG_JNI(register_android_opengl_jni_GLES11Ext),
REG_JNI(register_android_opengl_jni_GLES20),
....
};调用Java类的入口函数
Zygote进程启动
从C++层调用Java层的ZygoteInit类的main函数,从此开辟了Java世界。
public static void main(String argv[]) {
//传入的参数argv = ["com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit","true"]
try {
//设置虚拟机的最小堆栈大小
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setMinimumHeapSize(5 * 1024 * 1024);
// Start profiling the zygote initialization.启动性能统计
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
//注册zygote等待客户端连接的socket
registerZygoteSocket();
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START, SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
//预加载java类和资源
preloadClasses();
preloadResources();
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
// Finish profiling the zygote initialization.结束统计并生成结果文件
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeZygoteSnapshot();
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup,执行垃圾回收
gc();
// If requested, start system server directly from Zygote
if (argv.length != 2) {
throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
}
if (argv[1].equals("true")) {
//启动SystemServer进程
startSystemServer();
} else if (!argv[1].equals("false")) {
throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
//boolean ZYGOTE_FORK_MODE = false; 因此调用runSelectLoopMode()函数
if (ZYGOTE_FORK_MODE) {
runForkMode();
} else {
runSelectLoopMode();
}
closeServerSocket(); //关闭socket
} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
//捕获SytemServer进程调用RuntimeInit.java 中zygoteInit函数抛出的MethodAndArgsCaller异常
caller.run();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Zygote died with exception", ex);
closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}在以上ZygoteInit类的main中完成以下五个工作:
① registerZygoteSocket() 为zygote进程注册监听socket
② preload() 加载常用的JAVA类和系统资源
③ startSystemServer() 启动SystemServer进程
④ runSelectLoopMode() 进入循环监听模式
⑤ closeServerSocket() 进程退出时,关闭socket监听
启动Socket服务端口
zygote 并没有采用binder通信机制,而是采用基于AF_UNIX类型的socket通信方式
private static void registerZygoteSocket() {
if (sServerSocket == null) {
int fileDesc;
try {
//从环境变量中获取文件句柄,这个socket接口是通过文件描述符来创建的,这个文件描符代表的就是我们前面说的/dev/socket/zygote文件了。这个文件描述符是通过环境变量ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV得到的,关于socket的创建及环境变量的设置请参考init进程源码分析
String env = System.getenv(ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV);
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV + " unset or invalid", ex);
}
try {
//创建服务端socket,该socket将监听并接受客户端请求
sServerSocket = new LocalServerSocket(createFileDescriptor(fileDesc));
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error binding to local socket '" + fileDesc + "'", ex);
}
}
}函数首先调用System.getenv()获取系统为Zygote进程分配的Socket文件描述符,然后调用createFileDescriptor(fileDesc)创建一个真正的Socket文件描述符。Socket的使用方式有:
1. 阻塞方式:使用listen()监听某个端口,然后调用read()函数从这个端口读取数据,当Socket端口没有数据时,read()函数将一直等待,直到读取到数据才返回;
2. 非阻塞方式:使用Linux系统调用select()函数监测Socket文件描述符,当该文件描述符上有数据时,自动触发中断,在中断处理函数中去读取文件描述符上的数据,LocalServerSocket就是对非阻塞式Socket的封装;
预加载类和资源
private static void preloadClasses() {
final VMRuntime runtime = VMRuntime.getRuntime();
//通过反射机制获取输入流,类资源文件为"preloaded-classes"
InputStream is = ZygoteInit.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(PRELOADED_CLASSES);
if (is == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't find " + PRELOADED_CLASSES + ".");
} else {
Log.i(TAG, "Preloading classes...");
long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
// Drop root perms while running static initializers.
//设置有效组ID和有效用户ID
setEffectiveGroup(UNPRIVILEGED_GID);
setEffectiveUser(UNPRIVILEGED_UID);
// Alter the target heap utilization. With explicit GCs this
// is not likely to have any effect.
float defaultUtilization = runtime.getTargetHeapUtilization();
runtime.setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
// Start with a clean slate.
runtime.gcSoftReferences();
runtime.runFinalizationSync();
Debug.startAllocCounting();
try {
BufferedReader br= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is), 256);
int count = 0;
String line;
//一行一行读取文件内容
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// Skip comments and blank lines.
