- A*算法详解
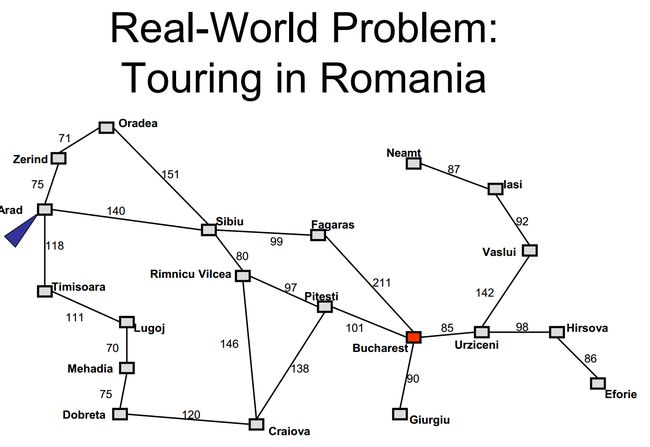
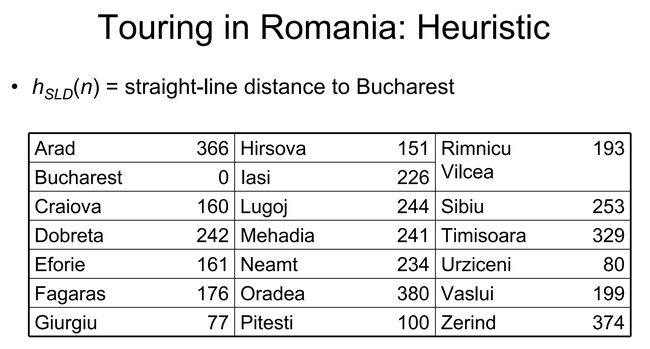
A*算法详解一、A*算法基础概念1.1算法定位1.2核心评估函数1.3关键数据结构二、A*算法的核心步骤三、启发函数设计3.1网格地图中的启发函数3.2启发函数的选择原则三、Java代码实现四、启发函数的设计与优化4.1启发函数的可采纳性4.2启发函数的效率影响4.3常见启发函数对比五、A*算法的应用场景与拓展5.1典型应用5.2算法拓展六、A*算法的优缺点优点缺点从游戏中的角色寻路到机器人导航,
- 目标检测YOLO实战应用案例100讲-基于深度学习的自动驾驶目标检测算法研究(续)
林聪木
目标检测YOLO深度学习
目录基于双蓝图卷积的轻量化自动驾驶目标检测算法5.1引言5.2DarkNet53网络冗余性分析5.3双蓝图卷积网络5.4实验结果及分析基于深度学习的自动驾驶目标检测算法研究与应用传统的目标检测算法目标检测基线算法性能对比与选择相关理论和算法基础2.1引言2.2人工神经网络2.3FCOS目标检测算法2.4复杂交通场景下的目标检测难点与FCOS改进方案基于FCOS的目标检测算法改进3.1引言3.2Re
- 华为OD机试专栏--1.3 算法基础:1.3.3 动态规划入门
xiaoheshang_123
华为OD机试真题题库解析华为od面试职场和发展算法
目录1.3算法基础1.3.3动态规划入门一、动态规划的核心思想1.1什么是动态规划?1.2动态规划的特点二、动态规划的基本步骤三、经典动态规划问题3.1斐波那契数列(FibonacciSequence)问题描述动态规划解法代码实现(Python)3.2背包问题(KnapsackProblem)问题描述动态规划解法代码实现(Python)3.3最长公共子序列(LongestCommonSubsequ
- 算法设计与分析 知识总结
vortex5
算法
一、算法基础算法是对特定问题求解步骤的描述,是指令的有限序列,具有输入、输出、有穷性、确定性和可行性五个性质。程序则是算法用某种编程语言的具体实现。优秀的算法应具备正确性、健壮性、可理解性、抽象分级和高效性,其中时间复杂度是衡量算法效率的重要标准。常用的时间复杂度符号包括O(上界)、Ω(下界)和Θ(紧确界)。1.1时间复杂度分析非递归算法以嵌套循环为例,分析以下代码的时间复杂度:for(i=1;i
- 【归纳】C++入门算法模版总结(超级详细!!!)(包括高精度,排序,枚举,二分,搜索,动态规划等)
0.前言本文针对有一定算法基础的选手制作,收录了大部分算法的模板,详细解说可以点进去我提供的链接了解。或者进入我的主页给一点支持!本人也是一名新手,如果这篇文章有不严谨的地方或者不懂的地方可以在评论区留言,我会为你们一一解答的。【归纳】C++入门算法模版总结(包括高精度,排序,枚举,二分,搜索,动态规划等)(超级详细!!!)0.前言1.高精度1.1.单独实现1.1.1.高精度加法1.1.2.高精度
