机器学习--决策树及泰坦尼克号生存预测
决策树是一个类似于流程图的树结构,分支节点表示对一个特征进行测试,根据测试结果进行分类,树叶节点代表一个类别。
要判断从哪个特征进行分裂,就要对信息进行量化,量化的方式有:
ID3: 信息增益
条件熵:
![]()
其中pi=P(X=xi),X,Y代表了两个事件,而它们之间有时有联系的(也就是联合概率分布),条件熵H(Y|X)代表了在一直随机变量X的情况下,Y的不确定性的大小。
信息增益:熵H(Y)和条件熵H(Y|X)的差。定义如下:
I(Y,X)=H(Y)−H(Y|X)
熵越大,事物越不确定,信息增益越大,该特征越适合做分裂点。
C4.5: 信息增益比
CART: 基尼系数
实例:预测泰坦尼克号生存率
a. 数据处理
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# 数据预处理,丢弃无用数据、处理数据、填充缺失值
def read_dataset(fname):
# 指定第一列为行索引
data = pd.read_csv(fname,index_col=0)
# 丢弃无用数据
data.drop(['Name','Ticket','Cabin'],axis=1,inplace=True)
# 处理性别数据,male为1,female为0
data['Sex']=(data['Sex']=='male').astype(int)
# 处理登船港口数据
labels = data['Embarked'].unique().tolist()
data['Embarked'] = data['Embarked'].apply(lambda s: labels.index(s))
# 处理缺失值
data = data.fillna(0)
return data
train = read_dataset('train.csv')
train.head()| Survived | Pclass | Sex | Age | SibSp | Parch | Fare | Embarked | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PassengerId | ||||||||
| 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 22.0 | 1 | 0 | 7.2500 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 38.0 | 1 | 0 | 71.2833 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 26.0 | 0 | 0 | 7.9250 | 0 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 35.0 | 1 | 0 | 53.1000 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 35.0 | 0 | 0 | 8.0500 | 0 |
b. 训练模型
# 划分数据集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
y = train['Survived'].values
X = train.drop(['Survived'],axis=1).values
X_train,X_test, y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2)
print('train dataset:{0}; test dataset: {1}'.format(X_train.shape,X_test.shape))train dataset:(712, 7); test dataset: (179, 7)
# 用决策树拟合
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier()
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
train_score = clf.score(X_train,y_train)
test_score = clf.score(X_test,y_test)
print('train score:{0}; test score:{1}'.format(train_score,test_score))train score:0.9859550561797753; test score:0.7877094972067039
可以看到训练分数非常高:98.6%,而测试分数只有78.8%,说明模型过拟合,需要进行剪枝。
c. 优化参数
可以用max_depth来控制决策树的深度,当决策树达到限定深度的时候,就不再进行分裂。
# 参数选择max_depth
def cv_score(d):
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=d)
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
tr_score = clf.score(X_train,y_train)
cv_score = clf.score(X_test,y_test)
return (tr_score,cv_score)
depths = range(2,15)
scores = [cv_score(d) for d in depths]
tr_scores = [s[0] for s in scores]
cv_scores = [s[1] for s in scores]
# 找出交叉验证数据集评分最高的索引
best_score_index = np.argmax(cv_scores)
best_score = cv_scores[best_score_index]
best_param = depths[best_score_index]