line = line.trim();
if (line.startsWith("#") || line.equals("")) {
continue;
}
try {
if (Config.LOGV) {
Log.v(TAG, "Preloading " + line + "...");
}
//通过Java反射机制加载类,每一行储存的是类名
Class.forName(line);
if (Debug.getGlobalAllocSize() > PRELOAD_GC_THRESHOLD) {
if (Config.LOGV) {
Log.v(TAG," GC at " + Debug.getGlobalAllocSize());
}
runtime.gcSoftReferences();
runtime.runFinalizationSync();
Debug.resetGlobalAllocSize();
}
count++;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Class not found for preloading: " + line);
} catch (Throwable t) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error preloading " + line + ".", t);
if (t instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) t;
}
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
}
throw new RuntimeException(t);
}
}
Log.i(TAG, "...preloaded " + count + " classes in "
+ (SystemClock.uptimeMillis()-startTime) + "ms.");
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error reading " + PRELOADED_CLASSES + ".", e);
} finally {
// Restore default.
runtime.setTargetHeapUtilization(defaultUtilization);
Debug.stopAllocCounting();
// Bring back root. We'll need it later.
setEffectiveUser(ROOT_UID);
setEffectiveGroup(ROOT_GID);
}
}
}预装载的类列表保存在framework.jar中的名为preloaded-classes的文本文件中,该文件是通过framework/base/tools/prload/WritePreloadedClassFile.java类生成的,产生preloaded-classes文件的方法是在Android源码根目录执行以下命令:
java -Xss512M -cp out/host/linux-x86/framework/preload.jar WritePreloadedClassFile frameworks/base/tools/preload/20100223.compiled
1517 classses were loaded by more than one app.
Added 147 more to speed up applications.
1664 total classes will be preloaded.
Writing object model...
Done!最后生成frameworks/base/preloaded-classes文本文件。preloadClasses函数就是读取preloaded-classes文件,该文件中的每一行代表一个具体的类,然后通过Class.forName()装载这些类,preloadClasses 执行时间比较长,也是导致android系统启动慢的原因。
加载共享资源
private static void preloadResources() {
final VMRuntime runtime = VMRuntime.getRuntime();
Debug.startAllocCounting();
try {
if(LESS_GC) {
System.gc();
runtime.runFinalizationSync();
}
mResources = Resources.getSystem();
mResources.startPreloading();
if (PRELOAD_RESOURCES) {
Log.i(TAG, "Preloading resources...");
long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
//获取frameworks/base/core/res/res/values/arrays.xml中定义的数组preloaded_drawables
TypedArray ar = mResources.obtainTypedArray(
com.android.internal.R.array.preloaded_drawables);
//加载drawable资源
int N = preloadDrawables(runtime, ar);
ar.recycle();
Log.i(TAG, "...preloaded " + N + " resources in "
+ (SystemClock.uptimeMillis()-startTime) + "ms.");
startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
//获取frameworks/base/core/res/res/values/arrays.xml中定义的数组preloaded_color_state_lists
ar = mResources.obtainTypedArray(
com.android.internal.R.array.preloaded_color_state_lists);
//加载color资源
N = preloadColorStateLists(runtime, ar);
ar.recycle();
Log.i(TAG, "...preloaded " + N + " resources in "
+ (SystemClock.uptimeMillis()-startTime) + "ms.");
}
mResources.finishPreloading();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failure preloading resources", e);
} finally {
Debug.stopAllocCounting();
}
}
- @drawable/toast_frame_holo
- @drawable/btn_check_on_pressed_holo_light
- @drawable/btn_check_on_holo_light
....
private static int preloadDrawables(VMRuntime runtime, TypedArray ar) {
int N = ar.length();
for (int i=0; i PRELOAD_GC_THRESHOLD) {
if (false) {
Log.v(TAG, " GC at " + Debug.getGlobalAllocSize());
}
if(LESS_GC) {
System.gc();
runtime.runFinalizationSync();
Debug.resetGlobalAllocSize();
}
}
int id = ar.getResourceId(i, 0);
if (false) {
Log.v(TAG, "Preloading resource #" + Integer.toHexString(id));
}
if (id != 0) {
//将资源加载到mResources全局变量中
Drawable dr = mResources.getDrawable(id);
if ((dr.getChangingConfigurations()&~ActivityInfo.CONFIG_FONT_SCALE) != 0) {
Log.w(TAG, "Preloaded drawable resource #0x"
+ Integer.toHexString(id)
+ " (" + ar.getString(i) + ") that varies with configuration!!");
}
}
}
return N;
}
- @color/primary_text_dark
- @color/primary_text_dark_disable_only
- @color/primary_text_dark_nodisable
....
