卫星图像分割--Effective Use of Dilated Convolutions for Segmenting Small Object Instances
Effective Use of Dilated Convolutions for Segmenting Small Object Instances in Remote Sensing Imagery
https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.00179
针对卫星图像中的小目标分割问题,本文从 dilated convolution 的有效使用给出了解决方法,主要是 先 increasing dilation factor,再 decreasing dilation factor
卫星图像的特征有以下两点:
1)Size of objects 目标的尺寸很小
2)Layout of objects 目标的排列很密集
为了分割出这些密集的小目标,图像中一个很重要的信息就是 context 周边信息。文献【26】指出在CNN中 context 对于识别小目标的主要性。尽管降采样层对于增加感受野是有帮助的,但是他们忽视了另一个重要的因素:resolution。分辨率对于解决密集小目标分割是很重要的。但是降采样层会导致CNN网络中特征图尺寸越来越小,这些小的特征图导致小目标信息的丢失。即使通过其他一些补偿如:skip connections [1, 5] or hypercolumns [6, 21] 也难以解决问题。所以我们需要在增加感受野的同时保持特征图的分辨率。
dilated convolutions 是一个不错的方法,它可以保持分辨率不变,但是目前dilated convolutions 使用方法不能很好的分割 小目标, aggressively increasing dilation factors fails to aggregate local features of small objects. This means that whereas increasing dilation factors is important in terms of resolution and context, it can be detrimental to small objects. This is especially undesirable for remote sensing scenario.
We solve this problem by simply going against the tide—decreasingly dilated convolutions.
Overview of the proposed network architecture

网络包括三个模块:front-end module, local feature extraction (LFE) module and head module
3.2. Front-end module
The front-end module is designed to extract features that cover large context, and thus the dilation factors are gradually increased
这个模块主要负责提取好的特征,主要使用递增的 dilation factors 来增加感受野来得到更大的 context
there are two problems concerning sparsity in dilated kernels.
3.3. Local feature extraction module
LFE module 主要是解决 front-end module 的问题。大量使用 dilated convolution 造成了两个问题
(1) spatial consistency between neighboring units becomes weak 相邻神经元直接的空间联系变弱
(2) local structure cannot be extracted in higher layer. 在后面的网络层提取不到图像中的局部结构信息
Problem on spatial inconsistency:
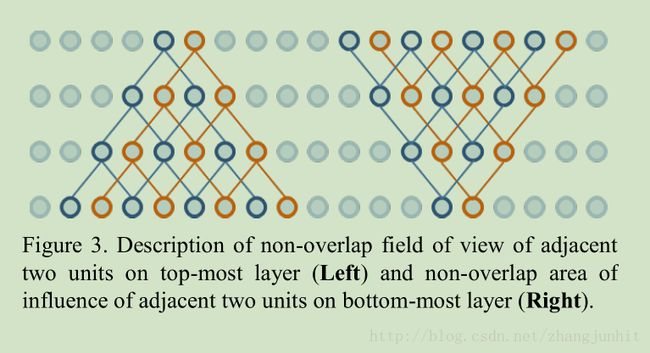
We can see that information pyramids of two adjacent units do not overlap due to the sparse connections of the dilated kernels
从上图我们可以看出因为 dilated kernels 中的稀疏连接,导致相邻神经元没有联系
In the case of the dilation factor of 2, two neighboring units have non-overlap information pyramids, and as we increase the dilation factor, number of
neighboring units which have non-overlap information pyramids grows larger.
当我们增加 dilation factor 时, 没有联系的神经元空隙会变大。
造成的后果就是分割结果有锯齿现象。
this causes spatial inconsistency between neighboring units and causes serious jaggy patterns in final output maps
Problem on local structure extraction:
上图的右边显示,网络前面层中间神经元的不联系导致网络后面层神经元之间不联系,局部结构信息的丢失
information pyramids do not overlap for two adjacent units in bottom most layer. All units in top most layer receive information from either of the two units, but not both. This means that all units in top most layer are unaware of local structure inside the two units.
Local feature extraction module:
解决的方法就是 先 increasing dilation factor,再 decreasing dilation factor
3.4. Post-processing
直接用二值化得到分割结果
4 Experiments
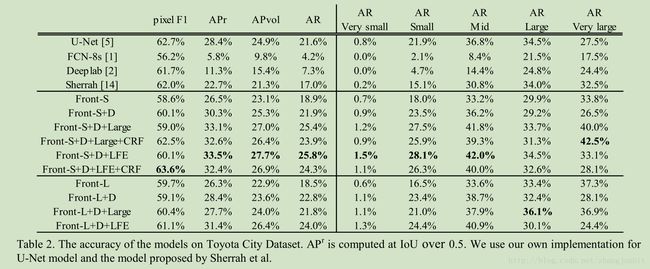
Toyota City Dataset
Massachusetts Buildings Dataset

Massachusetts Buildings Dataset 分割结果图