print('best param:{0};best score:{1}'.format(best_param, best_score))best param:6;best score:0.8212290502793296
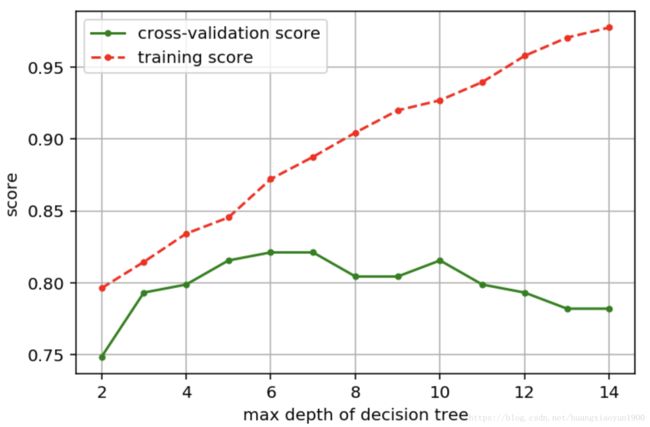
参数与评分关系:
plt.figure(figsize=(6,4),dpi=144)
plt.grid()
plt.xlabel('max depth of decision tree')
plt.ylabel('score')
plt.plot(depths, cv_scores,'.g-',label='cross-validation score')
plt.plot(depths, tr_scores,'.r--',label='training score')
plt.legend()随着树深增加,训练分数增加,而测试分数并不会随树深增加而增加。
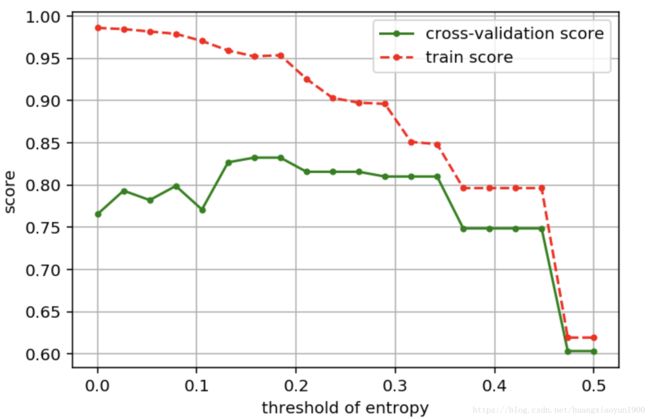
也可以考察min_impurity_split,用来指定信息熵或基尼不纯度的阈值,当决策树分裂后,其信息增益低于这个阈值时,不再分裂。
def cv_score(val):
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = 'gini', min_impurity_split = val)
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
tr_score = clf.score(X_train,y_train)
cv_score = clf.score(X_test,y_test)
return (tr_score,cv_score)
# 指定参数范围,分别训练模型并评分
values = np.linspace(0,0.5,20)
scores = [cv_score(v) for v in values]
tr_scores = [s[0] for s in scores]
cv_scores = [s[1] for s in scores]
# 找出评分最高的模型参数
best_score_index = np.argmax(cv_scores)
best_score = cv_scores[best_score_index]
best_param = values[best_score_index]
# 画出参数与评分关系
plt.figure(figsize=(6,4),dpi=144)
plt.grid()
plt.xlabel('threshold of entropy')
plt.ylabel('score')
plt.plot(values, cv_scores,'.g-',label='cross-validation score')
plt.plot(values, tr_scores,'.r--',label='train score')
plt.legend()当不纯度阈值接近0.5时,训练分数和测试分数都急剧下降,说明模型出现欠拟合。
d. 模型参数选择包
sklearn.model_selection里的GridSearchCV可以帮助选择多个最佳参数。
参数param_grid是一个字典,字典的key对应要调的参数,字典的value对应参数值,可以包含多个key-value组合。
参数cv是交叉验证数据集,cv=5表示把数据集分成5份,拿其中一份作为验证集,其他四份作为训练集。
输出:clf.best_params_最优参数,clf.best_scores_最优评分,clf.cv_results_计算过程中所有中间结果。
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
thresholds = np.linspace(0,0.5,50)
# 设置参数矩阵
param_grid = {'min_impurity_split': thresholds}
clf = GridSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(),param_grid,cv=5)
clf.fit(X,y)
print('best param:{0}\nbest score:{1}'.format(clf.best_params_,clf.best_score_))best param:{'min_impurity_split': 0.2040816326530612}
best score:0.8204264870931538
多组参数选择最优参数:
entropy_thresholds = np.linspace(0,1,50)
gini_thresholds = np.linspace(0,0.5,50)
# 设置参数矩阵
param_grid = [{'criterion':['entropy'],'min_impurity_split':entropy_thresholds},
{'criterion':['gini'],'min_impurity_split':gini_thresholds},
{'max_depth':range(2,10)},
{'min_samples_split':range(2,30,2)}]
clf = GridSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(),param_grid,cv=5)
clf.fit(X,y)
print('best_param:{0}\nbest score:{1}'.format(clf.best_params_,clf.best_score_))best_param:{'criterion': 'entropy', 'min_impurity_split': 0.5306122448979591}
best score:0.8294051627384961