- 近似算法与随机化算法:处理难解问题的实用方法
全息架构师
算法
近似算法与随机化算法:处理难解问题的实用方法引言“当精确解不可得时,如何高效获得满意解?近似与随机化算法给出答案!”在计算机科学中,许多重要问题是NP难解的,无法在多项式时间内找到精确解。近似算法和随机化算法为解决这类问题提供了实用方法。本文将深入探讨这两类算法的设计思想、分析技术和典型应用,帮助你掌握处理计算难解问题的有效工具。第一章近似算法基础1.1近似算法概述“在精度与效率间寻找平衡的艺术”
- 学而思编程周赛语言普及奠基组 | 2025年春第15周T1 新二进制
热爱编程的通信人
算法c++
欢迎大家订阅我的专栏:算法题解:C++与Python实现!本专栏旨在帮助大家从基础到进阶,逐步提升编程能力,助力信息学竞赛备战!专栏特色1.经典算法练习:根据信息学竞赛大纲,精心挑选经典算法题目,提供清晰的代码实现与详细指导,帮助您夯实算法基础。2.系统化学习路径:按照算法类别和难度分级,从基础到进阶,循序渐进,帮助您全面提升编程能力与算法思维。适合人群:准备参加蓝桥杯、GESP、CSP-J、CS
- 学而思编程周赛语言普及奠基组 | 2025年春第15周T2 散步
热爱编程的通信人
算法c++
欢迎大家订阅我的专栏:算法题解:C++与Python实现!本专栏旨在帮助大家从基础到进阶,逐步提升编程能力,助力信息学竞赛备战!专栏特色1.经典算法练习:根据信息学竞赛大纲,精心挑选经典算法题目,提供清晰的代码实现与详细指导,帮助您夯实算法基础。2.系统化学习路径:按照算法类别和难度分级,从基础到进阶,循序渐进,帮助您全面提升编程能力与算法思维。适合人群:准备参加蓝桥杯、GESP、CSP-J、CS
- ROS常用的路径规划算法介绍
Xian-HHappy
机器人-Robot算法机器人路径规划ROS
在ROS中,常用的路径规划算法主要有以下几种:全局路径规划算法A*算法:在Dijkstra算法基础上加入启发式函数,如曼哈顿距离或欧氏距离,优先探索靠近目标的节点,效率更高。需使用可容许的启发式函数以保证最优性,其通过配置启发式权重可平衡最优性与速度。在ROS中,nav2_planner中的SmacPlanner支持2D/3D的A*算法。Dijkstra算法:代价地图中的基础路径搜索方法,采用广度
- GESP认证C++编程真题解析 | GESP202409 三级 单选题和判断题
热爱编程的通信人
历年GESPCSP-JCSP-S真题解析c++开发语言
欢迎大家订阅我的专栏:算法题解:C++与Python实现!本专栏旨在帮助大家从基础到进阶,逐步提升编程能力,助力信息学竞赛备战!专栏特色1.经典算法练习:根据信息学竞赛大纲,精心挑选经典算法题目,提供清晰的代码实现与详细指导,帮助您夯实算法基础。2.系统化学习路径:按照算法类别和难度分级,从基础到进阶,循序渐进,帮助您全面提升编程能力与算法思维。适合人群:准备参加蓝桥杯、GESP、CSP-J、CS
