Farthest Point Sampling on 2d image
Farthest Point Sampling的原理是,先随机选一个点,然后呢选择离这个点距离最远的点(D中值最大的点)加入起点,然后继续迭代,直到选出需要的个数为止
其主要代码如下:
%main.m
clear options;
n = 400;
[M,W] = load_potential_map('mountain', n);
npoints_list = round(linspace(20,200,6));%采样点个数列表
landmark = [];
options.verb = 0;
ms = 15;
clf;
for i=1:length(npoints_list)
nbr_landmarks = npoints_list(i);
landmark = perform_farthest_point_sampling( W, landmark, nbr_landmarks-size(landmark,2), options );%nbr_landmarks-size(landmark,2) 减去已经存在的点数
%landmark为已采样的点(包括原来的点和新增的点)
% compute the associated triangulation
[D,Z,Q] = perform_fast_marching(W, landmark);
% display sampling and distance function
D = perform_histogram_equalization(D,linspace(0,1,n^2));%把D中的值拉到[0,1]范围内
subplot(2,3,i);
hold on;
imageplot(D');
plot(landmark(1,:), landmark(2,:), 'r.', 'MarkerSize', ms);
title([num2str(nbr_landmarks) ' points']);
hold off;
colormap jet(256);
end%perform_farthest_point_sampling.m
function [points,D] = perform_farthest_point_sampling( W, points, npoints, options )
% points为已经采样了的点,npoints表示需要加入采样点的个数
% perform_farthest_point_sampling - samples points using farthest seeding strategy
%
% points = perform_farthest_point_sampling( W, points, npoints );
%
% points can be [] or can be a (2,npts) matrix of already computed
% sampling locations.
%
% Copyright (c) 2005 Gabriel Peyre
options.null = 0;
if nargin<3
npoints = 1;
end
if nargin<2
points = [];
end
n = size(W,1);
aniso = 0;
d = nb_dims(W);
if d==4
aniso = 1;
d = 2; % tensor field
elseif d==5
aniso = 1;
d = 3; % tensor field
end
s = size(W);
s = s(1:d);
% domain constraints (for shape meshing)
L1 = getoptions(options, 'constraint_map', zeros(s) + Inf );
verb = getoptions(options, 'verb', 1);
mask = not(L1==-Inf);
if isempty(points)
% initialize farthest points at random
points = round(rand(d,1)*(n-1))+1;%随机一个点的d维坐标
% replace by farthest point
[points,L] = perform_farthest_point_sampling( W, points, 1 );%然后选点到points最远的距离
Q = ones(size(W));
points = points(:,end);%取最后一个点,即就是生成的离初始随机点最远的那个点
npoints = npoints-1;%需要生成的点数减1
else
% initial distance map
[L,Q] = my_eval_distance(W, points, options);%如果初始已存在一些采样点,则可以通过perform_fast_marching算距离了, points为初始点(距离为0的点)
% L = min(zeros(s) + Inf, L1);
% Q = zeros(s);
end
for i=1:npoints
if npoints>5 && verb==1
progressbar(i,npoints);
end
options.nb_iter_max = Inf;
options.Tmax = Inf; % sum(size(W));
% [D,S] = perform_fast_marching(W, points, options);
options.constraint_map = L;
pts = points;
if not(aniso)
pts = pts(:,end);%为何只取最一个点?因为前面的距离都算好了,存储在L中
end
D = my_eval_distance(W, pts, options);
Dold = D;
D = min(D,L); % known distance map to lanmarks
L = min(D,L1); % cropp with other constraints
if not(isempty(Q))
% update Voronoi
Q(Dold==D) = size(points,2);
end
% remove away data
