OpenGL学习笔记十八——批处理
批处理
- 什么是Draw Call
- 什么是批处理
- 使用批处理
- 使用gl_InstanceID对多个物体做偏移处理
- 实例测试
- 补充
什么是Draw Call
在渲染物体之前,物体模型顶点数据保存在内存中,CPU通过向GPU发送渲染指令后,数据会复制到显存中,然后进行渲染。在这个过程中,CPU向GPU发送渲染指令的过程,名为Draw Call。OpenGL中的渲染指令是指: glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, amount_of_vertices);函数
什么是批处理
当我们在渲染一个场景时,该场景中包含非常多的简单模型,比如星星,草等,这些模型的顶点数据极少,但是每次单独渲染一个简单模型时都会调用一次Draw Call,渲染的速度很快,但是发送指令的过程是很慢的(CPU告诉GPU该从哪个缓冲读取数据,从哪寻找顶点属性,而且这些都是在相对缓慢的CPU到GPU总线(CPU to GPU Bus)上进行的),这就会使渲染整个场景的速度变得非常慢,传统的方案就是:
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < amount_of_models_to_draw; i++)
{
DoSomePreparations(); // 绑定VAO,绑定纹理,设置uniform等
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, amount_of_vertices);
}
但如果我们能将这些星星或者草一次性全部发给GPU去渲染,速度就会非常快,这就是批处理
批处理能节省Draw Call的数量,极大提升渲染速度,因此在Unity中,批处理的作用非常大
使用批处理
使用批处理的前提是多个物体使用同一个shader做渲染,在Unity中,就是指使用相同的材质球。
在OpenGL中使用批处理,只需要将glDrawArrays和glDrawElements的渲染调用分别改为glDrawArraysInstanced和glDrawElementsInstanced就可以了。这些渲染函数的实例化版本需要一个额外的参数,叫做实例数量(Instance Count)
这个函数本身并没有什么用。渲染同一个物体一千次对我们并没有什么用处,每个物体都是完全相同的,而且还在同一个位置。我们只能看见一个物体!处于这个原因,GLSL在顶点着色器中嵌入了另一个内建变量,gl_InstanceID。
在使用实例化渲染调用时,gl_InstanceID会从0开始,在每个实例被渲染时递增1。比如说,我们正在渲染第43个实例,那么顶点着色器中它的gl_InstanceID将会是42。因为每个实例都有唯一的ID,我们可以建立一个数组,将ID与位置值对应起来,将每个实例放置在世界的不同位置。
使用gl_InstanceID对多个物体做偏移处理
物体顶点数据
float quadVertices[] = {
// 位置 // 颜色
-0.05f, 0.05f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.05f, -0.05f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.05f, -0.05f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.05f, 0.05f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.05f, -0.05f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.05f, 0.05f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f
};
顶点着色器:
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec2 aPos;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aColor;
out vec3 fColor;
uniform vec2 offsets[100];
void main()
{
vec2 offset = offsets[gl_InstanceID];
gl_Position = vec4(aPos + offset, 0.0, 1.0);
fColor = aColor;
}
片元着色器:
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in vec3 fColor;
void main()
{
FragColor = vec4(fColor, 1.0);
}
绘制:
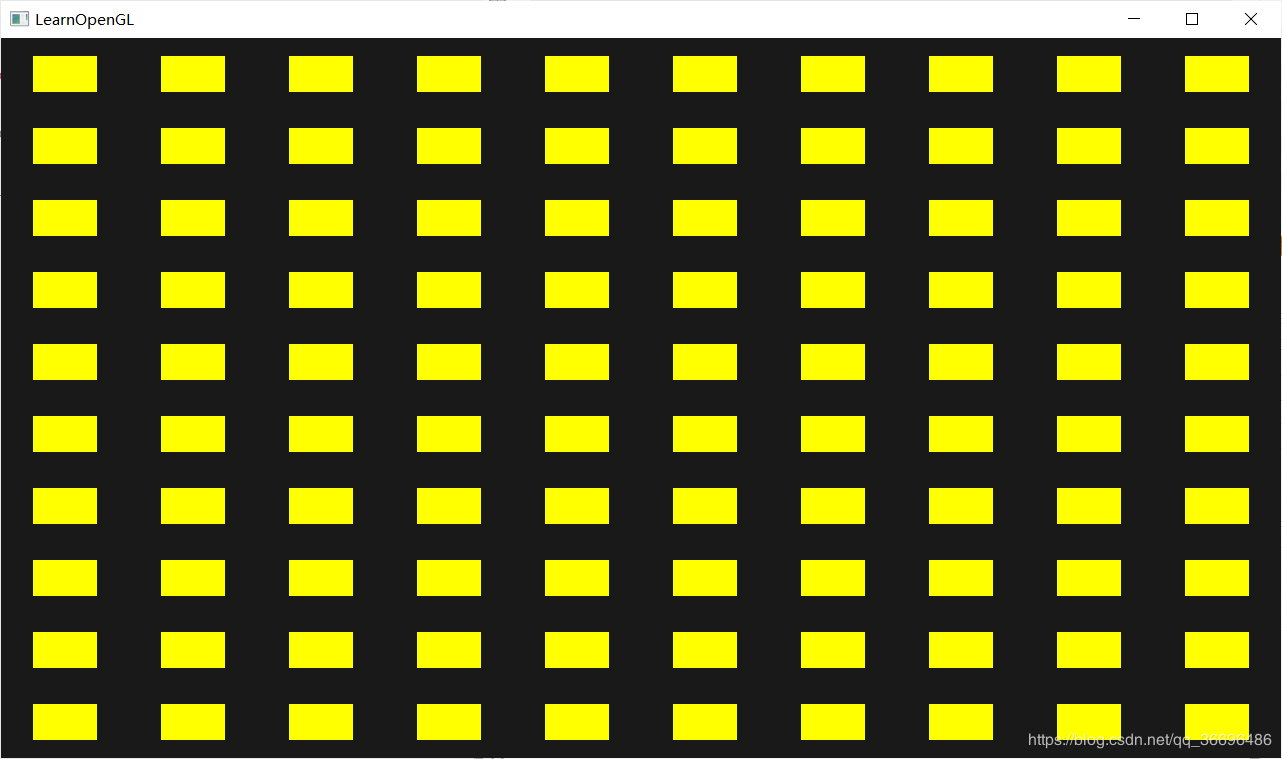
glBindVertexArray(quadVAO);
//绘制100个相同的图形
glDrawArraysInstanced(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 6, 100);
实例测试
顶点着色器:
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec2 aPos;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aColor;
layout (location = 2) in vec2 aOffset;
out vec3 fColor;
void main()
{
fColor = aColor;
gl_Position = vec4(aPos + aOffset, 0.0, 1.0);
}
片元着色器:
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in vec3 fColor;
void main()
{
FragColor = vec4(fColor, 1.0);
}
#include 补充
其他头文件请参考之前的内容补充:
之前的文章