private static int preloadColorStateLists(VMRuntime runtime, TypedArray ar) {
int N = ar.length();
for (int i=0; i PRELOAD_GC_THRESHOLD) {
if (false) {
Log.v(TAG, " GC at " + Debug.getGlobalAllocSize());
}
if(LESS_GC) {
System.gc();
runtime.runFinalizationSync();
Debug.resetGlobalAllocSize();
}
}
int id = ar.getResourceId(i, 0);
if (false) {
Log.v(TAG, "Preloading resource #" + Integer.toHexString(id));
}
if (id != 0) {
//将资源加载到mResources全局变量中
mResources.getColorStateList(id);
}
}
return N;
} 启动SystemServer进程
private static boolean startSystemServer()
throws MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException {
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,3001,3002,3003",
"--capabilities=130104352,130104352",
"--runtime-init",
"--nice-name=system_server",
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args); //把字符串数组中的参数转换为Arguments对象
/*
* Enable debugging of the system process if *either* the command line flags
* indicate it should be debuggable or the ro.debuggable system property
* is set to "1"
*/
int debugFlags = parsedArgs.debugFlags;
if ("1".equals(SystemProperties.get("ro.debuggable")))
debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER;
/* fork一个子进程作为SystemServer进程*/
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids, debugFlags, null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
//SystemServer进程的初始化设置
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return true;
}Zygote进程通过Zygote.forkSystemServer函数来创建一个新的进程来启动SystemServer组件,返回值pid等0的地方就是新的进程要执行的路径,即新创建的进程会执行handleSystemServerProcess函数。
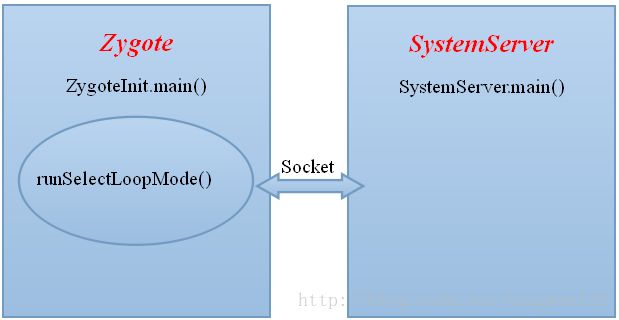
循环等待客户端的连接
private static void runSelectLoopMode() throws MethodAndArgsCaller {
ArrayList fds = new ArrayList(); //存储所有socket文件句柄
ArrayList peers = new ArrayList();//存储所有客户端连接
FileDescriptor[] fdArray = new FileDescriptor[4];
fds.add(sServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());//添加服务端socket文件描述符到fds中
peers.add(null);
int loopCount = GC_LOOP_COUNT;
while (true) {
int index;
/*
* Call gc() before we block in select().
* It's work that has to be done anyway, and it's better
* to avoid making every child do it. It will also
* madvise() any free memory as a side-effect.
*
* Don't call it every time, because walking the entire
* heap is a lot of overhead to free a few hundred bytes.