D(D==Inf) = 0;
if isempty(Q)
% compute farthest points
[tmp,I] = max(D(:));%找距离最远的点
[a,b,c] = ind2sub(size(W),I(1));
else
% compute farthest steiner point
[pts,faces] = compute_saddle_points(Q,D,mask);
a = pts(1,1); b = pts(2,1); c = [];%第1列,为距离D最大的值
if d==3
c = pts(3,1);
end
end
if d==2 % 2D
points = [points,[a;b]];
else % 3D
points = [points,[a;b;c]];
end
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function [D,Q] = my_eval_distance(W, x, options)%给点权值矩阵W, 初始点x(距离为0的点),则算各点的距离
% D is distance
% Q is voronoi segmentation
options.null = 0;
n = size(W,1);
d = nb_dims(W);
if std(W(:))1
D = zeros(n)+Inf;
Q = zeros(n);
for i=1:size(x,2)
Dold = D; Qold = Q;
D = min(Dold, my_eval_distance(W,x(:,i)));
% update voronoi segmentation
Q(:) = i;
Q(D==Dold) = Qold(D==Dold);
end
return;
end
if d==2
[Y,X] = meshgrid(1:n,1:n);
D = 1/W(1) * sqrt( (X-x(1)).^2 + (Y-x(2)).^2 );
else
[X,Y,Z] = ndgrid(1:n,1:n,1:n);
D = 1/W(1) * sqrt( (X-x(1)).^2 + (Y-x(2)).^2 + (Z-x(3)).^2 );
end
Q = D*0+1;
else
[D,S,Q] = perform_fast_marching(W, x, options);
end %perform_fast_marching.m
function [D,S,Q] = perform_fast_marching(W, start_points, options)
% perform_fast_marching - launch the Fast Marching algorithm, in 2D or 3D.
%
% [D,S,Q] = perform_fast_marching(W, start_points, options)
%
% W is an (n,n) (for 2D, d=2) or (n,n,n) (for 3D, d=3)
% weight matrix. The geodesics will follow regions where W is large.
% W must be > 0.
% 'start_points' is a d x k array, start_points(:,i) is the ith starting point .
%
% D is the distance function to the set of starting points.
% S is the final state of the points : -1 for dead (ie the distance
% has been computed), 0 for open (ie the distance is only a temporary
% value), 1 for far (ie point not already computed). Distance function
% for far points is Inf.(注意对于far来说,1是状态,Inf是距离)
% (按照书上的说法,-1为known的点,0为trial点,1为far点)
% Q is the index of the closest point. Q is set to 0 for far points.
% Q provide a Voronoi decomposition of the domain.
%
% Optional:
% - You can provide special conditions for stop in options :
% 'options.end_points' : stop when these points are reached
% 'options.nb_iter_max' : stop when a given number of iterations is
% reached.
% - You can provide an heuristic in options.heuristic (typically that try to guess the distance
% that remains from a given node to a given target).
% This is an array of same size as W.
% - You can provide a map L=options.constraint_map that reduce the set of
% explored points. Only points with current distance smaller than L
% will be expanded. Set some entries of L to -Inf to avoid any
% exploration of these points.
% - options.values set the initial distance value for starting points
% (default value is 0).
%
% See also: perform_fast_marching_3d.
