Spring 面试题
-
Spring aop的理解
AOP,一般称为面向切面,作为面向对象的一种补充,用于将那些与业务无关,但却对多个对象产生影响的公共行为和逻辑,抽取并封装为一个可重用的模块,这个模块被命名为“切面”(Aspect),减少系统中的重复代码,降低了模块间的耦合度,同时提高了系统的可维护性。可用于权限认证、日志、事务处理。
①JDK动态代理只提供接口的代理,不支持类的代理。核心InvocationHandler接口和Proxy类,InvocationHandler 通过invoke()方法反射来调用目标类中的代码,动态地将横切逻辑和业务编织在一起;接着,Proxy利用 InvocationHandler动态创建一个符合某一接口的的实例, 生成目标类的代理对象。②如果代理类没有实现 InvocationHandler 接口,那么Spring AOP会选择使用CGLIB来动态代理目标类。CGLIB(Code Generation Library),是一个代码生成的类库,可以在运行时动态的生成指定类的一个子类对象,并覆盖其中特定方法并添加增强代码,从而实现AOP。CGLIB是通过继承的方式做的动态代理,因此如果某个类被标记为final,那么它是无法使用CGLIB做动态代理的。 -
Spring的IoC理解
IOC就是控制反转,是指创建对象的控制权的转移,以前创建对象的主动权和时机是由自己把控的,而现在这种权力转移到Spring容器中,并由容器根据配置文件去创建实例和管理各个实例之间的依赖关系,对象与对象之间松散耦合,也利于功能的复用。DI依赖注入,和控制反转是同一个概念的不同角度的描述,即 应用程序在运行时依赖IoC容器来动态注入对象需要的外部资源。 -
Spring的流程
1> 首先是读取配置文件或者扫描包下的类文件,将bean元素转换为一个BeanDefination对象
public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinition extends BeanMetadataAttributeAccessor
implements BeanDefinition, Cloneable {
private volatile Object beanClass;
private String scope = SCOPE_DEFAULT;
private boolean abstractFlag = false;
private boolean lazyInit = false;
private int autowireMode = AUTOWIRE_NO;
private int dependencyCheck = DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE;
private String[] dependsOn;
private ConstructorArgumentValues constructorArgumentValues;
private MutablePropertyValues propertyValues;
private String factoryBeanName;
private String factoryMethodName;
private String initMethodName;
private String destroyMethodName;
}
beanClass保存bean的class属性,scop保存bean是否单例,abstractFlag保存该bean是否抽象,lazyInit保存是否延迟初始化,autowireMode保存是否自动装配,dependencyCheck保存是否坚持依赖,dependsOn保存该bean依赖于哪些bean(这些bean必须提取初始化),constructorArgumentValues保存通过构造函数注入的依赖,propertyValues保存通过setter方法注入的依赖,factoryBeanName和factoryMethodName用于factorybean,也就是工厂类型的bean,initMethodName和destroyMethodName分别对应bean的init-method和destory-method属性
2> 然后通过BeanDefinitionRegistry将这些bean注册到beanFactory中:
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistry extends AliasRegistry {
void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)throws
BeanDefinitionStoreException;
void removeBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName);
String[] getBeanDefinitionNames();
int getBeanDefinitionCount();
boolean isBeanNameInUse(String beanName);
}
BeanFactory的实现类,需要实现BeanDefinitionRegistry 接口:
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name */
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new
ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>(64);
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// ... ...
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
// ... ...