- LLMs基础学习(八)强化学习专题(7)
汤姆和佩琦
NLP学习Actor-Critic算法
LLMs基础学习(八)强化学习专题(7)文章目录LLMs基础学习(八)强化学习专题(7)Actor-Critic算法基础原理算法流程细节算法优缺点分析算法核心总结视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1MQo4YGEmq/?spm_id_from=333.1387.upload.video_card.click&vd_source=57e4865932ea6c
- 1995年NOIP试题解析与答案指南
红廉骑士兽
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:全国青少年计算机联赛(NOIP)是提升青少年计算机科学素养的重要赛事。本压缩包包含了1995年NOIP比赛的试题及答案,为参赛者和编程爱好者提供了一个宝贵的资源。试题涵盖基础编程概念、算法基础、逻辑思维、数据结构、输入输出处理、错误处理与调试以及程序效率优化等方面的知识点。通过回顾和学习这些试题,可以帮助学习者提升编程能力,加深对计算机科学基础的理解,并培养逻
- 关于结构体,排序,递推的详细讲解(从属于GESP四级)
本章内容排序算法基础结构体递推简单双指针一、排序算法基础三剑客冒泡Bubble、选择Selection、插入Insertion1.预备知识1.1排序算法评价指标指标含义影响答题的典型问法时间复杂度算法在最坏、平均或最好情况下所需比较/交换次数“写出此算法最坏复杂度”空间复杂度额外占用的内存字节数“此算法是否原地排序”稳定性等值元素排序后相对次序是否保持“选择排序稳定吗?为什么”交换/移动次数对不同
- Python 算法及其架构设计详解
conkl
python知识python算法开发语言
文章目录一、算法基础与架构概述二、经典算法实现与分析1.排序算法-快速排序2.搜索算法-二分查找3.图算法-广度优先搜索(BFS)三、算法架构设计模式1.策略模式(StrategyPattern)2.管道-过滤器模式(Pipeline-FilterPattern)四、Python算法优化与性能分析1.使用内置数据结构和库2.性能分析工具3.算法优化示例五、总结在计算机科学领域,算法是解决特定问题的
- 算法基础:贪心策略
Ym影子
算法算法贪心算法leetcode
贪心策略目录贪心策略概念思路算法考题概念贪心策略的百度解释是:在对问题求解时,总是做出在当前看来是最好的选择。也就是说,不从整体最优上加以考虑,算法得到的是在某种意义上的局部最优解。贪心算法不是对所有问题都能得到整体最优解,关键是贪心策略的选择。基本上所有的贪心算法都可以用回溯来解决(全排列),就是说如果真的想不到好的贪心策略去实现,全排列也可以解决这个算法问题,只是时间复杂度会非常高(>O(n!
