贪心算法
Leetcode 455
思路:
1、贪心度越低的孩子越容易满足
2、while循环。糖果价值按由小到大匹配贪心度按由小到大排序的孩子,如果最低糖果价值不能满足最低贪心度的孩子,则舍弃该糖果,直到匹配到等价的。
这样时间复杂度是O(nlogn),快速排序占的时间比较高。实现代码如下:
/*
题目:
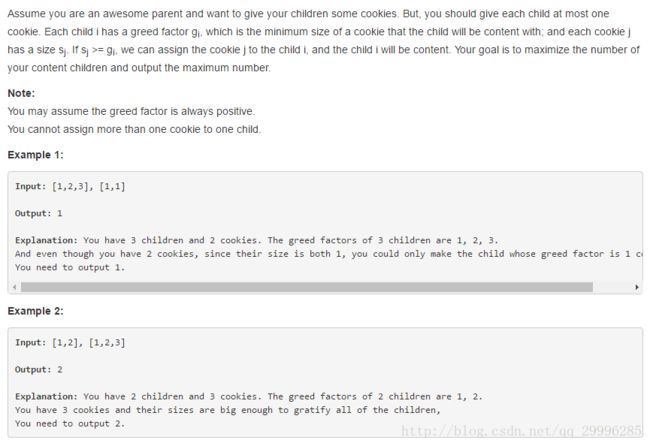
Assume you are an awesome parent and want to give your children some cookies.
But, you should give each child at most one cookie.
Each child i has a greed factor gi, which is the minimum size of a cookie that the child will be content with;
and each cookie j has a size sj.
If sj >= gi, we can assign the cookie j to the child i, and the child i will be content.
Your goal is to maximize the number of your content children and output the maximum number.
Note:
You may assume the greed factor is always positive.
You cannot assign more than one cookie to one child.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3], [1,1]
Output: 1
Explanation: You have 3 children and 2 cookies. The greed factors of 3 children are 1, 2, 3.
And even though you have 2 cookies, since their size is both 1,
you could only make the child whose greed factor is 1 content.
You need to output 1.
Example 2:
Input: [1,2], [1,2,3]
Output: 2
Explanation: You have 2 children and 3 cookies. The greed factors of 2 children are 1, 2.
You have 3 cookies and their sizes are big enough to gratify all of the children,
You need to output 2.
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
//学习一下怎么写宏
#define swap( i, j){int q=0;q=i;i=j;j=q; }
using namespace std;
//复习快速排序
void quickSort(int s[], int l, int r) {
if (l < r) {
int middle = (l + r) / 2;
int i = l - 1;
int j = r + 1;
while (true) {
//找出中间位置左侧大于等于中间位置值的数
while (s[++i] < s[middle]);
//找出中间位置右侧大于等于中间位置值的数
while (s[--j] > s[middle]);
//当i在j后面,就不需要交换
if (i >= j) break;
//调用宏,交换获取的两个位置的值
swap(s[i], s[j]);
}
//递归调用
quickSort(s, l, i - 1);
quickSort(s, j + 1, r);
}
}
//返回最佳匹配值
int Search(int Child[], int Candy[], int Child_num, int Candy_num) {
int answer = 0, temp_Child = 0, temp_Candy = 0;
while (temp_Child < Child_num && temp_Candy < Candy_num) {
//如果孩子贪心度小于等于糖果价值,则记录
if (Child[temp_Child] <= Candy[temp_Candy]) {
answer++;
temp_Candy++;
temp_Child++;
}
//此时糖果不满足孩子的贪心度,舍弃该糖果
else {
temp_Candy++;
}
}
return answer;
}
int main()
{
//Child_num用于记录孩子的个数,Candy_num记录糖果的个数
//temp_Child用于记录每一次输入的孩子的贪心度,temp_Candy用于记录每一次输入的糖果价值
int Child_num = 0, Candy_num = 0, temp_Child = 0, temp_Candy = 0;
cout << "请输入孩子的个数" << endl;
cin >> Child_num;
cout << "请输入糖果的块数" << endl;
cin >> Candy_num;
//创建数组,用于存储输入的数据
int*Child;
int*Candy;
Child = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*Child_num);
Candy = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*Candy_num);
cout << "请输入每个孩子的贪心度" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < Child_num; i++) {
cin >> temp_Child;
Child[i] = temp_Child;
}
cout << "请输入每个糖果的价值" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < Candy_num; i++) {
cin >> temp_Candy;
Candy[i] = temp_Candy;
}