}
}
DefaultListableBeanfactory 实现了BeanDefinationRegistry接口,将bean的信息 放入了ConcurrentHashMap 中
将BeanDefinition注册到了beanFactory之后,在这里Spring为我们提供了一个扩展的切口,允许我们通过实现接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor 在此处来插入我们定义的代码:
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws
BeansException;
}
典型的例子就是:PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,我们一般在配置数据库的dataSource时使用到的占位符的值,就是它注入进去的:
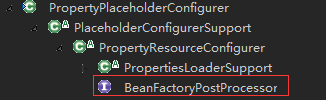
public abstract class PropertyResourceConfigurer extends PropertiesLoaderSupport
implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws
BeansException {
try {
Properties mergedProps = mergeProperties();
// Convert the merged properties, if necessary.
convertProperties(mergedProps);
// Let the subclass process the properties.
processProperties(beanFactory, mergedProps);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);
}
}
}
processProperties(beanFactory, mergedProps);在子类中实现的,功能就是将 ${jdbc_username}等等这些替换成实际值。
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc_url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc_username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc_password}" />
</bean>
bean的实例化阶段
实例化阶段主要是通过反射或者CGLIB对bean进行实例化,在这个阶段Spring又给我们暴露了很多的扩展点:
1> 各种的Aware接口,比如 BeanFactoryAware,MessageSourceAware,ApplicationContextAware
对于实现了这些Aware接口的bean,在实例化bean时Spring会帮我们注入对应的:BeanFactory, MessageSource,ApplicationContext的实例:
public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware {
/**
* Set the ApplicationContext that this object runs in.
* Normally this call will be used to initialize the object.
* <p>Invoked after population of normal bean properties but before an init callback such
* as {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()}
* or a custom init-method. Invoked after {@link ResourceLoaderAware#setResourceLoader},
* {@link ApplicationEventPublisherAware#setApplicationEventPublisher} and
* {@link MessageSourceAware}, if applicable.
* @param applicationContext the ApplicationContext object to be used by this object
* @throws ApplicationContextException in case of context initialization errors
* @throws BeansException if thrown by application context methods
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanInitializationException
*/
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}
2> BeanPostProcessor接口
实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的bean,在实例化bean时Spring会帮我们调用接口中的方法:
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.*/
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance after any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.*/
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}
从注释中可以知道 postProcessBeforeInitialization方法在 InitializingBean接口的 afterPropertiesSet方法之前执行,而postProcessAfterInitialization方法在 InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet方法之后执行。
-
Spring框架中的单例Beans是线程安全的么?
Spring框架并没有对单例bean进行任何多线程的封装处理。关于单例bean的线程安全和并发问题需要开发者自行去搞定 -
@Autowired和@Resource之间的区别?
(1) @Autowired默认是按照类型装配注入的,默认情况下它要求依赖对象必须存在(可以设置它required属性为false)。
(2) @Resource默认是按照名称来装配注入的,只有当找不到与名称匹配的bean才会按照类型来装配注入。
-
spring的事务传播行为?
① PROPAGATION_REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就创建一个新事务,如果当前存在事务,就加入该事务,该设置是最常用的设置。
如果当前没有事务 创建事务 有事务 加入该事务
② PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前存在事务,就加入该事务,如果当前不存在事务,就以非事务执行。‘
如果有事务 加入该事务 没有就按非事务执行
③ PROPAGATION_MANDATORY:支持当前事务,如果当前存在事务,就加入该事务,如果当前不存在事务,就抛出异常。
没事务 就异常 有事务 就加入
④ PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW:创建新事务,无论当前存不存在事务,都创建新事务。
无论存在与否 都要创建新事务 执行
⑤ PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。
非事务 执行 有事务 就挂起这个事务
⑥ PROPAGATION_NEVER:以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
有事务 就异常
⑦ PROPAGATION_NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则按REQUIRED属性执行。
有事务 嵌套事务 没事务 那就创建事务 -
Spring事务的隔离级别
① ISOLATION_DEFAULT:这是个 PlatfromTransactionManager 默认的隔离级别,使用数据库默认的事务隔离级别。
② ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED:读未提交,允许另外一个事务可以看到这个事务未提交的数据。
③ ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED:读已提交,保证一个事务修改的数据提交后才能被另一事务读取,而且能看到该事务对已有记录的更新。
④ ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ:可重复读,保证一个事务修改的数据提交后才能被另一事务读取,但是不能看到该事务对已有记录的更新。
⑤ ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE:一个事务在执行的过程中完全看不到其他事务对数据库所做的更新。 -
bean的声明方式
通过xml文件配置
bean 的申明、注册
@Component //注册所有bean
@Controller //注册控制层的bean
@Service //注册服务层的bean
@Repository //注册dao层的bean
@Autowired 作用于 构造方法、字段、方法,常用于成员变量字段之上。
@Autowired + @Qualifier 注入,指定 bean 的名称
@Resource JDK 自带注解注入,可以指定 bean 的名称和类型等 -
Spring bean的作用域?
