统计学习导论 Chapter5 -- Resampling Methods
Book: An Introduction to Statistical Learning
with Applications in R
http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~gareth/ISL/
重采样方法是现代统计中不可或缺的工具。他们主要通过从训练数据集上重复采样得到多组训练样本,对每组样本拟合一个模型,从这些模型中活得额外的信息。例如,为了顾及一个线性回归拟合的 variability,我们可以从训练数据集中重复采样,得到多组样本,每组样本拟合一个线性回归模型,然后观察这些线性回归模型的差异性。这种方法或许可以让我们获取一些额外的信息(这些信息无法从 直接对原始训练数据集进行一次模型拟合 得到)。
重采样方法的计算量可能比较大,因为他们涉及在多组数据对相同统计方法的拟合。但是随着今年计算能力的飞速发展,重采样方法也可以被使用。 本章主要讨论两种常用的 重采样方法: cross-validation and the bootstrap。 这两种方法在许多统计学习算法上都是重要的工具。例如,cross-validation 可以用于对一给定的统计方法估计其 test error 来评估其性能,或用于选择合适的模型复杂度。评估模型的性能称之为 model assessment,选择模型的复杂性称之为 model selection. bootstrap 主要用于度量一个参数估计的准确性或给定统计学习方法的准确性
5.1 Cross-Validation
首先来回顾一下 test error rate 和 training error rate,一个算法只有 test error rate ,其在实际应用中效果才可能比较好。如果有一个 designated test set,那么 test error rate 很容易被计算。 但是通常没有这个测试数据集。 training error rate 可以很容易在训练数据集中计算得到。但是 the training error rate often is quite different from the test error rate, and in particular the former can dramatically underestimate the latter.
如何在没有 a very large designated test set 来估计这个 test error rate 了?
5.1.1 The Validation Set Approach
我们将手中的样本分为两个部分:a training set and a validation set or hold-out set,我们首先在 训练数据集上拟合模型,然后再 validation set 测试模型 得到一个 validation set error rate,这个 validation set error rate 是 test error rate 的一个很好的估计 
validation set approach 概念简单,也很容易实现。但是它有两个可能的缺点:
1)the validation estimate of the test error rate can be highly variable, depending on precisely which observations are included in the training set and which observations are included in the validation set
2)the validation set error rate may tend to overestimate the test error rate for the model fit on the entire data set
cross-validation, a refinement of the validation set approach that addresses these two issues
cross-validation 是对上面两个问题的解决方案
5.1.2 Leave-One-Out Cross-Validation
Leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV) 和上面的 validation set approach 很紧密,但是可以解决其缺陷
和 validation set approach 类似, LOOCV 也是将数据集分为两个部分,但是我们每次只选择一个样本作为 validation set,剩下的样本作为 training set。统计学习方法在 这 n-1 个样本的 training set 进行模型拟合,在 validation set 进行测试,得到误差 MSE1 。如果数据集中每个样本都当过一次 validation set,我们就有 n 个 MSE。The LOOCV estimate for the test MSE is the average of these n test error estimates 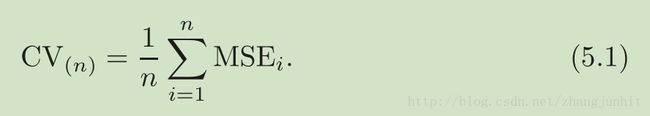
LOOCV 相对于 validation set approach 的优点:
1) it has far less bias
2) performing LOOCV multiple times will always yield the same results: there is no randomness in the training/validation set splits
LOOCV 的缺点就是计算量比较大
With least squares linear or polynomial regression, an amazing shortcut makes the cost of LOOCV the same as that of a single model fit! 
其中 h_i equation (3.37) on page 99
5.1.3 k-Fold Cross-Validation
An alternative to LOOCV is k-fold CV. This approach involves randomly dividing the set of observations into k groups, or folds, of approximately
equal size. The first fold is treated as a validation set, and the method is fit on the remaining k − 1 folds 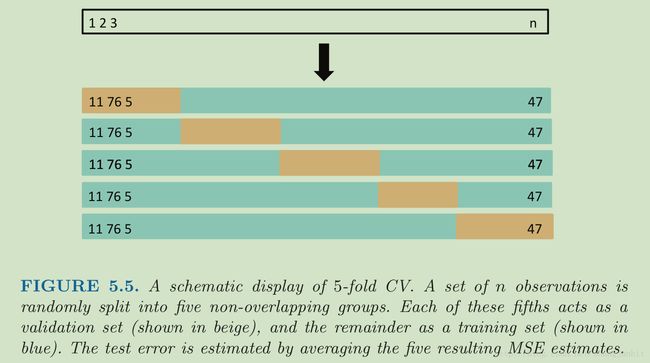
In practice, one typically performs k-fold CV using k = 5 or k = 10. What is the advantage of using k = 5 or k = 10 rather than k = n? The most obvious advantage is computational
5.1.4 Bias-Variance Trade-Off for k-Fold Cross-Validation
如果暂时不考虑计算量的问题
a less obvious but potentially more important advantage of k-fold CV is that it often gives more accurate estimates of the test error rate than does LOOCV. This has to do with a bias-variance trade-off.
To summarize, there is a bias-variance trade-off associated with the choice of k in k-fold cross-validation. Typically, given these considerations, one performs k-fold cross-validation using k = 5 or k = 10, as these values have been shown empirically to yield test error rate estimates that suffer neither from excessively high bias nor from very high variance.
5.2 The Bootstrap
we instead obtain distinct data sets by repeatedly sample observations from the original data set. 

