数据压缩原理 实验三 Huffman编解码算法实现与压缩效率分析
实验原理
Huffman编码是一种无失真编码方式,是一种可变长编码,它将出现概率大的信源符号短编码,出现概率小的信源符号长编码。
编码步骤:
①将文件以ASCII字符流的形式读入,统计每个符号的发生概率
②将所有文件中出现过的字符按照概率从小到大的顺序排列
③每一次选出最小的两个值,作为二叉树的两个子节点,将和作为他们的父节点,这两个子节点不再参与比较,新的父节点参与比较
④重复上一步,直到最后得到和为1的根节点
⑤将形成的二叉树的左节点标0,右节点标1,把从最上面的根节点到最下面的树叶节点途中遇到的0和1按序串联,即为该字符的编码表示
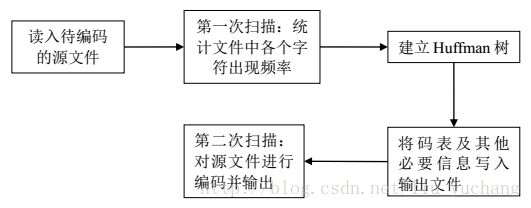
实验流程
代码分析
实验中将实际完成编码工作的工程Huff_code封装成一个静态链接库,由工程huff_run来调用,huff_run完成的工作包括解析命令行参数,打开、读取、关闭输入文件,打开关闭输出文件,调用Huff_code完成编码。
Huff_run
huffcode.c
#include "huffman.h"
#include getopt.c
#include Huff_code
huffman.c
#include bits[i][j] = p->bits[j];//把码字结构体里面的码字赋给输出信息的码字
}
else
st->numbits[i] =0; //如果该码字结构体为空,则该符号没有在文件中出现,没有编码
}
return 0;
}
//////////输出统计信息表文件//////////
void output_huffman_statistics(huffman_stat *st,FILE *out_Table)
{
int i,j;
unsigned char c;
fprintf(out_Table,"symbol\t freq\t codelength\t code\n"); //在输出文件中打印表头
for(i = 0; i < MAX_SYMBOLS; ++i)
{
fprintf(out_Table,"%d\t ",i); //输出 符号的ASCII码十进制表示
fprintf(out_Table,"%f\t ",st->freq[i]); //输出 符号在输入文件中出现的频率
fprintf(out_Table,"%d\t ",st->numbits[i]); //输出 符号码字的码长
if(st->numbits[i]) //码长不为0 就输出码字
{
for(j = 0; j < st->numbits[i]; ++j) //循环取码字的每一位,从高到低输出到文件中
{
c =get_bit(st->bits[i], j);
fprintf(out_Table,"%d",c);
}
}
fprintf(out_Table,"\n");
}
}
//////////进行Huffman编码//////////
int huffman_encode_file(FILE *in, FILE *out, FILE *out_Table)
//Huffman编码,增加一个FILE *out_Table,用于输出表格
{
SymbolFrequencies sf; //含有256个节点的数组
SymbolEncoder *se; //指向256个编码的指针
huffman_node *root = NULL; //根节点
int rc;
unsigned int symbol_count; //文件中总ASCII码数
huffman_stat hs; //输出结果的表 包括符号频率 码长 码字等
/////获取输入文件的每个符号的出现概率/////
symbol_count = get_symbol_frequencies(&sf, in); //演示扫描完一遍文件后,SF指针数组的每个元素的构成
//sf中每个节点所代表的信源符号出现的次数count已经被赋值
huffST_getSymFrequencies(&sf,&hs,symbol_count);
/////从符号统计来建立一个最理想的表格来/////
se = calculate_huffman_codes(&sf); //编码 256个节点传入得到256个码字
root = sf[0]; //根节点
huffST_getcodeword(se, &hs); //为输出信息赋值
output_huffman_statistics(&hs,out_Table); //输出信息
/////再次扫描文件,用预先建立的表格把它编成输出文件/////
rewind(in); //将输入文件的内部指针重新指向文件开头
rc = write_code_table(out, se, symbol_count); //写码表
if(rc == 0) //成功写入码表后,rc就被赋值为0
rc = do_file_encode(in, out, se); //写编码后的文件,返回值为0
/////释放Huffman码树/////
free_huffman_tree(root); //释放码树
free_encoder(se); //释放码字结构体
return rc;
}
//////////读取Huffman码字,并解码输出//////////
int huffman_decode_file(FILE *in, FILE *out)
{
huffman_node *root, *p;
int c;
unsigned int data_count;
/* Read the Huffman code table. */
root = read_code_table(in, &data_count);
if(!root)
return 1; //Huffman树建立失败
/* Decode the file. */
p = root;
while(data_count > 0 && (c = fgetc(in)) != EOF)
//data_count>0:逻辑上仍有数据;(c=fgetc(in)!=EOF):文件中仍有数据
{
unsigned char byte = (unsigned char)c; //1byte的码字