singleton:单例模式,在整个Spring IoC容器中,使用 singleton 定义的 bean 只有一个实例
prototype:原型模式,每次通过容器的getbean方法获取 prototype 定义的 bean 时,都产生一个新的 bean 实例
只有在 Web 应用中使用Spring时,request、session、global-session 作用域才有效
request:对于每次 HTTP 请求,使用 request 定义的 bean 都将产生一个新实例,即每次 HTTP 请求将会产生不同的 bean 实例。
session:同一个 Session 共享一个 bean 实例。
global-session:同 session 作用域不同的是,所有的Session共享一个Bean实例。
-
简单讲一下 SpringMVC的执行流程?
1、 用户向服务器发送请求,请求被 Spring 前端控制 Servelt DispatcherServlet 捕获(捕获)
2、 DispatcherServlet对请求 URL进行解析,得到请求资源标识符(URI)。然后根据该 URI,调用 HandlerMapping获得该Handler配置的所有相关的对象(包括 Handler对象以及 Handler对象对应的拦截器),最后以 HandlerExecutionChain对象的形式返回;(查找 handler)
3、 DispatcherServlet 根据获得的 Handler,选择一个合适的 HandlerAdapter。 提取Request 中的模型数据,填充 Handler 入参,开始执行 Handler(Controller), Handler执行完成后,向 DispatcherServlet 返回一个 ModelAndView 对象(执行 handler)
4、DispatcherServlet 根据返回的 ModelAndView,选择一个适合的 ViewResolver(必须是已经注册到 Spring 容器中的 ViewResolver) (选择 ViewResolver)
5、通过 ViewResolver 结合 Model 和 View,来渲染视图,DispatcherServlet 将渲染结果返回给客户端。(渲染返回) -
编写一个自定义的SpringBoot starter
在resource下的META-INF 下新建Spring,factories文件
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=RedisAutoConfiguration
标示出 要去自动配置的类的全类名
@Configuration
//只有当 Jedis存在的时候 才会执行这个配置
@ConditionalOnClass(Jedis.class)
// 引入属性类
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MyRedisProperties.class)
public class RedisAutoConfiguration {
/* @Bean
// 当这个bean不存在的时候才执行
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public Jedis jedis(MyRedisProperties properties){
Jedis jedis = new Jedis(properties.getHost(), properties.getPort());
jedis.auth(properties.getPassword());
jedis.select(properties.getIndex());
return jedis;
}*/
@Bean
public String testBootAutoConfigure(MyRedisProperties properties){
System.out.println("==========================>Hello Boot<==========================");
return "hello";
}
}
用@ConditionOnxxx注解来标示该配置类生效的条件
用@EnableConfigurationPropertis 来引入配置类
- spring Boot自动配置原理
@SpringBootApplication是一个复合注解或派生注解,在@SpringBootApplication中有一个注解@EnableAutoConfiguration,翻译成人话就是开启自动配置其中的关键功能由@Import提供,其导入的AutoConfigurationImportSelector的selectImports()方法通过SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()扫描所有具有META-INF/spring.factories的jar包。spring-boot-autoconfigure-x.x.x.x.jar里就有一个这样的spring.factories文件。
这个spring.factories文件也是一组一组的key=value的形式,其中一个key是EnableAutoConfiguration类的全类名,而它的value是一个xxxxAutoConfiguration的类名的列表