%
% Copyright (c) 2007 Gabriel Peyre
options.null = 0;
end_points = getoptions(options, 'end_points', []);
verbose = getoptions(options, 'verbose', 1);
nb_iter_max = getoptions(options, 'nb_iter_max', Inf);
values = getoptions(options, 'values', []);
L = getoptions(options, 'constraint_map', []);
H = getoptions(options, 'heuristic', []);
dmax = getoptions(options, 'dmax', Inf);
d = nb_dims(W);
if (d==4 && size(W,3)==2 && size(W,4)==2) || (d==4 && size(W,4)==6) || (d==5 && size(W,4)==3 && size(W,5)==3)
% anisotropic fast marching
if d==4 && size(W,3)==2 && size(W,4)==2
% 2D vector field -> 3D field
W1 = zeros(size(W,1), size(W,2), 3, 3);
W1(:,:,1:2,1:2) = W;
W1(:,:,3,3) = 1;
W = reshape(W1, [size(W,1) size(W,2), 1 3 3]);
% convert to correct size
W = cat(4, W(:,:,:,1,1), W(:,:,:,1,2), W(:,:,:,1,3), W(:,:,:,2,2), W(:,:,:,2,3), W(:,:,:,3,3) );
end
if d==5
% convert to correct size
W = cat(4, W(:,:,:,1,1), W(:,:,:,1,2), W(:,:,:,1,3), W(:,:,:,2,2), W(:,:,:,2,3), W(:,:,:,3,3) );
end
if size(start_points,1)==2
start_points(end+1,:) = 1;
end
if size(start_points,1)~=3
error('start_points should be of size (3,n)');
end
% padd to avoid boundary problem
W = cat(1, W(1,:,:,:), W, W(end,:,:,:));
W = cat(2, W(:,1,:,:), W, W(:,end,:,:));
W = cat(3, W(:,:,1,:), W, W(:,:,end,:));
% if isempty(L)
L = ones(size(W,1), size(W,2), size(W,3));
% end
if dmax==Inf
dmax = 1e15;
end
% start_points = start_points-1;
alpha = 0;
[D,Q] = perform_front_propagation_anisotropic(W, L, alpha, start_points,dmax);
% remove boundary problems
D = D(2:end-1,2:end-1,2:end-1);
Q = Q(2:end-1,2:end-1,2:end-1);
S = [];
D(D>1e20) = Inf;
return;
end
if d~=2 && d~=3
error('Works only in 2D and 3D.');
end
if size(start_points,1)~=d
error('start_points should be (d,k) dimensional with k=2 or 3.');
end
L(L==-Inf)=-1e9;
L(L==Inf)=1e9;
nb_iter_max = min(nb_iter_max, 1.2*max(size(W))^d);
% use fast C-coded version if possible
if d==2
if exist('perform_front_propagation_2d')~=0
[D,S,Q] = perform_front_propagation_2d(W,start_points-1,end_points-1,nb_iter_max, H, L, values);
%讲下vonoroi的分类原理, 假设初始sample点有k个,那么就把这k个sample点作为k个cell的中心,然后将剩下的点距离哪个sample点近就把归于哪个cell里
%跟那种用平面切出来的cell虽然过程不一样,但是原理是一样的.每一个sample点会拥有一个cell
else
[D,S] = perform_front_propagation_2d_slow(W,start_points,end_points,nb_iter_max, H);
Q = [];
end
elseif d==3
[D,S,Q] = perform_front_propagation_3d(W,start_points-1,end_points-1,nb_iter_max, H, L, values);
end
Q = Q+1;
% replace C 'Inf' value (1e9) by Matlab Inf value.
D(D>1e8) = Inf;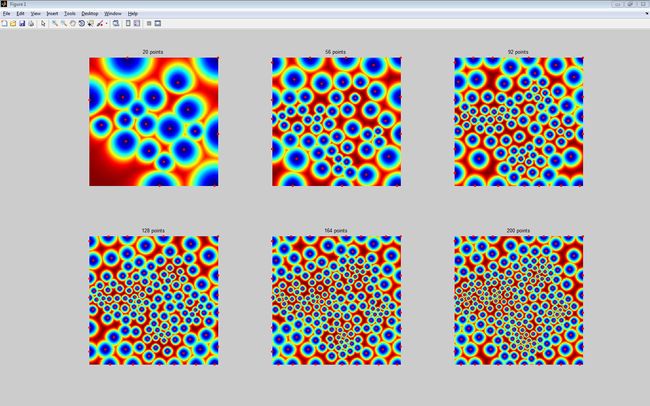
蓝色表示距离为0, 红色表示距离为1.
最后讲下该方法与medial axis的共同之处:
1. 最远点一定会落在中轴上面
证明: 最远点是指至少到两个点的距离相等,则此距离最远,那么它肯定满足距离相等这一条件,即它一定会落在中轴上面
2.它与power diagram的关系为:powder diagram插入球后, 相等于将把weight对应的球的区域设为0. weight值越小,排斥力越强, 越大,吸引力越强.如果把整个球的区域设为0.5,那么产生的中轴可能就是弧形,而不是直线.而且该弧开是比较靠近值大的球.
matlab完整源代码