- GIS算法基础知识点总结
熊猫_luoul
GIS算法基础算法
绪论基本计算方法:穷举法、贪心算法、分治法、动态规划法、迭代法、分支界限法(BranchandBound)穷举法:通过枚举所有可能的解来寻找最优解。优点是简单直接,缺点是计算量大,适用于小规模问题。贪心算法:每一步都选择当前最优的局部解,期望通过局部最优达到全局最优。优点是计算速度快,缺点是不一定能得到全局最优解。分治法:将问题分解为若干子问题,分别解决后再合并结果。(归并排序和快速排序)动态规划
- 扩展欧几里德算法 递归法 递推法 手算法 原理及实现
黎哩吖
算法人工智能机器学习
扩展欧几里德算法递归法递推法手算法原理及实现顾名思义,扩展欧几里德算法是在欧几里德算法基础上扩展的算法.欧几里德算法和扩展欧几里德算法在用途上的区别:欧几里德算法(gcd):即求两个整数的最大公约数.扩展欧几里德算法:用于求乘法逆元.用于求贝组等式的一个解.欧几里德算法即辗转相除法.C语言实现:intgcd(inta,intb){returnb==0?a:gcd(b,a%b);}注意此算法的终止条
- 学而思编程周赛语言普及奠基组 | 2025年春第2周T3 全都为1
欢迎大家订阅我的专栏:算法题解:C++与Python实现!本专栏旨在帮助大家从基础到进阶,逐步提升编程能力,助力信息学竞赛备战!专栏特色1.经典算法练习:根据信息学竞赛大纲,精心挑选经典算法题目,提供清晰的代码实现与详细指导,帮助您夯实算法基础。2.系统化学习路径:按照算法类别和难度分级,从基础到进阶,循序渐进,帮助您全面提升编程能力与算法思维。适合人群:准备参加蓝桥杯、GESP、CSP-J、CS
- 高级算法设计技巧:分治、回溯与剪枝策略深度解析
全息架构师
算法剪枝java
高级算法设计技巧:分治、回溯与剪枝策略深度解析引言“掌握算法设计范式,让你面对复杂问题时游刃有余!”算法设计是计算机科学的核心,良好的算法设计能力能让你高效解决各类复杂问题。本文将深入探讨分治法、回溯法和剪枝策略这三种经典算法设计范式,通过理论分析、代码实现和实战应用,帮助你提升算法设计能力,从容应对技术面试和实际工程挑战。第一章分治算法精要1.1分治算法基础“分而治之:将大问题拆解为小问题的艺术
- Python 算法基础篇:冒泡排序和选择排序
挣扎的蓝藻
Python算法初阶:入门篇算法python排序算法冒泡排序选择排序
Python算法基础篇:冒泡排序和选择排序引言1.冒泡排序算法概述2.冒泡排序算法实现实例1:冒泡排序3.选择排序算法概述4.选择排序算法实现实例2:选择排序5.冒泡排序与选择排序的对比总结引言冒泡排序和选择排序是两种常用的排序算法,用于将一个无序列表按照特定顺序重新排列。本篇博客将介绍冒泡排序和选择排序的基本原理,并通过实例代码演示它们的应用。❤️❤️❤️1.冒泡排序算法概述冒泡排序是一种简单的
- 哈希算法实战全景:安全加密到分布式系统的“核心引擎”
星之尘1021
「高频算法题·从原理到优化」哈希算法安全算法
哈希算法实战全景:安全加密到分布式系统的“核心引擎”作者:星之辰标签:#哈希算法#分布式#安全加密#唯一标识#工程实战适用场景:技术面试、工程项目架构、算法基础进阶引子:一串随机值,撑起了大厂工程的“半壁江山”还记得CSDN明文密码泄漏那一幕吗?又或者你用过网盘查重、P2P下载、分布式缓存…你可知,这些背后都在靠哈希算法——看似简单的字符串变换,实则是无数工程问题的底层基石。哈希的魔力不只在于“查
- 【算法基础】高精度加减乘除法
UrSpecial
算法算法
目录高精度加法高精度减法高精度乘法高精度除法总结高精度加法题目链接:P1601A+BProblem(高精)-洛谷总的思想就是模拟列竖式的加法运算。1)字符串的形式读入两个数据。2)分别把这两个数据的每一位拆分,然后逆序存到数组中。3)数组中的对应位相加然后将结果存到结果数组中的相应位置上,同时处理进位。4)逆序输出结果数组中的值。这里顺带说明一下数组要开多大,也就是下面代码中N要定为多大的值。高精
- 学而思编程2025年CodeStars年度综合评估真题解析 | 基础算法组 T1 除虫计划
热爱编程的通信人
算法
欢迎大家订阅我的专栏:算法题解:C++与Python实现!本专栏旨在帮助大家从基础到进阶,逐步提升编程能力,助力信息学竞赛备战!专栏特色1.经典算法练习:根据信息学竞赛大纲,精心挑选经典算法题目,提供清晰的代码实现与详细指导,帮助您夯实算法基础。2.系统化学习路径:按照算法类别和难度分级,从基础到进阶,循序渐进,帮助您全面提升编程能力与算法思维。适合人群:准备参加蓝桥杯、GESP、CSP-J、CS
