storage 和 memory的区别
storage 和 memory 的比较分析
1. 概念
主要考虑两点:
智能合约如何存储数据,是在memory还是在storage;solidity变量如何存储数据,是在memory还是在storage;
2. 智能合约的数据存储
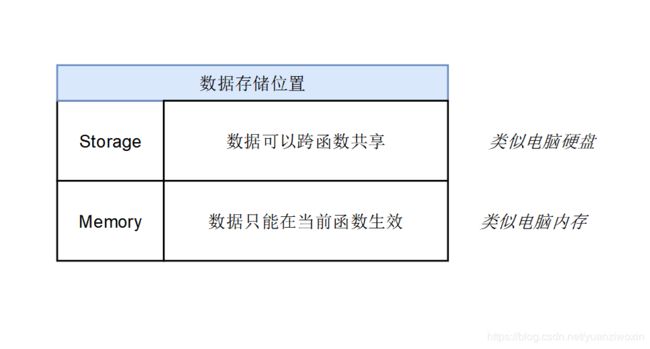
- memory:修饰的变量的数据存储在内存中;
- storage:修饰的变量的数据将永久存储在区块链上。
- calldata:一般只有在外部函数(external)的参数被强制指定为calldata,这种数据位置是只读的,不会持久化到区块链中。
| 存储位置属性类型 | 修饰的变量的存储位置 |
|---|---|
| memory | 内存中 |
| storage | 永久存储在区块链中 |
| calldata | 只读(不会持久化到区块链中) |
函数的参数,函数的返回值的默认数据位置是memory,函数内局部变量的默认数据位置为storage。状态变量的默认数据位置是storage。
pragma solidity ^0.4.17;
constract StorageTest(){
//状态变量(默认数据位置为storage)
uint256 storedData;
//data参数为局部变量,其为函数参数,所以默认数据位置为memory
function set(uint256 data){
uint temp = data; //这里的temp就是函数内的局部变量,默认数据位置为storage
storedData = data;
}
function get() constant returns (uint256){
return storedData;
}
}
状态变量: 合约中定义的变量(在函数之外);
局部变量: 函数中的参数、函数内声明的变量。
3. solidity变量的数据存储
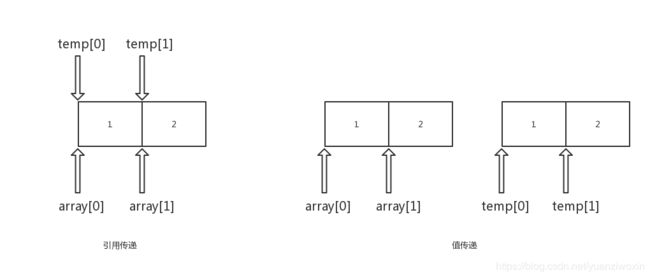
值传递和引用传递
memory:值传递
storage:引用传递
pragma solidity ^0.4.17;
contract testStorageandMemory{
uint[] public array;
function initTest() public{
array.push(1);
array.push(2);
uint[] temp = array; //这里相当于unit [] storage temp = array;
temp[0] = 99;
}
}
结果如下:
array[0] = 99
分析:
uint[] temp = array; //这里相当于unit [] storage temp = array;
这一句会有一个警告:
Warning: Variable is declared as a storage pointer. Use an explicit "storage" keyword to silence this warning.
即这里的变量被定义为一个storage的指针。可以使用“storage”关键字去消除这个警告。
也就是说,这里虽然没有使用“storage”关键字去定义temp数组,即没有将temp数组定义为引用传递,但这里仍然将temp数组当作引用传递。
因此,这里temp[0] = 99的时候,相应的array数组也发生的了改变, 即array[0] = 99。
为什么呢?且看下面的分解!!!
- (1)引用传递:temp数组和array数组指向的是同一个数组(地址),一旦temp数组改变时,array数组也发生改变;
- (2)值传递:temp数组和array数组指向的并不是同一个数组(地址),temp数组只能说是array数组的值的一个复制,temp数组的地址和array数组的地址是不一样的;所以当temp数组改变的时候,array数组并不会发生改变;
我们修改temp定义为memory,即将其改为值传递
pragma solidity ^0.4.17;
contract testStorageandMemory{
uint[] public array;
function initTest() public{
array.push(1);
array.push(2);
uint[] memory temp = array; //注意这里与上面的区别
temp[0] = 99;
}
}
结果为:
array[0] = 1
因为temp被定义为memory,这里采用的是值传递,temp和array指向的并不是同一个数组,temp只是将array的值复制过来了,所以当temp数组发生改变的时候array数组并不会发生改变。
pragma solidity ^0.4.17;
contract testStorageandMemory{
uint[] public array;
function initTest() public{
array.push(1);
array.push(2);
change(array);
}
function change(uint[] temp) public{
temp[0] = 88;
}
}
结果为:
array[0] = 1
分析:
虽然调用了change()函数,并且将array作为实参传入该函数,因为函数的参数可以理解为memory类型,采用的是值传递,所以并没有改变array数组中的值。
pragma solidity ^0.4.17;
contract testStorageandMemory{
uint[] public array;
function initTest() public{
array.push(1);
array.push(2);
change(array);
}
//注意:这里的如果要使用引用传递(传递地址),则需要将参数定义为storage,并必须将函数指定为private
function change(uint[] storage temp) private{
temp[0] = 88;
}
}
结果为:
array[0] = 88
因为这里采用的是引用传递,所以change函数可以改变array数组。
如果函数参数被定义为storage,但change函数没有指定为private,则会报如下错误:
TypeError: Location has to be memory for publicly visible functions (remove the "storage" keyword).
function change(uint[] storage temp) public{4. 数据位置之间的互相转换(storage与memory的相互转换)
(1)storage转换为storage
当我们把一个storage类型的变量赋值给另一个storage类型的变量时,我们只是修改了它(另一个变量)的指针。这两个变量指向的是同一个位置,即为引用传递,所以一旦有一个变量的数据改变,另一个也跟着改变。
(2)storage转换memory
将storage转换为memory,会将数据从storage拷贝到memory中。
(3)memory转换为storage
- (1)memory赋值为状态变量
将一个memory类型的变量赋值给一个状态变量时,实际上将内存变量拷贝到存储中。 - (2)memory赋值给函数内的局部变量
在区块链中storage必须是静态分配存储空间的。函数内的局部变量虽然是一个storage的,但它仅仅是一个storage类型的指针。如果进行memory赋值给函数内的局部变量,实际会产生一个错误。
pragma solidity ^0.4.20;
contract JustTest{
function test(uint[] memoryArray) pure private{
//TypeError: Type uint256[] memory is not implicitly convertible to expected type uint256[] storage pointer.( 即不能把memory的变量隐式地转换为storage类型的指针)
//uint[] y = memoryArray;
uint[] memory x = memoryArray;
}
}
具体报错如下:
TypeError: Type uint256[] memory is not implicitly convertible to expected type uint256[] storage pointer.
uint[] y = memoryArray;
^--------------------^memory类型不能隐式地转换为storage类型的指针。