视觉里程计4(SLAM十四讲ch7)-ICP
ICP 3D3D
SVD方法
非线性方法
实践
使用两幅图的RGB-D图像,通过特征匹配获取两组3D点,最后利用ICP计算他们的位姿变换。
pose_estimation_3d3d
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void find_feature_matches (
const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2,
std::vector& keypoints_1,
std::vector& keypoints_2,
std::vector< DMatch >& matches );
// 像素坐标转相机归一化坐标
Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K );
void pose_estimation_3d3d (
const vector& pts1,
const vector& pts2,
Mat& R, Mat& t
);
void bundleAdjustment(
const vector& points_3d,
const vector& points_2d,
Mat& R, Mat& t
);
// g2o edge
class EdgeProjectXYZRGBDPoseOnly : public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<3, Eigen::Vector3d, g2o::VertexSE3Expmap>
{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
EdgeProjectXYZRGBDPoseOnly( const Eigen::Vector3d& point ) : _point(point) {}
virtual void computeError()
{
const g2o::VertexSE3Expmap* pose = static_cast ( _vertices[0] );
// measurement is p, point is p'
_error = _measurement - pose->estimate().map( _point );
}
virtual void linearizeOplus()
{
g2o::VertexSE3Expmap* pose = static_cast(_vertices[0]);
g2o::SE3Quat T(pose->estimate());
Eigen::Vector3d xyz_trans = T.map(_point);
double x = xyz_trans[0];
double y = xyz_trans[1];
double z = xyz_trans[2];
_jacobianOplusXi(0,0) = 0;
_jacobianOplusXi(0,1) = -z;
_jacobianOplusXi(0,2) = y;
_jacobianOplusXi(0,3) = -1;
_jacobianOplusXi(0,4) = 0;
_jacobianOplusXi(0,5) = 0;
_jacobianOplusXi(1,0) = z;
_jacobianOplusXi(1,1) = 0;
_jacobianOplusXi(1,2) = -x;
_jacobianOplusXi(1,3) = 0;
_jacobianOplusXi(1,4) = -1;
_jacobianOplusXi(1,5) = 0;
_jacobianOplusXi(2,0) = -y;
_jacobianOplusXi(2,1) = x;
_jacobianOplusXi(2,2) = 0;
_jacobianOplusXi(2,3) = 0;
_jacobianOplusXi(2,4) = 0;
_jacobianOplusXi(2,5) = -1;
}
bool read ( istream& in ) {}
bool write ( ostream& out ) const {}
protected:
Eigen::Vector3d _point;
};
int main ( int argc, char** argv )
{
if ( argc != 5 )
{
cout<<"usage: pose_estimation_3d3d img1 img2 depth1 depth2"< keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
vector matches;
find_feature_matches ( img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches );
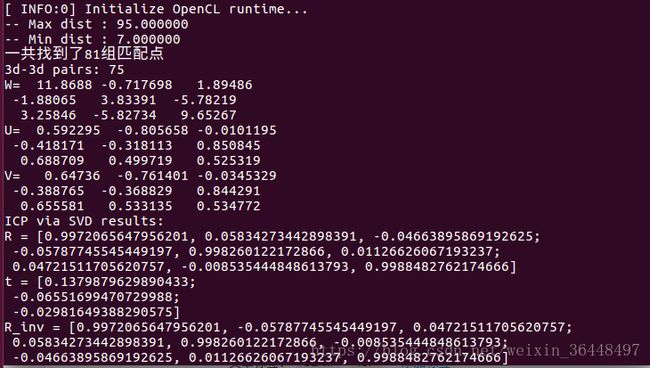
cout<<"一共找到了"< ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 );
vector pts1, pts2;
for ( DMatch m:matches )
{
ushort d1 = depth1.ptr ( int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y ) ) [ int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x ) ];
ushort d2 = depth2.ptr ( int ( keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt.y ) ) [ int ( keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt.x ) ];
if ( d1==0 || d2==0 ) // bad depth
continue;
Point2d p1 = pixel2cam ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K );
Point2d p2 = pixel2cam ( keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt, K );
float dd1 = float ( d1 ) /5000.0;
float dd2 = float ( d2 ) /5000.0;
pts1.push_back ( Point3f ( p1.x*dd1, p1.y*dd1, dd1 ) );
pts2.push_back ( Point3f ( p2.x*dd2, p2.y*dd2, dd2 ) );
}
cout<<"3d-3d pairs: "< descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" );
Ptr matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");
//-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置
detector->detect ( img_1,keypoints_1 );
detector->detect ( img_2,keypoints_2 );
//-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子
descriptor->compute ( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
descriptor->compute ( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离
vector match;
// BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );
matcher->match ( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match );
//-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选
double min_dist=10000, max_dist=0;
//找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离
for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = match[i].distance;
if ( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if ( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
printf ( "-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist );
printf ( "-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist );
//当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.
for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if ( match[i].distance <= max ( 2*min_dist, 30.0 ) )
{
matches.push_back ( match[i] );
}
}
}
Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K )
{
return Point2d
(
( p.x - K.at ( 0,2 ) ) / K.at ( 0,0 ),
( p.y - K.at ( 1,2 ) ) / K.at ( 1,1 )
);
}
void pose_estimation_3d3d (
const vector& pts1,
const vector& pts2,
Mat& R, Mat& t
)
{
Point3f p1, p2; // center of mass
int N = pts1.size();
for ( int i=0; i q1 ( N ), q2 ( N ); // remove the center
for ( int i=0; i