- 【算法】力扣体系分类
患得患失949
面试考题专栏(前后端)算法leetcode分类
第一章算法基础题型1.1排序算法题1.1.1冒泡排序相关题冒泡排序是一种简单的排序算法,它重复地走访过要排序的数列,一次比较两个元素,如果它们的顺序错误就把它们交换过来。走访数列的工作是重复地进行直到没有再需要交换,也就是说该数列已经排序完成。常见题型数组排序:给定一个无序数组,使用冒泡排序将其按升序或降序排列。例如,对于数组[5,3,8,4,2],经过冒泡排序后变为[2,3,4,5,8]。排序过
- 2024年粤港澳青少年信息学创新大赛初中组真题解析(C++)
热爱编程的通信人
c++开发语言
欢迎大家订阅我的专栏:算法题解:C++与Python实现!本专栏旨在帮助大家从基础到进阶,逐步提升编程能力,助力信息学竞赛备战!专栏特色1.经典算法练习:根据信息学竞赛大纲,精心挑选经典算法题目,提供清晰的代码实现与详细指导,帮助您夯实算法基础。2.系统化学习路径:按照算法类别和难度分级,从基础到进阶,循序渐进,帮助您全面提升编程能力与算法思维。适合人群:准备参加蓝桥杯、GESP、CSP-J、CS
- 【软考】数据结构与算法基础 - 树结构 - B树和B+树
本本本添哥
归档-Inbox1013-软考学习(计算机基础)数据结构b树
一、B树(B-Tree)介绍1.1B树(B-Tree)是什么?B树(B-Tree)是一种常用的、高效的、自平衡的树形数据结构B树(B-Tree)是一种平衡查找树B树(B-Tree)是一种多路搜索树1.2B树(B-Tree)的用途B树(B-Tree)适用于外部存储B树(B-Tree)主要用于磁盘存储和文件系统B树(B-Tree)可以高效地进行文件索引和数据库索引。B树(B-Tree)可用于在磁盘上高
- 蓝桥杯Python全攻略:从0到1的算法与企业级开发实战指南
Android洋芋
蓝桥杯算法神技:从0到企业级的进阶攻略蓝桥杯python算法广度优先搜索(BFS)API设计数据库优化嵌入与优化
简介Python凭借其简洁语法和丰富的标准库,成为蓝桥杯竞赛的热门选择,也是企业级开发的首选语言。本攻略将从零开始,系统梳理Python算法基础、企业级开发技术和实战案例,帮助您全面掌握Python编程能力,同时为蓝桥杯竞赛和企业级开发奠定坚实基础。通过本指南,您将学习到如何高效解决蓝桥杯真题,并掌握构建完整Web应用所需的Django框架、数据库优化和API设计等企业级开发技术。一、蓝桥杯Pyt
- python opencv图片旋转180度_图像旋转90/180 opencv坐标系
小子骚骚
pythonopencv图片旋转180度
问题描述:图像旋转90、180、270等使用类似下面的代码,会有黑边,图像变形之类的问题其实windows系统自带类似的功能,但是我需要批量处理图像,因此尝试自己写算法基础:这种直角的旋转,个人理解不涉及到一些插值的东西,只是像素坐标变换示例图图像:逆时针旋转90度:计算好旋转后各像素点的位置,映射过去就行就像图像中黄色的点,逆时针旋转90度之后是图像的原点opencvpython(numpy)实
- 机器学习(11)——xgboost
追逐☞
机器学习机器学习人工智能
文章目录1.算法背景和动机1.1.提升算法(Boosting)1.2.XGBoost的改进动机2.算法基础3.核心创新3.4稀疏感知算法4.系统优化4.1列块(ColumnBlock)4.2缓存感知访问4.3外存计算5.算法细节5.1树生长策略5.2特征重要性评估5.3自定义目标函数6.关键参数详解6.1通用参数6.2提升器参数6.3学习任务参数7.与LightGBM对比8.实践建议9.代码示例1
- 光流 | Matlab工具中的光流算法
单北斗SLAMer
OpticalFlow(光流)算法图像处理信息与通信matlab
在MATLAB中,光流算法用于估计图像序列中物体的运动。以下是详细解释及实现步骤:1.光流算法基础光流基于两个核心假设:亮度恒定:同一物体在连续帧中的像素亮度不变。微小运动:相邻帧之间的时间间隔短,物体运动幅度小。常见算法:Lucas-Kanade(局部方法):假设局部窗口内光流恒定,通过最小二乘法求解。Horn-Schunck(全局方法):引入全局平滑性约束,通过优化整体能量函数求解。Farne
- 统一思想认识
永夜-极光
思想
1.统一思想认识的基础,才能有的放矢
原因:
总有一种描述事物的方式最贴近本质,最容易让人理解.