//调用乱序函数,将输入的数据打乱,这样可以提高快排的效率
int* a_begin = Child;
int* a_end = Child + Child_num;
random_shuffle(a_begin, a_end);
a_begin = Candy;
a_end = Candy + Candy_num;
random_shuffle(a_begin, a_end);
//调用快速排序函数 O(nlogn)
quickSort(Child, 0, Child_num - 1);
quickSort(Candy, 0, Candy_num - 1);
int answer = Search(Child, Candy, Child_num, Candy_num);
cout << "满意值为:" << answer << endl;
return 0;
}
LeetCode 376
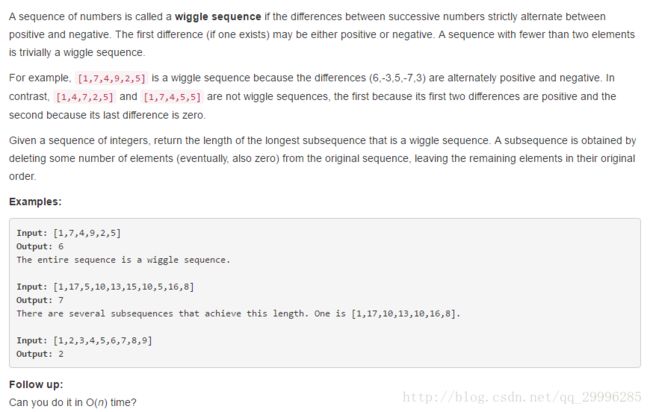
理解:给定一组序列,如果前者与后者的差值依次在正负整数之间交叉出现(开头值正负皆可),则该序列是交叉序列。输出序列中所含最长的交叉序列中元素的个数。(可以删除序列中的某个位置的值(0也可以)来延长交叉序列的长度)。
时间复杂度控制在O(n)
思路:用贪心算法,如果出现两个连续的同符差值,差值为负则证明此段输入序列是三个递增的数,去掉中间的那个数,差值为正则证明此段序列是三个递减数,则去掉中间的数。如此,如果按例题1中的输入序列,最终保留的输出序列应为[1,17,5,15,5,16,8],与例子1给出的输出序列不一致,但是结果是对的。而且可以保证是O(n)。
以下为思路3的实现代码:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int Output(vector&receive) {
/*
v.empty() 如果v为空,则返回true,否则返回false
v.size() 返回v中元素的个数
v.push_back() 在v的末尾增加一个值为t的元素
v[n] 返回v中位置为n的元素
v1=v2 把v1中的元素替换为v2中元素的副本
v1==v2 如果v1与v2相等,则返回true
!=,<,<=,>,>= 保持这些操作符惯有含义
*/
//标记
int count = 0;
vectortemp;
for (int i = 0; i < receive.size()-1; i++) {
//算出序列差值
temp.push_back ( receive[i] - receive[i + 1]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < temp.size()-1; i++) {
if ((temp[i] > 0 && temp[i + 1] > 0) || (temp[i] < 0 && temp[i + 1] < 0)) {
//[1,17,5,10,13,15,10,5,16,8]
//[-16, 12,-5,-3,-2, 5, 5,-11, 8]
//将三个值的中间值制为零
receive[i + 1] = 0;
}
}
//我现在不确定vector中值为0的位置会不会被size出来,所以先用temp的长度
for (int i = 0; i < temp.size() + 1; i++) {
if (receive[i] != 0) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
cout << "请输入序列中的元素" << endl;
cout << "结束输入请输入“999”" << endl;
//试试用容器存数据,不用数组了
vector receive;
//存储每次输入的数据
int temp = 0;
while (cin >> temp) {
if (temp == 999)break;
receive.push_back(temp);
}
int output = Output(receive);
cout << "最长差值列中元素的个数是:" << output << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
LeetCode 402
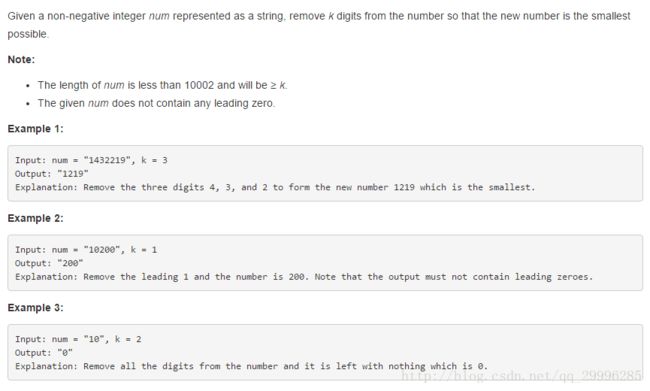
题意:由非负整数构成的字符串,从字符串中取出k个数使得新的数最小。
注意:输入的数字串长度小于10002且大于k;输入的数字串不会以0开头。
思路:将字符串中字符依次入栈,如果当前字符串比栈顶元素小,并且还可以继续删除元素,那么就将栈顶元素删掉,这样会得到最小数字序列。
实现代码如下:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
string removeKdigits(string num, int k) {
int n = k, index=0;
string answer;
for (size_t i = 0; i < num.size(); i++) {
while (answer.size() != 0 && n > 0 && num[i] < answer.back()) {
n--;
answer.pop_back();
}
answer.push_back(num[i]);
}
//去除开头的0
for (size_t i = 0; i < answer.size(); i++) {
if (answer[i] != '0') {
index = i;
break;
}
//此时说明answer里面存的全是0
else if(answer[i]=='0'&&i==answer.size()-1){
answer = "0";
}
}
//获取答案
//string a=s.substr(0,5);
//获得字符串s中 从第0位开始的长度为5的字符串
answer = answer.substr(index, num.size() - k - index);
if (answer.size()==0) answer.push_back('0');
return answer;
}
int main()
{
int k = 0;
char num[10002];
cin >> num;
cin >> k;
string answer=removeKdigits( num, k);
return 0;
}
LeetCode 55
题意:给出一组非负整数,你位于数组索引位置为0的地方,数组中的每个值代表你在当前位置所能向后跳跃的最大“格数”(你可以不跳最大格数)。判断你是否能到达索引位置的最后一位。