unsigned char mask = 1; //mask用于逐位读出码字
while(data_count > 0 && mask) //loop9:mask=0x00000000,跳出循环
{
p = byte & mask ? p->one : p->zero; //沿Huffman树前进
mask <<= 1; //loop1:byte&0x00000001
//loop2:byte&0x00000010
//……
//loop8:byte&0x10000000
if(p->isLeaf) //至叶节点(解码完毕)
{
fputc(p->symbol, out);
p = root;
--data_count;
}
}
}
free_huffman_tree(root); //所有Huffman码字均已解码输出,文件解码完毕
return 0;
}
#define CACHE_SIZE 1024
int huffman_encode_memory(const unsigned char *bufin,
unsigned int bufinlen,
unsigned char **pbufout,
unsigned int *pbufoutlen)
{
SymbolFrequencies sf;
SymbolEncoder *se;
huffman_node *root = NULL;
int rc;
unsigned int symbol_count;
buf_cache cache;
/* Ensure the arguments are valid. */
if(!pbufout || !pbufoutlen)
return 1;
if(init_cache(&cache, CACHE_SIZE, pbufout, pbufoutlen))
return 1;
/* Get the frequency of each symbol in the input memory. */
symbol_count = get_symbol_frequencies_from_memory(&sf, bufin, bufinlen);
/* Build an optimal table from the symbolCount. */
se = calculate_huffman_codes(&sf);
root = sf[0];
/* Scan the memory again and, using the table
previously built, encode it into the output memory. */
rc = write_code_table_to_memory(&cache, se, symbol_count);
if(rc == 0)
rc = do_memory_encode(&cache, bufin, bufinlen, se);
/* Flush the cache. */
flush_cache(&cache);
/* Free the Huffman tree. */
free_huffman_tree(root);
free_encoder(se);
free_cache(&cache);
return rc;
}
int huffman_decode_memory(const unsigned char *bufin,
unsigned int bufinlen,
unsigned char **pbufout,
unsigned int *pbufoutlen)
{
huffman_node *root, *p;
unsigned int data_count;
unsigned int i = 0;
unsigned char *buf;
unsigned int bufcur = 0;
/* Ensure the arguments are valid. */
if(!pbufout || !pbufoutlen)
return 1;
/* Read the Huffman code table. */
root = read_code_table_from_memory(bufin, bufinlen, &i, &data_count);
if(!root)
return 1;
buf = (unsigned char*)malloc(data_count);
/* Decode the memory. */
p = root;
for(; i < bufinlen && data_count > 0; ++i)
{
unsigned char byte = bufin[i];
unsigned char mask = 1;
while(data_count > 0 && mask)
{
p = byte & mask ? p->one : p->zero;
mask <<= 1;
if(p->isLeaf)
{
buf[bufcur++] = p->symbol;
p = root;
--data_count;
}
}
}
free_huffman_tree(root);
*pbufout = buf;
*pbufoutlen = bufcur;
return 0;
}
实验结果与总结
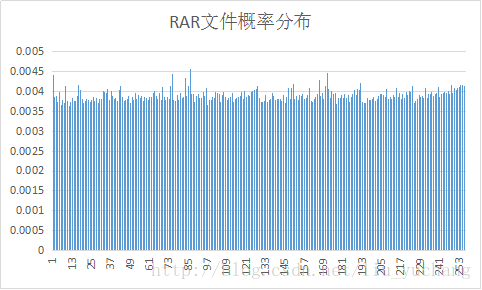
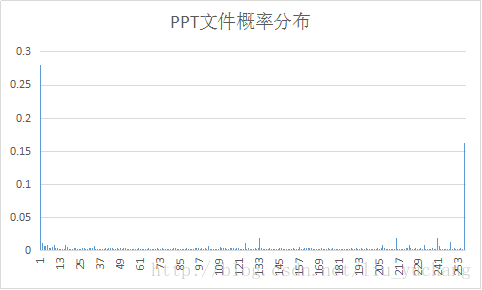
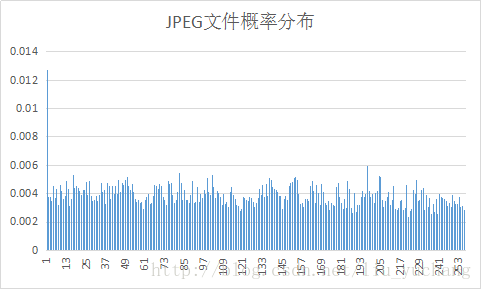
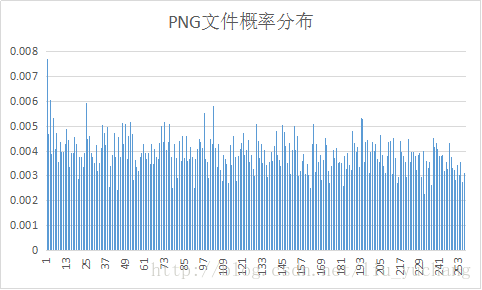
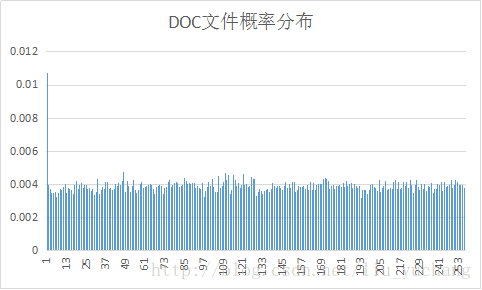
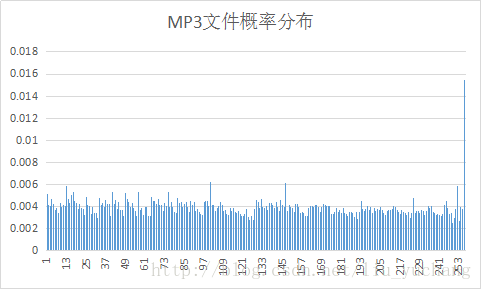
实验选取了十种文件进行编码,并对编码后输出的excel文件进行了分析。

其中:
p*code列为符号出现概率与码长之积
-p*log(p)列为符号的自信息与出现概率之积*
整理得出

文件的平均码长与信源熵大小相近。
实验中YUV信源符号出现概率分布变化较大,其余文件信源符号接近等概分布,而BMP文件压缩效率较高。