如何让教育更轻松,在于找到最适合学生的方式.
难点在于,如何模拟对方的思维基础选择合适的方式. &
- Joda Time使用笔记
bylijinnan
javajoda time
Joda Time的介绍可以参考这篇文章:
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-jodatime.html
工作中也常常用到Joda Time,为了避免每次使用都查API,记录一下常用的用法:
/**
* DateTime变化(增减)
*/
@Tes
- FileUtils API
eksliang
FileUtilsFileUtils API
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2217374 一、概述
这是一个Java操作文件的常用库,是Apache对java的IO包的封装,这里面有两个非常核心的类FilenameUtils跟FileUtils,其中FilenameUtils是对文件名操作的封装;FileUtils是文件封装,开发中对文件的操作,几乎都可以在这个框架里面找到。 非常的好用。
- 各种新兴技术
不懂事的小屁孩
技术
1:gradle Gradle 是以 Groovy 语言为基础,面向Java应用为主。基于DSL(领域特定语言)语法的自动化构建工具。
现在构建系统常用到maven工具,现在有更容易上手的gradle,
搭建java环境:
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-cn-gradle/
搭建android环境:
http://m
- tomcat6的https双向认证
酷的飞上天空
tomcat6
1.生成服务器端证书
keytool -genkey -keyalg RSA -dname "cn=localhost,ou=sango,o=none,l=china,st=beijing,c=cn" -alias server -keypass password -keystore server.jks -storepass password -validity 36
- 托管虚拟桌面市场势不可挡
蓝儿唯美
用户还需要冗余的数据中心,dinCloud的高级副总裁兼首席营销官Ali Din指出。该公司转售一个MSP可以让用户登录并管理和提供服务的用于DaaS的云自动化控制台,提供服务或者MSP也可以自己来控制。
在某些情况下,MSP会在dinCloud的云服务上进行服务分层,如监控和补丁管理。
MSP的利润空间将根据其参与的程度而有所不同,Din说。
“我们有一些合作伙伴负责将我们推荐给客户作为个
- spring学习——xml文件的配置
a-john
spring
在Spring的学习中,对于其xml文件的配置是必不可少的。在Spring的多种装配Bean的方式中,采用XML配置也是最常见的。以下是一个简单的XML配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.or
- HDU 4342 History repeat itself 模拟
aijuans
模拟
来源:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4342
题意:首先让求第几个非平方数,然后求从1到该数之间的每个sqrt(i)的下取整的和。
思路:一个简单的模拟题目,但是由于数据范围大,需要用__int64。我们可以首先把平方数筛选出来,假如让求第n个非平方数的话,看n前面有多少个平方数,假设有x个,则第n个非平方数就是n+x。注意两种特殊情况,即
- java中最常用jar包的用途
asia007
java
java中最常用jar包的用途
jar包用途axis.jarSOAP引擎包commons-discovery-0.2.jar用来发现、查找和实现可插入式接口,提供一些一般类实例化、单件的生命周期管理的常用方法.jaxrpc.jarAxis运行所需要的组件包saaj.jar创建到端点的点到点连接的方法、创建并处理SOAP消息和附件的方法,以及接收和处理SOAP错误的方法. w
- ajax获取Struts框架中的json编码异常和Struts中的主控制器异常的解决办法
百合不是茶
jsjson编码返回异常
一:ajax获取自定义Struts框架中的json编码 出现以下 问题:
1,强制flush输出 json编码打印在首页
2, 不强制flush js会解析json 打印出来的是错误的jsp页面 却没有跳转到错误页面
3, ajax中的dataType的json 改为text 会
- JUnit使用的设计模式
