本文作者:hhh5460
本文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/hhh5460/p/10146554.html
说明:将之前 q-learning 实现的例一,用 saras 重新写了一遍。具体问题这里就不多说了。
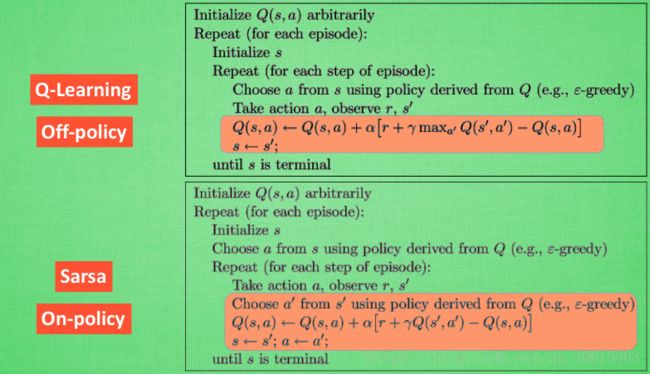
0. q-learning 与 saras 伪代码的对比
图片来源:https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/machine-learning/reinforcement-learning/3-1-A-sarsa/(莫凡)
1. q-learning 与 saras 真实代码对比
a). q-learning 算法
# 探索学习13次 for i in range(13): # 0.从最左边的位置开始(不是必要的) current_state = 0 # 1.进入循环,开始探索学习 while current_state != states[-1]: # 2.取当前状态下的合法动作中,随机(或贪婪)地选一个作为 当前动作 if random.uniform(0,1) > epsilon: # 探索 current_action = random.choice(get_valid_actions(current_state)) else: #current_action = q_table.ix[current_state].idxmax() # 这种写法是有问题的!二维迷宫有机会陷入死锁 s = q_table.ix[current_state].filter(items=get_valid_actions(current_state)) current_action = random.choice(s[s==s.max()].index) # 可能多个最大值,当然,一个更好 #3.执行当前动作,得到下一个状态(位置) next_state = get_next_state(current_state, current_action) # 4.下个状态的奖励 next_state_reward = rewards[next_state] # 5.取下一个状态所有的Q value,待取其最大值 next_state_q_values = q_table.ix[next_state, get_valid_actions(next_state)] # 6.根据贝尔曼方程,更新 Q table 中当前状态-动作对应的 Q value,有max! q_table.ix[current_state, current_action] += alpha * (rewards[next_state] + gamma * next_state_q_values.max() - q_table.ix[current_state, current_action]) # 7.进入下一个状态(位置) current_state = next_state
b). saras 算法
# 探索学习13次 for i in range(13): # 0.从最左边的位置开始(不是必要的) current_state = 0 # 1.取当前状态下的一个合法动作 if random.uniform(0,1) > epsilon: # 探索 current_action = random.choice(get_valid_actions(current_state)) else: # 利用(贪婪) s = q_table.ix[current_state].filter(items=get_valid_actions(current_state)) current_action = random.choice(s[s==s.max()].index) # 可能多个最大值,当然,一个更好 # 2.进入循环,开始探索学习 while current_state != states[-1]: # 3.执行当前动作,得到下一个状态(位置) next_state = get_next_state(current_state, current_action) # 4.取下个状态下的一个合法动作 if random.uniform(0,1) > epsilon: # 探索 next_action = random.choice(get_valid_actions(next_state)) else: # 利用(贪婪) s = q_table.ix[next_state].filter(items=get_valid_actions(next_state)) next_action = random.choice(s[s==s.max()].index) # 可能多个最大值,当然,一个更好 # 5.下个状态的奖励 next_state_reward = rewards[next_state] # 6.取下个状态,下个动作对应的一个Q value next_q_value = q_table.ix[next_state, next_action] # 7.更新 Q table 中当前状态-动作对应的 Q value,无max! q_table.ix[current_state, current_action] += alpha * (next_state_reward + gamma * next_q_value - q_table.ix[current_state, current_action]) # 8.进入下一状态、下一动作 current_state, current_action = next_state, next_action
2. 完整代码
''' -o---T # T 就是宝藏的位置, o 是探索者的位置 ''' # 作者: hhh5460 # 时间:20181219 import pandas as pd import random import time epsilon = 0.9 # 贪婪度 greedy alpha = 0.1 # 学习率 gamma = 0.8 # 奖励递减值 states = range(6) # 状态集。从0到5 actions = ['left', 'right'] # 动作集。也可添加动作'none',表示停留 rewards = [0,0,0,0,0,1] # 奖励集。只有最后的宝藏所在位置才有奖励1,其他皆为0 q_table = pd.DataFrame(data=[[0 for _ in actions] for _ in states], index=states, columns=actions) def update_env(state): '''更新环境,并打印''' env = list('-----T') # 环境 env[state] = 'o' # 更新环境 print('\r{}'.format(''.join(env)), end='') time.sleep(0.1) def get_next_state(state, action): '''对状态执行动作后,得到下一状态''' global states # l,r,n = -1,+1,0 if action == 'right' and state != states[-1]: # 除末状态(位置),向右+1 next_state = state + 1 elif action == 'left' and state != states[0]: # 除首状态(位置),向左-1 next_state = state -1 else: next_state = state return next_state def get_valid_actions(state): '''取当前状态下的合法动作集合,与reward无关!''' global actions # ['left', 'right'] valid_actions = set(actions) if state == states[0]: # 首状态(位置),则 不能向左 valid_actions -= set(['left']) if state == states[-1]: # 末状态(位置),则 不能向右 valid_actions -= set(['right']) return list(valid_actions) for i in range(13): #current_state = random.choice(states) current_state = 0 if random.uniform(0,1) > epsilon: # 探索 current_action = random.choice(get_valid_actions(current_state)) else: # 利用(贪婪) #current_action = q_table.ix[current_state].idxmax() # 这种写法是有问题的! s = q_table.ix[current_state].filter(items=get_valid_actions(current_state)) current_action = random.choice(s[s==s.max()].index) # 可能多个最大值,当然,一个更好 update_env(current_state) # 环境相关 total_steps = 0 # 环境相关 while current_state != states[-1]: next_state = get_next_state(current_state, current_action) if random.uniform(0,1) > epsilon: # 探索 next_action = random.choice(get_valid_actions(next_state)) else: # 利用(贪婪) #next_action = q_table.ix[next_state].idxmax() # 这种写法是有问题的!可能会陷入死锁 s = q_table.ix[next_state].filter(items=get_valid_actions(next_state)) next_action = random.choice(s[s==s.max()].index) # 可能多个最大值,当然,一个更好 next_state_reward = rewards[next_state] next_q_value = q_table.ix[next_state, next_action] q_table.ix[current_state, current_action] += alpha * (next_state_reward + gamma * next_q_value - q_table.ix[current_state, current_action]) current_state, current_action = next_state, next_action update_env(current_state) # 环境相关 total_steps += 1 # 环境相关 print('\rEpisode {}: total_steps = {}'.format(i, total_steps), end='') # 环境相关 time.sleep(2) # 环境相关 print('\r ', end='') # 环境相关 print('\nq_table:') print(q_table)