*/
if (loopCount <= 0) {
gc();
loopCount = GC_LOOP_COUNT;
} else {
loopCount--;
}
try {
fdArray = fds.toArray(fdArray);
//selectReadable内部调用select,使用多路复用I/O模型
//当有客户端连接时,selectReadable返回
index = selectReadable(fdArray);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error in select()", ex);
}
if (index < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error in select()");
} else if (index == 0) {
//有一个客户端连接
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer();
peers.add(newPeer);
fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());
} else {
boolean done;
//客户端发送了请求,peers.get(index)获取当前客户端的ZygoteConnection,并调用当前连接的runOnce()函数创建新的应用程序
done = peers.get(index).runOnce();
if (done) {
peers.remove(index);
fds.remove(index);
}
}
}
} 函数runSelectLoopMode()使Zygote进入非阻塞读取socket操作,函数selectReadable()用于监听服务端Socket文件描述是否有客户端的连接,该函数使用的是Linux多路I/O服务select系统调用:
do {
err = select (nfds, &fdset, NULL, NULL, NULL);
} while (err < 0 && errno == EINTR);当selectReadable返回-1时,表示内部错误;返回值为0时,表示没有可处理的连接;返回值大于0时,表示客户端连接的个数。
zygote总结:
1.创建AppRuntime对象,并调用它的start函数;
2.调用startVm创建Java虚拟机;
3.调用startReg函数来注册JNI函数;
4.调用ZygoteInit类的main函数,从此就进入了Java世界;
5.调用registerZygoteSocket 注册一个服务端socket;
6.调用preloadClasses 函数加载类资源;
7.调用preloadResources函数加载系统资源;
8.调用startSystemServer函数创建SystemServer进程;
9.调用runSelectLoopMode函数进入服务端socket监听;
Zygote孵化新进程
fork是Linux系统的系统调用,用于复制当前进程,产生一个新的进程。新进程被创建后,和父进程共享已经分配的内存空间,除了进程ID外,新进程拥有和父进程完全相同的进程信息,直到向内存写入数据时,操作系统才复制一份目标地址空间,并将要写的数据写入到新的地址空间中,这就是所谓的copy-on-write机制,这种机制最大限度地在多个进程中共享物理内存。fork函数的返回值大于0时,代表的是父进程,当等于0时,代表的是被复制的子进程,父子进程的区分就是通过fork的返回值来区分。当一个客户端进程请求Zygote孵化一个新的进程时,Zygote首先会得到该客户端的Socket连接,并将该连接封装为ZygoteConnection对象,并调用该对象的runOnce()函数来fork出一个新进程:done = peers.get(index).runOnce();
boolean runOnce() throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
String args[];
Arguments parsedArgs = null;
FileDescriptor[] descriptors;
try {
args = readArgumentList();
descriptors = mSocket.getAncillaryFileDescriptors();
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.w(TAG, "IOException on command socket " + ex.getMessage());
closeSocket();
return true;
}
if (args == null) {
// EOF reached.
closeSocket();
return true;
}
/** the stderr of the most recent request, if avail */
PrintStream newStderr = null;
if (descriptors != null && descriptors.length >= 3) {
newStderr = new PrintStream(
new FileOutputStream(descriptors[2]));
}
int pid = -1;
FileDescriptor childPipeFd = null;
FileDescriptor serverPipeFd = null;
try {
parsedArgs = new Arguments(args);
applyUidSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer);
applyRlimitSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer);
applyCapabilitiesSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer);
applyInvokeWithSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer);
applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
int[][] rlimits = null;
if (parsedArgs.rlimits != null) {
rlimits = parsedArgs.rlimits.toArray(intArray2d);
}
if (parsedArgs.runtimeInit && parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
FileDescriptor[] pipeFds = Libcore.os.pipe();
childPipeFd = pipeFds[1];
serverPipeFd = pipeFds[0];
ZygoteInit.setCloseOnExec(serverPipeFd, true);
}
//复制新进程
pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids, parsedArgs.debugFlags, rlimits);
} catch (IOException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Exception creating pipe", ex);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Exception creating pipe", ex);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Invalid zygote arguments", ex);
} catch (ZygoteSecurityException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr,
"Zygote security policy prevents request: ", ex);
}
try {
//区分父子进程
if (pid == 0) {
// in child
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
serverPipeFd = null;
handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr);
// should never get here, the child is expected to either
// throw ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller or exec().
return true;
} else {
// in parent...pid of < 0 means failure
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
childPipeFd = null;
return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);
}
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
}
}普通进程启动
base=/system
export CLASSPATH=$base/framework/am.jar
exec app_process $base/bin com.android.commands.am.Am "$@"runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit",application ? "application" : "tool");public static final void main(String[] argv) {
if (argv.length == 2 && argv[1].equals("application")) {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application");
redirectLogStreams();
} else {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting tool");
}
commonInit();
//通过JNI调用C++函数,更换Java入口
nativeFinishInit();
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Leaving RuntimeInit!");
}static void com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_nativeFinishInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
{
gCurRuntime->onStarted();
}virtual void onStarted()
{
sp proc = ProcessState::self();
ALOGV("App process: starting thread pool.\n");
//启动Binder线程池
proc->startThreadPool();
AndroidRuntime* ar = AndroidRuntime::getRuntime();
//更换Java入口类,在app_process的main函数中,如果启动的不是zygote进程,就为虚拟机设置了启动类及启动参数
ar->callMain(mClassName, mClass, mArgC, mArgV);
IPCThreadState::self()->stopProcess();
} public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
(new Am()).run(args);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
showUsage();
System.err.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(System.err);
System.exit(1);
}
}