bijian1013
java设计模式JUnit
JUnit源代码涉及使用了大量设计模式
1、模板方法模式(Template Method)
定义一个操作中的算法骨架,而将一些步骤延伸到子类中去,使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构,即可重新定义该算法的某些特定步骤。这里需要复用的是算法的结构,也就是步骤,而步骤的实现可以在子类中完成。
- Linux常用命令(摘录)
sunjing
crondchkconfig
chkconfig --list 查看linux所有服务
chkconfig --add servicename 添加linux服务
netstat -apn | grep 8080 查看端口占用
env 查看所有环境变量
echo $JAVA_HOME 查看JAVA_HOME环境变量
安装编译器
yum install -y gcc
- 【Hadoop一】Hadoop伪集群环境搭建
bit1129
hadoop
结合网上多份文档,不断反复的修正hadoop启动和运行过程中出现的问题,终于把Hadoop2.5.2伪分布式安装起来,跑通了wordcount例子。Hadoop的安装复杂性的体现之一是,Hadoop的安装文档非常多,但是能一个文档走下来的少之又少,尤其是Hadoop不同版本的配置差异非常的大。Hadoop2.5.2于前两天发布,但是它的配置跟2.5.0,2.5.1没有分别。 &nb
- Anychart图表系列五之事件监听
白糖_
chart
创建图表事件监听非常简单:首先是通过addEventListener('监听类型',js监听方法)添加事件监听,然后在js监听方法中定义具体监听逻辑。
以钻取操作为例,当用户点击图表某一个point的时候弹出point的name和value,代码如下:
<script>
//创建AnyChart
var chart = new AnyChart();
//添加钻取操作&quo
- Web前端相关段子
braveCS
web前端
Web标准:结构、样式和行为分离
使用语义化标签
0)标签的语义:使用有良好语义的标签,能够很好地实现自我解释,方便搜索引擎理解网页结构,抓取重要内容。去样式后也会根据浏览器的默认样式很好的组织网页内容,具有很好的可读性,从而实现对特殊终端的兼容。
1)div和span是没有语义的:只是分别用作块级元素和行内元素的区域分隔符。当页面内标签无法满足设计需求时,才会适当添加div
- 编程之美-24点游戏
bylijinnan
编程之美
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Set;
public class PointGame {
/**编程之美
- 主页面子页面传值总结
chengxuyuancsdn
总结
1、showModalDialog
returnValue是javascript中html的window对象的属性,目的是返回窗口值,当用window.showModalDialog函数打开一个IE的模式窗口时,用于返回窗口的值
主界面
var sonValue=window.showModalDialog("son.jsp");
子界面
window.retu
- [网络与经济]互联网+的含义
comsci
互联网+
互联网+后面是一个人的名字 = 网络控制系统
互联网+你的名字 = 网络个人数据库
每日提示:如果人觉得不舒服,千万不要外出到处走动,就呆在床上,玩玩手游,更不能够去开车,现在交通状况不
- oracle 创建视图 with check option
daizj
视图vieworalce
我们来看下面的例子:
create or replace view testview
as
select empno,ename from emp where ename like ‘M%’
with check option;
这里我们创建了一个视图,并使用了with check option来限制了视图。 然后我们来看一下视图包含的结果:
select * from testv
- ToastPlugin插件在cordova3.3下使用
dibov
Cordova
自己开发的Todos应用,想实现“
再按一次返回键退出程序 ”的功能,采用网上的ToastPlugins插件,发现代码或文章基本都是老版本,运行问题比较多。折腾了好久才弄好。下面吧基于cordova3.3下的ToastPlugins相关代码共享。
ToastPlugin.java
package&nbs
- C语言22个系统函数
dcj3sjt126com
cfunction
C语言系统函数一、数学函数下列函数存放在math.h头文件中Double floor(double num) 求出不大于num的最大数。Double fmod(x, y) 求整数x/y的余数。Double frexp(num, exp); double num; int *exp; 将num分为数字部分(尾数)x和 以2位的指数部分n,即num=x*2n,指数n存放在exp指向的变量中,返回x。D
- 开发一个类的流程
dcj3sjt126com
开发
本人近日根据自己的开发经验总结了一个类的开发流程。这个流程适用于单独开发的构件,并不适用于对一个项目中的系统对象开发。开发出的类可以存入私人类库,供以后复用。
以下是开发流程:
1. 明确类的功能,抽象出类的大概结构
2. 初步设想类的接口
3. 类名设计(驼峰式命名)
4. 属性设置(权限设置)
判断某些变量是否有必要作为成员属
- java 并发
shuizhaosi888
java 并发
能够写出高伸缩性的并发是一门艺术
在JAVA SE5中新增了3个包
java.util.concurrent
java.util.concurrent.atomic
java.util.concurrent.locks
在java的内存模型中,类的实例字段、静态字段和构成数组的对象元素都会被多个线程所共享,局部变量与方法参数都是线程私有的,不会被共享。
- Spring Security(11)——匿名认证
234390216
Spring SecurityROLE_ANNOYMOUS匿名
匿名认证
目录
1.1 配置
1.2 AuthenticationTrustResolver
对于匿名访问的用户,Spring Security支持为其建立一个匿名的AnonymousAuthenticat
- NODEJS项目实践0.2[ express,ajax通信...]
逐行分析JS源代码
Ajaxnodejsexpress
一、前言
通过上节学习,我们已经 ubuntu系统搭建了一个可以访问的nodejs系统,并做了nginx转发。本节原要做web端服务 及 mongodb的存取,但写着写着,web端就
- 在Struts2 的Action中怎样获取表单提交上来的多个checkbox的值
lhbthanks
javahtmlstrutscheckbox
第一种方法:获取结果String类型
在 Action 中获得的是一个 String 型数据,每一个被选中的 checkbox 的 value 被拼接在一起,每个值之间以逗号隔开(,)。
所以在 Action 中定义一个跟 checkbox 的 name 同名的属性来接收这些被选中的 checkbox 的 value 即可。
以下是实现的代码:
前台 HTML 代码:
- 003.Kafka基本概念
nweiren
hadoopkafka
Kafka基本概念:Topic、Partition、Message、Producer、Broker、Consumer。 Topic: 消息源(Message)的分类。 Partition: Topic物理上的分组,一
- Linux环境下安装JDK
roadrunners
jdklinux
1、准备工作
创建JDK的安装目录:
mkdir -p /usr/java/
下载JDK,找到适合自己系统的JDK版本进行下载:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html
把JDK安装包下载到/usr/java/目录,然后进行解压:
tar -zxvf jre-7
- Linux忘记root密码的解决思路
tomcat_oracle
linux
1:使用同版本的linux启动系统,chroot到忘记密码的根分区passwd改密码 2:grub启动菜单中加入init=/bin/bash进入系统,不过这时挂载的是只读分区。根据系统的分区情况进一步判断. 3: grub启动菜单中加入 single以单用户进入系统. 4:用以上方法mount到根分区把/etc/passwd中的root密码去除 例如: ro
- 跨浏览器 HTML5 postMessage 方法以及 message 事件模拟实现
xueyou
jsonpjquery框架UIhtml5
postMessage 是 HTML5 新方法,它可以实现跨域窗口之间通讯。到目前为止,只有 IE8+, Firefox 3, Opera 9, Chrome 3和 Safari 4 支持,而本篇文章主要讲述 postMessage 方法与 message 事件跨浏览器实现。postMessage 方法 JSONP 技术不一样,前者是前端擅长跨域文档数据即时通讯,后者擅长针对跨域服务端数据通讯,p